Assign User to Role Members
Role Based Access becomes enabled within Enterprise Auditor as soon as the first role has been assigned in the Access Role wizard. When saving the first role or set of roles added to the Role Membership list in the Roles view, the Administrator role must be included for a least one user or an error message displays.
Follow the steps to assign roles in the Enterprise Auditor Console.
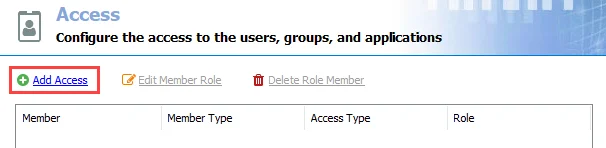
Step 1 – On the Access page, click Add Access. The Access Type wizard opens.
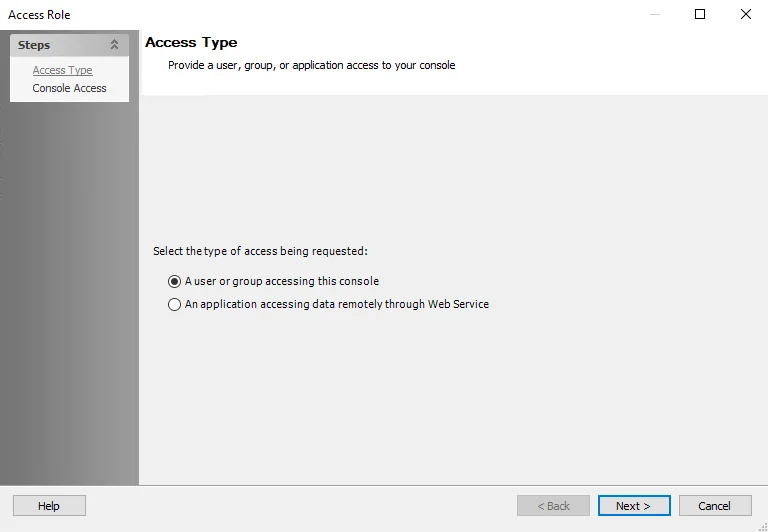
Step 2 – Select the A user or group accessing this console option. Click Next.
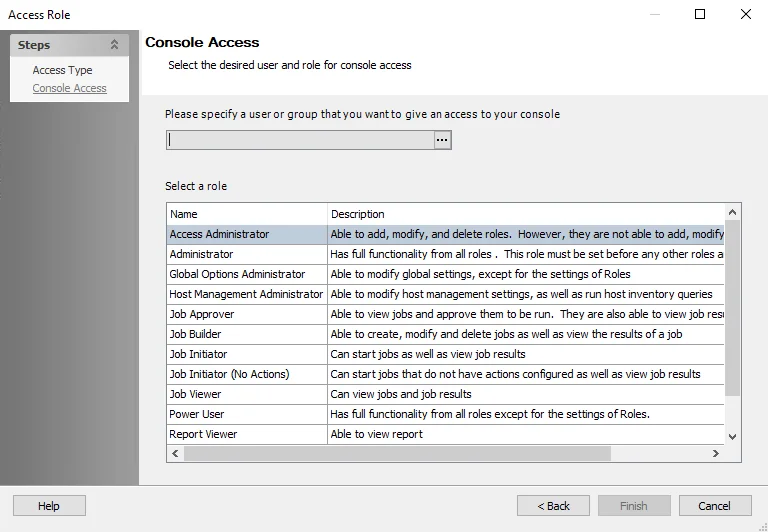
Step 3 – On the Console Access page, specify a group or user in the Name field. Use the ellipsis (…) to browse for accounts with the Select User or Group window.
-
(Optional) To use previously configured MSA and gMSAs for authentication, select the gMSA option from the Object Types list. See the Microsoft Group Managed Service Accounts article for additional information.
- Change the location to the desired domain and click Object Types, then select Service Accounts.
- Add the gMSA name (
gMSAadmin$), then click OK. - The Member Type will show as
msDS-GroupManagedServiceAccounton the Access page.
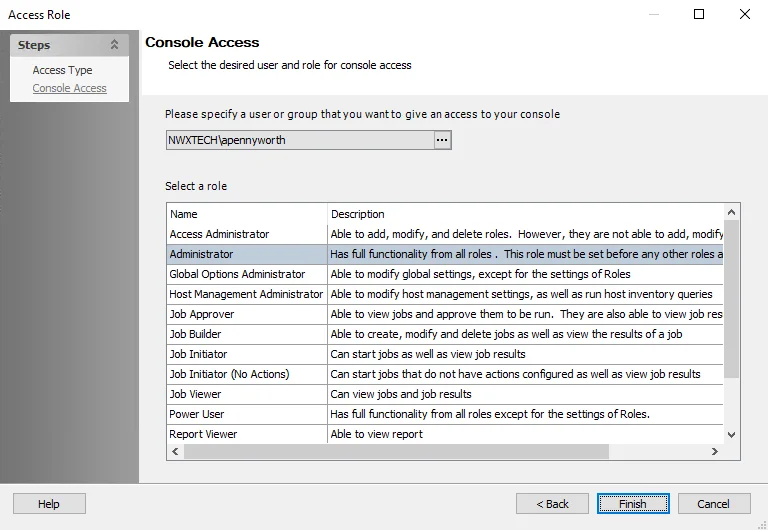
Step 4 – Select a role for the group or user from the Role list. Click Finish. The group or user and role is added to the Role Membership list in the Roles view.
Step 5 – Repeat Steps 1-4 to assign roles to other groups or users.
Step 6 – Click Save and then OK to confirm the changes. All applied roles are lost if they are not saved.
Role Based Access is enabled when the first role has been assigned.
The first role or set of roles saved must include the Administrator role. Clicking Save for the first role or set or roles without including the Administrator generates an error message in the Enterprise Auditor Console.
When Role Based Access is first enabled, restart the Enterprise Auditor application to ensure all roles are properly active. When saving roles for the first time, permissions for the local Users group are applied to the Enterprise Auditor directory. This allows roles to be leveraged without requiring local Administrator rights.
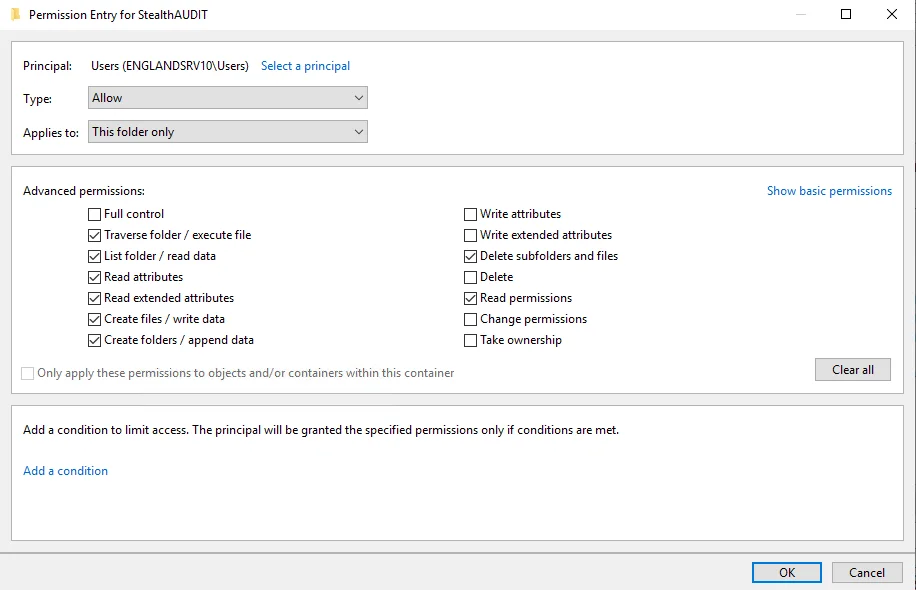 | 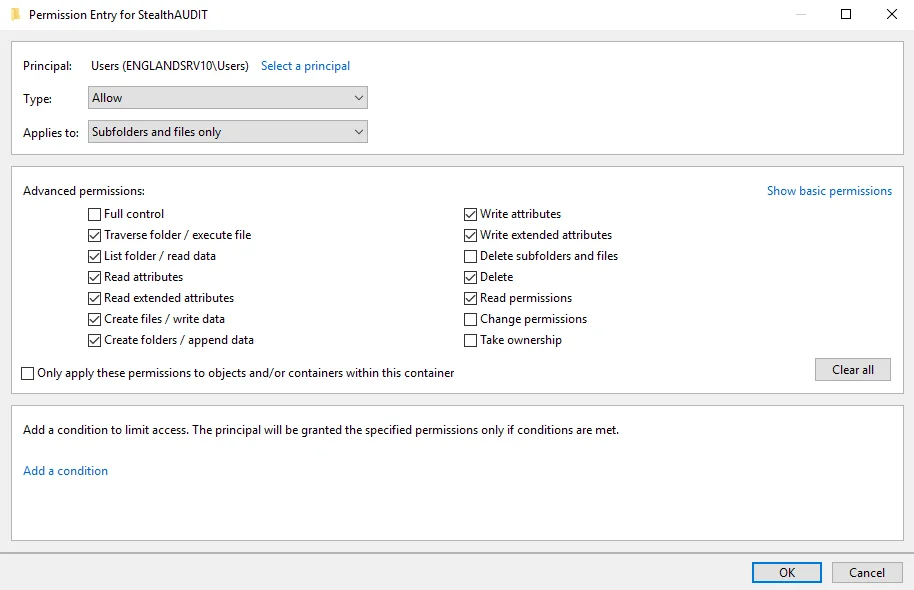 |
There are two separate sets of permissions:
- Applies to This folder only
- Applies to Subfolders and files only
Edit Role Members' Responsibilities
Follow the steps to edit a Enterprise Auditor user’s role.
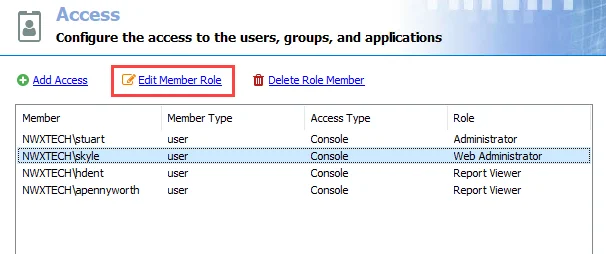
Step 1 – On the Access page, select the desired user and click Edit Member Role.
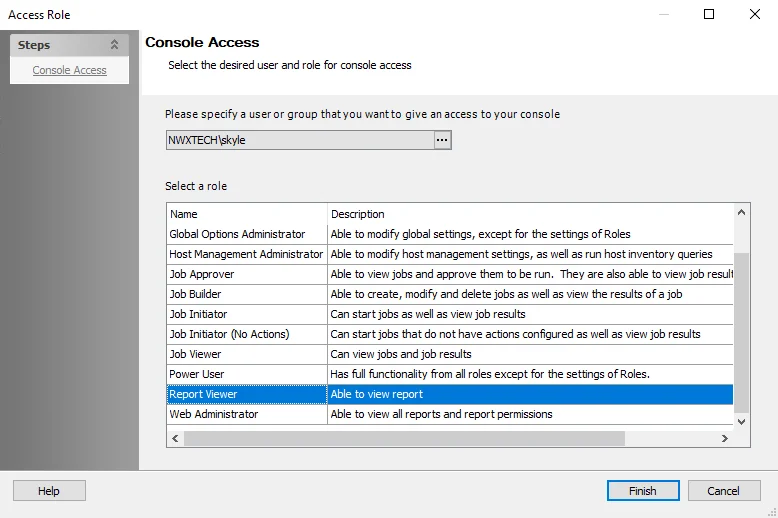
Step 2 – Select a new role for the user from the Roles list.
Step 3 – Click Finish. The role is updated on the Access page.
Step 4 – Repeat Steps 1-3 to edit other users’ roles.
Step 5 – Click Save and then OK to confirm the changes. All applied roles are lost if they are not saved.
The changed roles take affect the next time the users logs into the Enterprise Auditor application. If a user is actively logged into Enterprise Auditor at the same time the role for that user is changed, then the user needs to exit and re-launch the application for the role to take effect.
Delete Role Member
Follow the steps to delete a user from having access to the Enterprise Auditor Console.
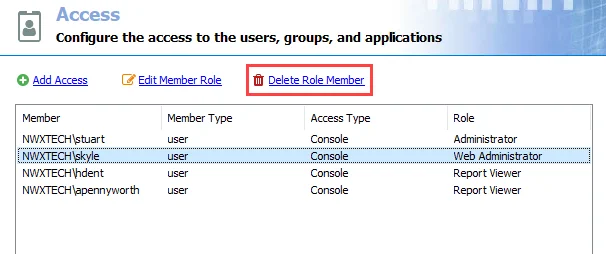
Step 1 – On the Access page, select the desired user and click Delete Role Member. The selected user will be removed from the list.
NOTE: No confirmation will be requested. However the changes will not be finalized until Step 3 is completed.
Step 2 – Repeat Step 1 to remove other users as desired.
Step 3 – Click Save and then OK to confirm the deletions. The users will not be deleted if the changes are not saved.
The deleted users will no longer be able to log into the Enterprise Auditor application. If a user is actively logged into Enterprise Auditor at the same time of the deletion, the user will need to exit the application for the deletion to take effect.
Configuring Roles
To ensure a least privilege access model, roles need to be configured within both the Enterprise Auditor Console for folder rights and SQL Management Studio for database access rights.
This is a three-part process:
-
Configure the Enterprise Auditor Installation Account
-
Configure Roles in SQL Management Studio
- Create SQL Server Database Roles
- Assign Users to SQL Roles
-
Assign User Roles in the Enterprise Auditor Console
- Edit Role Members’ Responsibilities
- Delete Role Members
NOTE: This configuration process is not required if only using Role Based Access to secure Published Reports. See the Securing Published Reports Only topic for additional information.
Configure the Installation Account
The Enterprise Auditor Installation Account is used both to perform the initial installation of Enterprise Auditor and to change Storage Profile settings. It needs additional rights in order to query objects in the master database. This is only necessary so the user can enumerate the available databases to choose from when configuring the Enterprise Auditor Storage Profile.
The following script can be executed to give these necessary rights only to the account performing the initial installation of Enterprise Auditor and any changes to the database where Enterprise Auditor writes data:
--Create a login for the user if one does not already exist
IF NOT EXISTS (SELECT *FROM sys.server_principals WHERE [name] = '<DOMAIN>\<USERNAME>')
BEGIN
create login [<DOMAIN>\<USERNAME>] from windows
END
GO
--Grant that user rights to query the master database to get a list of all database objects
USE [master]
GRANT VIEW ANY DEFINITION TO [<DOMAIN>\<USERNAME>]
GRANT CREATE DATABASE TO [<DOMAIN>\<USERNAME>]
GO
Configure Roles in SQL Management Studio
It is necessary to provision rights to the SQL Server database so the Enterprise Auditor application rights and database access rights are consistent and provide the minimum rights necessary to support the Enterprise Auditor roles. This approach involves creating custom database roles which will be assigned rights and privileges. Then, individual domain user accounts must be assigned to these roles.
NOTE: For any SQL Server version prior to 2012, Windows groups cannot be used because SQL Server does not allow the assignment of default schemas to Windows groups. Enterprise Auditor requires the default schema of [dbo] to function properly.
Create SQL Server Database Roles
To create the roles within the SQL Server database, run the following script.
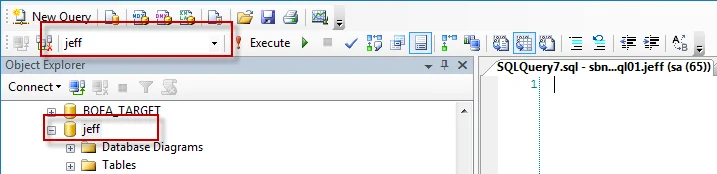
Be sure to set the context of this query to the Enterprise Auditor database by selecting the right
database from the drop-down window. Alternatively, prefix the script with a
USE [Enterprise Auditor DATABASE NAME] clause.
--create SMP Viewer role
CREATE ROLE SMP_Viewer
--grant role permissions at the schema level
GRANT SELECT
ON SCHEMA::dbo
TO SMP_Viewer
Go
--create SMP Builder role
CREATE ROLE SMP_Builder
--grant role permissions at the schema level
GRANT SELECT,INSERT,DELETE
ON SCHEMA::dbo
TO SMP_Builder
Go
--grant additional creation rights
GRANT CREATE TABLE TO [SMP_Builder]
GO
--create SMP Admin role
CREATE ROLE SMP_Admin
--grant role permissions at the schema level
GRANT ALTER,EXECUTE,INSERT,UPDATE,REFERENCES
ON SCHEMA::dbo
TO SMP_Admin
Go
--grant additional creation rights
GRANT CREATE TABLE TO [SMP_Admin]
GO
GRANT CREATE VIEW TO [SMP_Admin]
GO
GRANT CREATE PROCEDURE TO [SMP_Admin]
GO
GRANT CREATE FUNCTION TO [SMP_Admin]
GO
GRANT CREATE TYPE TO [SMP_Admin]
GO
Once the script has been successfully executed, assign domain users to these database roles.
Assigning Users to SQL Roles
Now that the SQL Server database roles have been created the next step is to assign domain users to those roles. This can be done interactively in SQL Management Studio. Follow the steps to assign users to SQL Server database roles.
Step 1 – Connect to the Enterprise Auditor database through SQL Management Studio.
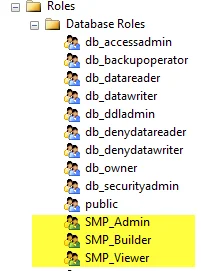
Step 2 – Validate that the roles have been properly created by navigating to Security > Roles > Database Roles. The three new roles should be visible:
- SMP_Admin
- SMP_Builder
- SMP_Viewer
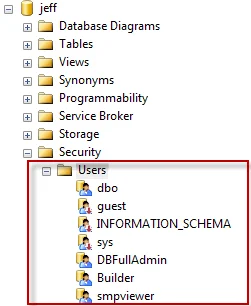 |
Step 3 – After confirmation of role creation, the next step is to map users to these roles. Right-click on the Security > Users node and select New User.
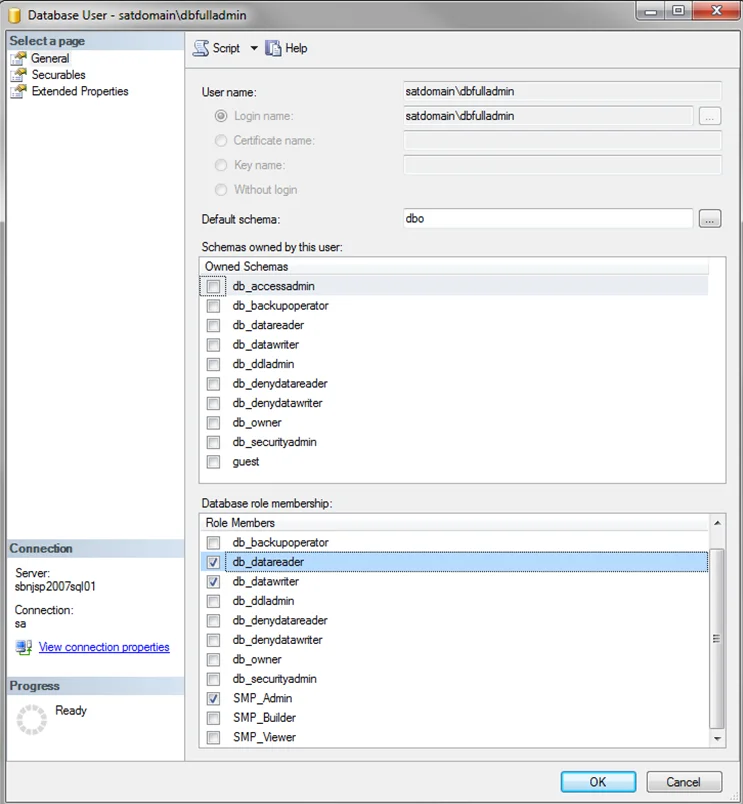
Step 4 – Enter the user information in the dialog as follows:
-
User Name – Display name given to the user which is shown under the user’s folder.
RECOMMENDED: Use a descriptive name.
-
Login name – Qualified domain name of the user:
[DOMAIN]\[Username] -
Default Schema – Should be set to
dbo -
Database role membership – Should be set to the appropriate role for this user. See the Role Definitions topic for more information.
When all of the users have been assigned to the appropriate SQL Server database roles, complete the process by assigning users to roles within the Enterprise Auditor Console.
Custom Roles
A custom role can be created within Enterprise Auditor to combine the rights of other defined roles. Follow the steps below to create a custom role.
Step 1 – In the Enterprise Auditor directory, navigate to PrivateAssemblies and edit the rba-roles.conf file. Add a new section for the custom role as shown in the following instructions:
<role name="Special User">
<translations>
<translation displayname= "Special User" description="Description of Special User" />
</translations>
<privileges>
</privileges>
</role>
- Replace
Special Userbetween the double quotes in the script above with the name of the new role. - Replace
Description of Special Userbetween the double quotes in the script above with a description of what a user assigned the new role is able to do.
Step 2 – Add privileged values for the desired rights on new lines between the beginning comment
<privileges> and ending comment </privileges> in the script above.
- For example, to create a single role which has the same privileges as the Host Management Administrator and Global Options Administrator roles, copy the privileges from the sections of the rba-roles.conf file to the newly added section, and remove duplicate values if there is any overlap.
See the sections below for examples of how roles should be added in the rba-roles.conf file.
Default Global Options Administrator Privileges
The following example shows what is currently contained in the Global Options Administrator role, and how the created role should be added in the rba-roles.conf file.
<role name="GlobalOptionsAdministrator">
<translations>
<translation displayname= "Global Options Administrator" description="Able to modify global settings, except for the settings of Roles" />
</translations>
<privileges>
<privilege value="RunSA"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsModify"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsAddOrModifyStorage"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsDeleteStorage"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsSetDefaultStorage"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsHistoryModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsConnectionAddOrModifyProfile"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsConnectionDeleteProfile"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsConnectionSetDefaultProfile"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsScheduledTaskProfileModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsNotificationMailServerModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsNotificationUserInformationModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsExchangeConnectionSettingsModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsReportingSettingsModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsHMDiscoverySettingsModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsHMDiscoveryLogSettingsModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsHMDiscoveryPerformanceTuningSettingsModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsHMInventoryItemsModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsHMInventoryPerformanceSettingsModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsHMInventoryHostListViewsModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsServiceNowSettingsModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsOtherCulumnNamingModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsOtherGridViewParametersModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsOtherAppLogSettingsModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsOtherHelpSettingsModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsOtherDatabaseCleanupSettingModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsOtherJobEngineFolderRetentionSettingsModification"/>
<privilege value="ScheduleDelete"/>
<privilege value="ScheduleEdit"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsAllowExamineSettingsTree"/>
</privileges>
</role>
Default Host Management Administrator Privileges
The following example shows what is currently contained in the Host Management Administrator role, and how the created role should be added in the rba-roles.conf file.
<role name="HostManagementAdministrator">
<translations>
<translation displayname= "Host Management Administrator" description="Able to modify host management settings, as well as run host inventory queries" />
</translations>
<privileges>
<privilege value="RunSA"/>
<privilege value="HMManageHostInventoryRunState"/>
<privilege value="HMRefreshHosts"/>
<privilege value="HMScheduleHostInventory"/>
<privilege value="HMExportHosts"/>
<privilege value="HMCreateHostsList"/>
<privilege value="HMRenameHostList"/>
<privilege value="HMDeleteHostList"/>
<privilege value="HMEditHostList"/>
<privilege value="HMRunExternalCommand"/>
<privilege value="HMEditHost"/>
<privilege value="HMDiscoveryCreateQuery"/>
<privilege value="HMDiscoveryEditQuery"/>
<privilege value="HMDiscoveryDeleteQuery"/>
<privilege value="HMDiscoveryQueryRunStateManagement"/>
<privilege value="HMDiscoveryScheduleQuery"/>
<privilege value="HMAllowExamineHostManagementTree"/>
<privilege value="ScheduleDelete"/>
<privilege value="ScheduleEdit"/>
</privileges>
</role>
New Role Combining the Global Options Administrator and Host Management Administrator Roles
The following is an example of a custom role that combines the Global Options Administrator and Host
Management Administrator roles. The script contains duplicate privileges of RunSA,
ScheduleDelete, and ScheduleEdit that need to be removed.
<role name="HMGOAdmin"><translations>
<translation displayname= "Host and Global Administrator" description="Able to modify host management, run host inventory queries, and modify global settings except for the settings of Roles" />
</translations>
<privileges>
<privilege value="RunSA"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsModify"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsAddOrModifyStorage"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsDeleteStorage"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsSetDefaultStorage"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsHistoryModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsConnectionAddOrModifyProfile"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsConnectionDeleteProfile"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsConnectionSetDefaultProfile"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsScheduledTaskProfileModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsNotificationMailServerModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsNotificationUserInformationModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsExchangeConnectionSettingsModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsReportingSettingsModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsHMDiscoverySettingsModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsHMDiscoveryLogSettingsModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsHMDiscoveryPerformanceTuningSettingsModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsHMInventoryItemsModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsHMInventoryPerformanceSettingsModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsHMInventoryHostListViewsModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsServiceNowSettingsModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsOtherCulumnNamingModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsOtherGridViewParametersModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsOtherAppLogSettingsModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsOtherHelpSettingsModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsOtherDatabaseCleanupSettingModification"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsOtherJobEngineFolderRetentionSettingsModification"/>
<privilege value="ScheduleDelete"/>
<privilege value="ScheduleEdit"/>
<privilege value="GlobalSettingsAllowExamineSettingsTree"/>
<privilege value="RunSA"/>
<privilege value="HMManageHostInventoryRunState"/>
<privilege value="HMRefreshHosts"/>
<privilege value="HMScheduleHostInventory"/>
<privilege value="HMExportHosts"/>
<privilege value="HMCreateHostsList"/>
<privilege value="HMRenameHostList"/>
<privilege value="HMDeleteHostList"/>
<privilege value="HMEditHostList"/>
<privilege value="HMRunExternalCommand"/>
<privilege value="HMEditHost"/>
<privilege value="HMDiscoveryCreateQuery"/>
<privilege value="HMDiscoveryEditQuery"/>
<privilege value="HMDiscoveryDeleteQuery"/>
<privilege value="HMDiscoveryQueryRunStateManagement"/>
<privilege value="HMDiscoveryScheduleQuery"/>
<privilege value="HMAllowExamineHostManagementTree"/>
<privilege value="ScheduleDelete"/>
<privilege value="ScheduleEdit"/>
</privileges>
</role>
Roles and the Event Log
The Enterprise Auditor Event Log includes a list of the following activities related to Role Based Access. The logged activities include information regarding the user who initiated the activity and their corresponding role:
-
Job Query Modifications
-
Host List Modifications
-
All Global Settings Modifications
- Connection Profiles
- Role Based Access
- All other settings found in Settings node
-
Job and Group Properties/Settings
-
Job Schedules
-
Job Deletions
-
Job Creations
-
Job Moves in the Jobs tree
-
Job/Group Executions
-
Enterprise Auditor Console launches and exits
See the Application Maintenance and Best Practices topic for additional information.
Role Based Access: FAQ
This topic lists some commonly asked questions about Role Based Access functionality in Enterprise Auditor.
How do locked jobs affect the role functionality?
A lock on a job represents the approval by the Job Approver, and is therefore deemed acceptable to execute. Once a job is locked, Job Builders can no longer modify the job configuration. Furthermore, only locked jobs can be run. Therefore, the Job Initiator can only run or schedule jobs which have already been locked.
NOTE: Locked jobs do not affect the functionality of the Administrator role. See the Role Definitions topic for more information.
How can I make sure that a lock on a job will not get tampered with through the associated XML file?
The Scheduling Service Account provides limited rights for the Job Approver. Previously, the Job Approver required permissions on the Jobs folder in order to apply the lock to a job. Now, the credentials specified in the Scheduling Service Account will be used to apply the locks. Therefore, the Job Approver no longer needs access to the Jobs folder and cannot manually remove or tamper with the associated XML file.
NOTE: If using a Job Initiator’s credentials for a Schedule Service Account, all jobs must be locked in order for them to be executed. See the Role Definitions and Roles & the Schedule Service Account topics for more information.
Why can the Host Management Administrator not manage settings for the Host Discovery and Host Inventory nodes under Settings?
The Host Management Administrator role is designed specifically to access the Host Management node. Therefore, this role does not grant access to the global settings menu under the Settings node.
NOTE: In order to access this node, the user must have either the Administrator or the Global Options Administrator role. See the Role Definitions topic for more information.
What rights do I need to give the user on the local machine in order to use Enterprise Auditor?
Enabling Role Based Access removes the necessity to explicitly provide users rights on the Enterprise Auditor folder structure. Instead, when the Administrator role is first assigned and Role Based Access is enabled, the roles will set permissions to allow all members of the local users group the necessary access to Enterprise Auditor.
When a user’s role is changed, when does the new role take affect?
If a user’s role has been altered while they are in an active Enterprise Auditor session, the user must exit the Enterprise Auditor Console and re-open the application for the new role to take effect. This is also true if a user has been given an additional role or removed from role membership. The capabilities of the new role will not come into effect until the Enterprise Auditor application has been restarted.
NOTE: See the Edit Role Members' Responsibilities and Delete Role Member topics for more information.
I locked a job, but when going back to it, it appears to be unlocked. Why?
A locked job signifies that the job has been approved for execution and should not be modified. If a job is modified in any way, the lock is immediately removed. Although most roles should not be able to modify locked jobs, the Administrator role can. This role is not governed by the limitations of Role Based Access. Thus, if a locked job is modified by an Administrator, the job will become unlocked. This event will be logged as a job-change related event by Administrator in the Enterprise Auditor Event Log.
NOTE: If using a Job Initiator’s credentials for the Schedule Service Account, all jobs must be locked in order for them to execute. See the Role Definitions, Workflow with Role Based Access Enabled, and Roles and the Event Log topics for more information.
What should be the group type when assigning Role Based Access to an AD group in a multi-domain environment?
When assigning an Role Based Access to an AD group, it is important to consider the domain relationship between the AD group and the Enterprise Auditor server.
If the Enterprise Auditor server and the AD group are in different domains then the AD group must be a universal group. If the group type is not universal then it will result in the RBA being unable to access the user's group membership and the user who is a member of that AD group will be unable to view any reports.
However, if both the Enterprise Auditor server and the AD group are in the same domain, the AD group can be either a local group, global group, or universal group.
Role Based Access
Role Based Access allows Enterprise Auditor users to not have local Administrator rights on the console server. This is done through the creation of different roles which cover all aspects of the Enterprise Auditor work flow introduced by enabling Role Based Access. These roles can be leveraged without such elevated rights. Responsibilities within the Enterprise Auditor Console have been divided among these roles.
Role Based Access also allows users to secure published reports when accessed through the Web Console. This is done by first enabling Role Based Access and then by assigning users/groups as viewers to the reports to which they should have access.
Report security through Role Based Access can be applied without implementing a least privileged access model to the Enterprise Auditor Console. See the Securing Published Reports Only topic for additional information.
NOTE: The least privileged access model to the Enterprise Auditor Console does not work in conjunction with the Exchange Solution. Role Based Access can be enabled, but the Administrator role is required to run the Exchange Solution jobs.
CAUTION: Please use caution when enabling Role Based Access, as it is a very powerful tool within the console designed to be difficult to disable once activated. If Role Based Access is enabled by accident, please contact Netwrix Support for assistance in disabling it.
The account used to perform the initial Enterprise Auditor installation, as well as to change Storage Profile settings after installation, require additional rights in order to query objects in the master database. See the Configure the Installation Account topic for additional information on this account.
To enable Role Based Access within Enterprise Auditor, corresponding roles must first be created within SQL Management Studio. Then Enterprise Auditor users must be assigned roles both in SQL Management Studio and in Enterprise Auditor.
The first Enterprise Auditor user assigned a role must be an Administrator. Assigning this first user role officially enables Role Based Access within Enterprise Auditor. See the Configuring Roles topic for additional configuration details.
Role Definitions
The following is a list of all roles leveraged within Enterprise Auditor once Role Based Access is enabled, including their intended functionality. A user may have more than one role assigned to them.
NOTE: When a job is moved or copied to a separate job group, it inherits the assigned roles at the parent and global level from the new job group. Any previous role inheritance is overwritten.
-
OS Administrator – Used only for installation purposes
- This is not not a configured role, but rather the access required during installation
-
Administrator – At least one must be set before any other roles are assigned
- Full functionality from all roles within the Enterprise Auditor Console
- Rights to view all reports, tags, and report permissions within the Web Console
- Rights to preform an upgrade on Enterprise Auditor
NOTE: In order to use Role Base Access with the Exchange Solution, all Exchange users must be assigned the Administrator role. This is because the solution requires local Administrator rights on the Enterprise Auditor Console server.
-
Power User
- Rights to add, modify, and delete global settings, except for the Setting > Access node
- Not able to view or modify Roles at the global level
- Has rights to add and break inheritance on report viewers at the job group, job, and report configuration levels
- Rights to modify host management settings as well as run host inventory queries
- Rights to create, modify, and delete jobs as well as view the results of a job. They need to be able to manage all configuration settings related to those jobs.
- Rights to view previously configured jobs and approve them to be run. They are also able to view the results of a job.
- Rights to run jobs which have been approved, as well as disable or enable jobs and job groups
- Rights to view all reports, tags, and report permissions within the Web Console
-
Access Administrator
- Rights to add, modify, and delete global roles except for own roles. This is to restrict Access Administrators from stepping outside intended rights.
- Not able to view or modify report roles at any other level
- Rights to view report Tags within the Web Console but not report content or permissions
-
Global Options Administrator
- Able to modify global settings, except for the Setting > Access node
- The Exchange node is the exception due to its requirements. Therefore, this node cannot be modified by the Global Options Administrator.
- Rights to view report Tags within the Web Console but not report content or permissions
-
Host Management Administrator
- Rights to modify host management settings as well as run host inventory queries
- Rights to view report Tags within the Web Console but not report content or permissions
-
Job Builder
- Rights to create, modify, and delete jobs as well as view the results of a job. They need to be able to manage all configuration settings related to those jobs.
- Rights to view or modify report viewers at the job group, job, and report levels but not the global level
- Rights to view all reports and tags within the Web Console but not the report permissions
-
Job Approver
- Rights to view previously configured jobs and approve them to be run. They are also able to view the results of a job.
- Rights to view all reports and tags within the Web Console but not the report permissions
-
Job Initiator
- Rights to start jobs which have been approved as well as view the results of a job
- Rights to disable and enable job and job groups
- Rights to view all reports and tags within the Web Console but not the report permissions
-
Job Initiator (No Actions)
- Rights to start jobs which have been approved as long as there are no configured Actions in the job. They are also able to view the results of a job.
- Rights to disable and enable job and job groups
- Rights to view all reports and tags within the Web Console but not the report permissions
-
Job Viewer
- Only able to view the results of a job
- Rights to view all reports and tags within the Web Console but not the report permissions
-
Web Administrator
- Not able to access the Enterprise Auditor Console
- Rights to view all reports, tags, and report permissions within the Web Console
-
Report Viewer
-
Not able to access the Enterprise Auditor Console
-
Only able to view reports and tags within the Web Console but not the report permissions
-
Access to reports is restricted according to where the Report Viewer role is assigned:
- Assigned at the Global level (Settings > Roles) – Able to view all published reports
- Assigned at the Job Group level (Jobs > [Job Group] > Settings > Reporting) – Able to view all reports published by the jobs within this job group
- Assigned at the Job level (Jobs > [Job Group] > [Job] > Job Properties > Report Roles tab) – Able to view all reports published by this job
- Assigned at the Report configuration level (Jobs >[Job Group] >[Job] > Configure > Reports> Configure > Publish Security page) – Able to view only this report
-
By default, many roles are granted rights to view all reports and report content. The inheritance of the Report Viewer role can be broken at the job group, job, or report configuration levels. See the Report Viewer Inheritance topic for additional information.
Enterprise Auditor Console Roles & Rights
These tables show the rights granted to different user levels to the Enterprise Auditor Console.
Administrators
This table identifies the rights granted to administrative users to the Enterprise Auditor Console.
| Action | Administrator | Global Options Administrator | Access Administrator | Host Management Administrator | OS Administrator |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| View Reports within the Web Console | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| View Report Tags within the Web Console | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| View Report Permissions within the Web Console | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| Access the Enterprise Auditor Console (after Role Based Access is enabled) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Read All Configuration Logs | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Manage / Edit Access Roles | Yes | No | Yes | No | No |
| Manage Global Settings (includes Connection Profiles) | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| Manage / Edit Hosts in Job | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| Manage / Edit Job Definitions | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| Run Jobs | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| Manage / Edit Job Schedules | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| Manage Host Management Settings (includes scheduling and running of host discovery, but not host related nodes in Global Settings) | Yes | No | No | Yes | No |
| Lock / Unlock Jobs | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| Enable/Disable Jobs | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| Install / Uninstall Data Collectors (or other tool components) | Yes | No | No | No | Yes |
| Upgrade Enterprise Auditor Console | Yes | No | No | No | No |
Users
This table identifies the rights granted to users who have access to the Enterprise Auditor Console.
| Action | Power User | Job Builder | Job Approver | Job Initiator | Job Initiator (No Actions) | Job Viewer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| View Reports within the Web Console | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| View Report Tags within the Web Console | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| View Report Permissions within the Web Console | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| Access the Enterprise Auditor Console (after Role Based Access is enabled) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Read All Configuration Logs | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Manage / Edit Access Roles | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Manage Global Settings (includes Connection Profiles) | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| Manage / Edit Hosts in Job | Yes | Yes* | No | No | No | No |
| Manage / Edit Job Definitions | Yes | Yes* | No | No | No | No |
| Run Jobs | Yes | No | No | Yes** | Yes*** | No |
| Manage / Edit Job Schedules | Yes | No | No | Yes** | Yes*** | No |
| Manage Host Management Settings (includes scheduling and running of host discovery, but not host related nodes in Global Settings) | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| Lock / Unlock Jobs | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| Enable/Disable Jobs | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Install / Uninstall Data Collectors (or other tool components) | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| Upgrade Enterprise Auditor Console | No | No | No | No | No | No |
*When jobs are unlocked
**When jobs are locked
***When jobs are locked and have no actions
Web Console Roles & Rights
This table identifies the rights granted to users who have access only to the Web Console.
| Action | Web Administrator | Report Viewer |
|---|---|---|
| View Reports within the Web Console | Yes | Yes* |
| View Report Tags within the Web Console | Yes | Yes* |
| View Report Permissions within the Web Console | Yes | No |
*According to where the role is assigned
SQL Server Database Roles & Rights
This table describes the roles that will be created within the SQL Server database and what rights they will have to the Enterprise Auditor database. It also describes which Enterprise Auditor roles they are mapped to.
| Database Role(s) | Enterprise Auditor Role | Rights | Role Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| SMP Administrator db_datareader db_datawriter | Administrator Job Initiator Job Initiator (No Actions) | On the dbo schema: ALTER, EXECUTE, INSERT, UPDATE, REFERENCES On the Enterprise Auditor database: CREATE TABLE, CREATE VIEW, CREATE PROCEDURE, CREATE FUNCTION, CREATE TYPE | This role is used by full Administrators and Job Initiators who must run the 2-FSAA Bulk Import Job which requires manipulation of the Enterprise Auditor database |
| SMP Builder | Job Builder Host Management Administrator | On the dbo schema: ELECT, INSERT, DELETE On the Enterprise Auditor database: CREATE TABLE | This role is used by the Job Builder who must be able to create/delete tables, view data, and insert and delete hosts from the Enterprise Auditor Console |
| SMP Viewer | Job Viewer Access Administrator Job Approver All other roles | On the dbo schema: SELECT | This role is used by all roles who do not require anything more than just reading data and information from the database |
Report Viewer Inheritance
When Role-Based Access is enabled, users assigned the following roles inherit rights to view all reports and their content:
- Administrator role
- Power User role
- Job Builder role
- Job Approver role
- Job Initiator role
- Job Initiator (No Actions) role
- Job Viewer
- Web Administrator
Additional users can be assigned the Report Viewer role at the global, job group, job, or report configuration levels. These rights are inherited down through child objects. However, the Report Viewer role inheritance can be broken at any level. Break inheritance to remove the right to view specific reports at:
- Job Group level – [Job Group] >Settings > Reporting node
- Job level – [Job] > Properties >Report Roles tab
- Report Configuration level – [Job] > Configure > Reports node. Click Configure next to the report, and navigate to the Publish Security page of the Report Configuration wizard. See the Publish Security Page topic for additional information.
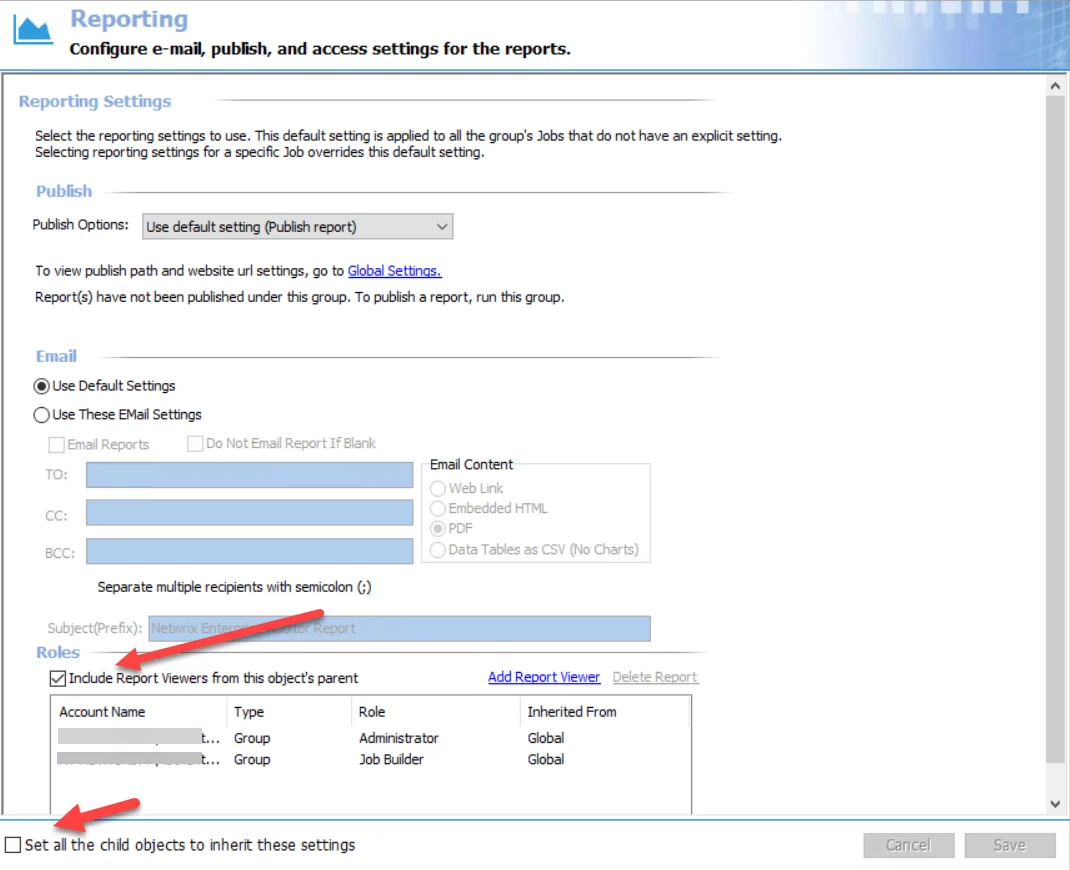 | 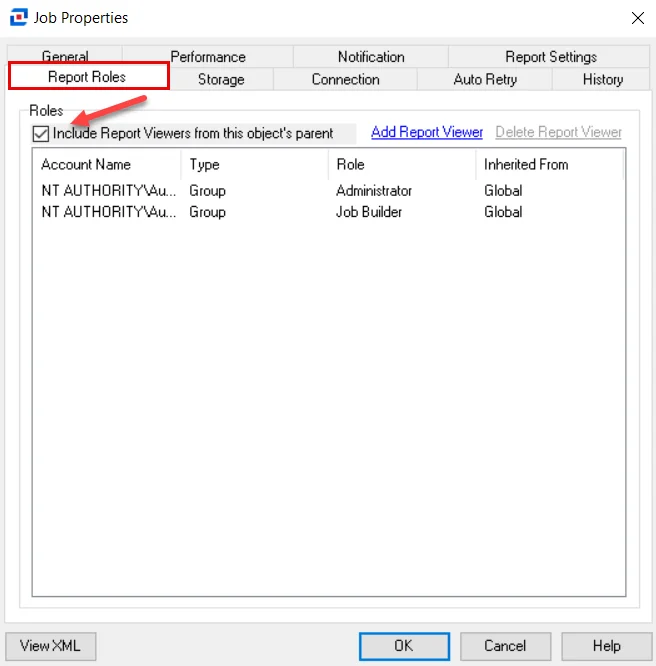 | 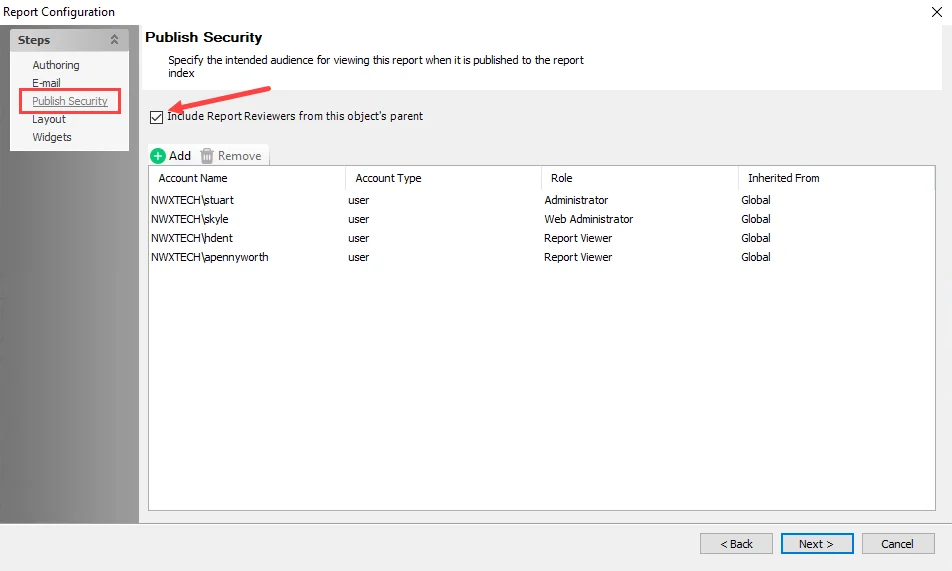 |
|---|---|---|
| Job Group Level | Job Level | Report Configuration Level |
There are two options that control inheritance for Report Viewers when selected:
- Include Report Viewers from this object’s parent – Automatically removes any user with the Report Viewer role inherited from a parent object at the lower levels
- Set all the child objects to inherit these settings – Only available at the Job Group level. Sets all Jobs and Reports to inherit group settings for all child objects by automatically selecting the Include Report Viewers from this object’s parent option. Any previous configurations are overwritten once Yes is selected in the confirmation window.
Roles & the Schedule Service Account
Once Role-Based Access is enabled, a user or group with the appropriate access role has the ability to schedule a job or job group as a Schedule Service Account at the Settings > Schedule node. Multiple accounts can be added as needed.
Who Configures This Account?
- Administrator role
- Power User role
- Global Options Administrator role
Whose Credentials Should Be Used as the Schedule Service Account?
-
A user with either:
- Administrator role
- Power User role
- Job Initiator role
NOTE: In order to run or schedule a Host Inventory query, the Schedule Service Account must have an Administrator, Power User, or Host Management Administrator role. Therefore, if the account has the Job Initiator role assigned, it must have the Host Management Administrator role as well.
The Schedule Service Account is used to access the Task folders when scheduling tasks and to apply locks on jobs.
-
Schedule Tasks
-
In order to have the appropriate level of rights to schedule tasks, the credentials specified must at least have the following:
- Create Files/Write Data rights on the Windows Task Folder
- Create Files/Write Data rights on the System 32 Task folder
- Otherwise, they should have local Administrator privileges on the Enterprise Auditor Console server
-
The user whose credentials are specified must also have a role that allows the scheduling of tasks – Administrator, Power User, or Job Initiator
-
-
Apply Locks
NOTE: If the Enterprise Auditor user whose credentials are used has the role of Job Initiator, the job must be locked in order for it to execute successfully.
-
These credentials are used to apply locks on jobs, enabling the Job Approver to have fewer rights on the Jobs directory. Therefore, the credentials specified must at least have the following:
- Modify rights on this directory
- Otherwise, these credentials should have local Administrator privileges on the Enterprise Auditor Console server
-
The Job Approver uses these credentials to apply locks. Therefore, the Job Approver must be added to the local policy Impersonate a client after Authentication.
-
Do not choose the Use local System account to schedule tasks option. This account does not have the appropriate rights to apply locks on jobs. Therefore, it does not work in conjunction with Role Based Access.
See the Schedule topic for additional instructions on configuring the Schedule Service Account.
Remember, these credentials must be for a user with local Administrator privileges or rights to the Windows Task Folder and the System 32 Task folder on the Enterprise Auditor Console server.
Securing Published Reports Only
In order to secure published reports through the Web Console, it is necessary to enable Role Based Access within the Enterprise Auditor Console. If that is the only reason the Role Based Access feature is being enabled, ensure the following requirements are met:
-
Administrator role assigned to all Enterprise Auditor Console users
- Anyone not assigned an Administrator role are unable to access the Enterprise Auditor Console after Role Based Access is enabled
-
Web Administrator role assigned to individuals who should have access to all reports, tags, and report permissions but not the Enterprise Auditor Console
-
Report Viewer assigned to individuals who should have access to reports and tags but not report permissions or the Enterprise Auditor Console
- Global Level Assignment – Access to all reports
- Job Group Level Assignment – Access to reports published by jobs within the job group
- Job Level Assignment – Access to reports published by the job
- Report Configuration Level Assignment – Access to the specific report
Follow the steps to assign roles at the global level.
Step 1 – Navigate to the Settings > Access node.

Step 2 – On the Access page, click Add Access. The Access Type wizard opens.

Step 3 – Select the A user or group accessing this console option. Click Next.

Step 4 – On the Console Access page, specify a group or user in the Name field. Use the ellipsis (…) to browse for accounts with the Select User or Group window.

Step 5 – Select a role for the group or user from the Role list. Click Finish. The group or user and role is added to the Role Membership list in the Roles view.
CAUTION: The first role or set of roles saved must include the Administrator role. Clicking Save for the first role or set or roles without including the Administrator generates an error message in the Enterprise Auditor Console.
Step 6 – Repeat Steps 2-4 to assign the Administrator, Web Administrator, and Report Viewer roles to other groups or users.
Step 7 – Click Save and then OK to confirm the changes. All applied roles are lost if they are not saved.
Role Based Access is enabled when the first role has been assigned.
The first role or set of roles saved must include the Administrator role. Clicking Save for the first role or set or roles without including the Administrator generates an error message in the Enterprise Auditor Console.
When Role Based Access is first enabled, restart the Enterprise Auditor application to ensure all roles are properly active. The Report Viewer role can be assigned at the job group, job, and report configuration levels. See the Reporting Node, Report Roles Tab, and Publish Security Page topics for additional information.
Workflow with Role Based Access Enabled
The following workflow summarizes the necessary steps involved to deploy a job once Role Based Access is enabled and roles have been assigned.
Step 1 – The Job Builder creates and configures a Enterprise Auditor job
Step 2 – The Job Approver reviews a new or edited job’s configuration, and either approves or rejects it
- If a job is approved, then a lock needs to be applied by right-clicking the job title in the Jobs tree and selecting Lock Job
- If a job is rejected, then the job remains unlocked
- If the Lock Job option is visible, then the job has not yet been approved
- If the Lock Job option is not visible, then the job has been approved
Step 3 – The Job Initiator can choose to run the job directly through the Enterprise Auditor Console or schedule it to run with the Schedule Service Account. This user will know the job was approved by the grayed-out Unlock Job option in the right-click menu.
-
Job Initiator/Job Initiator (No Actions) – The Job Initiator can only execute locked job.
- For the Job Initiator (No Actions) role, the user is unable to execute a job which contains configured actions, even if it is approved and locked
- Both roles can enable and disable job groups and jobs regardless of whether or not they are locked. Disabled jobs are grayed out with a red x next to it and are not executed with the job group. When applied at the job group level, all nested jobs are disabled and do not run. However, any new job added to that group is enabled by default.
NOTE: The Job initiator can also publish the reports already generated by the job.
-
Publish – To publish reports which have already been generated to the Web Console
- See the Report Settings Tab topic for additional information
Step 4 – After a job has been successfully run, the Job Viewer can now view the results of the job under the job’s Status and Results node, or in the Web Console. See the Viewing Generated Reports topic for additional information.
NOTE: The Job Builder, Job Approver, and Job Initiator may also view these results within the Enterprise Auditor Console. Additionally, users with these roles can view reports within the Web Console.
Other Console Roles
Any modifications needed in the Settings or Host Management nodes must be done by the corresponding administrator role (Global Options Administrator, Access Administrator, or Host Management Administrator). These roles can be used in conjunction with any other role (for example, a user can be a Job Builder and Global Options Administrator in order to build jobs and manage corresponding Connection Profiles).
Web Administrator
The Web Administrator can view all reports within the Web Console.
In addition to viewing report content, Web Administrators can view tags and report permissions.
Remember, a user with only the Web Administrator role is unable to access the Enterprise Auditor Console.
Report Viewer
The Report Viewer can view reports within the Web Console according to where the user’s role was assigned: global, job group, job, or report configuration.
Remember, a user with only the Report Viewer role is unable to access the Enterprise Auditor Console.