SQLscripting Analysis Module
Use the SQLscripting analysis module to apply SQL scripting to the selected job.
The SQLscripting analysis module evaluates the Enterprise Auditor user’s permission level to determine whether to allow the connected user to run the scripted command. Since this evaluation is based on specific SQL database permissions and is not always under Enterprise Auditor’s control, some scripts with correct syntax may fail due to insufficient permissions.
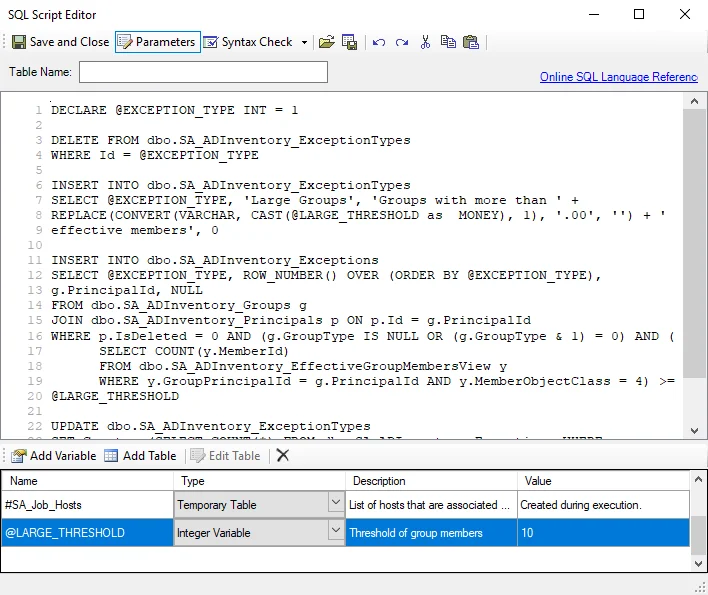
The SQL Script Editor window has the following options:
-
Save and Close – Saves script and closes window
-
Parameters – Establishes parameters for SQL scripts in the editor
- Clicking Parameters opens the Parameters interface. See the Parameters topic for additional information.
-
Syntax Check – Checks SQL script syntax
- Syntax Check does not identify logic errors, only instances where syntax is incorrect. Click Syntax Check to open the Script Errors window which identifies syntax errors.
- Syntax Check reports back syntax errors starting from the beginning of the script to the end. Syntax Check does not return a list of errors.
-
Load file – Opens a File Explorer which can be used to navigate to a SQL file
-
Save to File – Saves the currently configured script into a SQL file
-
Undo – Undo the previous changes made to script (Ctrl+Z)
-
Redo – Redo the previous changes made to script (Ctrl+Y)
-
Cut – Cuts the highlighted script from the SQL script editor (Ctrl+X)
-
Copy – Copies the highlighted script into the SQL script editor (Ctrl+C)
-
Paste – Pastes cut or copied script into the SQL script editor (Ctrl+V)
-
Online SQL Language Reference – Opens the Microsoft Transact-SQL Reference article
Click Save and Close to return to the Analysis Properties page. If no changes were made or intended, it is best practice to click Cancel to close the SQL Script Editor wizard to ensure no accidental changes are saved.
Parameters
Use the Parameters window to add, edit, and delete temporary variables and tables defined by SQLscripting and users. The window only displays when Parameters is clicked.
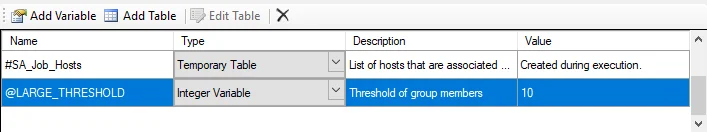
CAUTION: not modify any parameters where the Value states Created during execution.
The Parameters window has the following options:
-
Add Variable – Adds a new variable
- Double-click in the Name, Description, and Value fields to enter custom labels
- Select the variable Type from the dropdown menu
- Variable names must begin with the
@sign
-
Add Table – Adds a new table
-
Edit Table – Opens the Edit Table window. See the Edit Table topic for additional information.
-
Delete – Deletes the selected variable or table
The parameters have the following properties:
-
Name – Name of the variable or table
-
Type – Type of variable or table
- String variables utilize a text string input
- Integers and floats are able to handle invalid inputs
- Boolean variables only take True/False input, in SQL they are 1/0
- Percentages only take whole numbers 0-100, converted to 0.0 to 1.0 in SQL
- Temporary and Variable Tables
-
Description – Description of the variable or table. See the Edit Table topic for additional information.
-
Value – Input value
Edit Table
Click Edit Table to open the Edit Table window to modify parameters for the selected table.
The Edit table window has the following options:
-
Name – Use the Parameters window to edit the table name.
-
If the name begins with a
#it is a temporary table -
If the name begins with a
@it is a table variable- In SQLCommand, these can be passed in as structured table parameters
-
If neither is specified, Enterprise Auditor assumes it is a temporary table
-
-
Description – Use the Parameters window to edit the description
-
Values – Add, edit, and remove values from the table
- Add – Select from the dropdown to either Add New Row or Add New Column to the table
- Edit a value – Edits the selected value
- Delete – Deletes the selected value
- Up/Down – Changes the value position higher or lower
A CSV file is created under the job’s directory when a parameter table is added to the analysis. A pre-existing CSV file can also be uploaded to populate the table.
Click OK to confirm changes to the table. If no changes were made or intended, click Cancel to close the Edit Table window to ensure no accidental changes are saved.
VBscripting Analysis Module
Use the VBscripting analysis module to access the VBScript Editor and apply VB scripting to the current analysis.
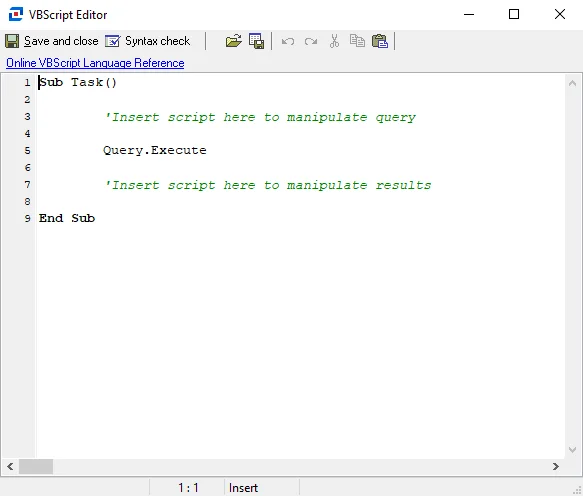
The VBScript Editor has the following options:
-
Save and Close – Saves the script and closes the window
-
Syntax Check – Checks VB script syntax
- Syntax Check does not identify logic errors, only instances where syntax is incorrect. Click Syntax Check to open the Script Errors window which identifies syntax errors.
- Syntax Check reports back syntax errors starting from the beginning of the script to the end. Syntax Check does not return a list of errors.
-
Load file – Opens a File Explorer which can be used to navigate to a VBS file
-
Save to File – Saves the currently configured script into a VBS file
-
Undo – Undo the previous changes made to script (Ctrl+Z)
-
Redo – Redo the previous changes made to script (Ctrl+Y)
-
Cut – Cuts the highlighted script from the VB script editor (Ctrl+X)
-
Copy – Copies the highlighted script in the VB script editor (Ctrl+C)
-
Paste – Pastes cut or copied script into the VB script editor (Ctrl+V)
When done using the editor, click Save and Close to return to the Analysis Properties page. Make sure to save the analysis.