SQL: Category
The Category page in the SQL Data Collector Wizard lists the available query categories, sub-divided by auditing focus.
The query categories are:
-
Permissions
- Permissions Collection – Gather permissions on server and database objects
-
Server Audits
- Server Audits Events Collection – Gather events from SQL server audits
-
Sensitive Data
- Sensitive Data Collection – Scan databases for sensitive data
NOTE: The Sensitive Data category options require the Sensitive Data Discovery Add-on to have been installed on the Enterprise Auditor Console before the SQL Data Collector can collect sensitive data. See the Sensitive Data Discovery Add-On Installation topic for additional information.
-
Microsoft SQL Server
-
Discovery
- Enumerate Network – Enumerate local network for browsable SQL server instances visible to the storage host
-
Custom SQL Query
- Custom Query – Run a custom SQL query against a SQL database
-
Infrastructure
- Server Properties – Information about the server
- Configuration Properties – Information about server configuration
- Version Information – Version information about Microsoft SQL server
- File Groups – File group information
- Files – File information
- Database Information – Information about databases
-
Operations
- Database Without Backups – List of all databases without backups
- Latest Week Backups – List of latest week database backups
-
Utilities
- Remove Storage Tables – Removes the tables created and used by the SQL server data collector
-
Legacy Queries
- Server Principles – Data for every server level principal
- Database Principles – Data for every database level principal
- Server Permissions – Data about server permissions
- Database Permissions – Data about database permissions
- Server Roles – Data about server roles
- Database Roles – Data about database roles
- System Objects – Data about system objects
- Object Collection – Collects SQL server objects
-
-
Oracle
-
Custom Oracle Query
- Custom Oracle Query – Run a custom SQL query against an Oracle container
-
Infrastructure
- Version Information – Version information about the Oracle database
- File Group Information – Information about file groups and tablespaces
- Data File Information – Information about data files
- Database Information – Information about database configurations
- Initialization Parameter Information – Information about initialization parameters
- System Parameter Information – Information about system parameters
- Container Information – Information about the containers of the databases, both root and pluggable
- Pluggable Databases History – View of the pluggable databases (PBD) history
- Database Instance Information – Shows information about the current instance of the database
- Free Space in Tablespaces – Describes the free extents in all tablespaces in the database
-
Operations
- Latest Week Backup – Information about the latest week backup
- Oldest and Newest Backup – Information about the oldest and the most recent backups
- Database File Without Backup – Indicates file names of the files that are not present in the RMAN backup
-
Utilities
- Remove Storage Tables – Removes the tables created and used by the Oracle Data Collector
-
-
Azure SQL
-
Discovery
- Enumerate Azure SQL Instances – Enumerate Azure SQL instances and Azure resources
-
Utilities
- Remove Storage tables – Removes the tables created and used by Azure SQL Discovery
-
-
MySQL
-
Custom MySQL Query
- Custom Query – Run a custom SQL query against a SQL database
-
Utilities
- Remove Storage Tables – Removes tables created for MySQL Data Collector
-
-
PostgreSQL
-
Custom PostgreSQL Query
- Custom Query – Run a custom SQL query against a SQL database
-
Utilities
- Remove Storage Tables – Removes tables created for PostgreSQL Data Collector
-
-
Db2LUW
-
Custom Db2LUW Query
- Custom Query – Run a custom SQL query against a SQL database
-
Utilities
- Remove Storage Tables – Removes tables created for Db2LUW Data Collector
-
Db2LUW Permissions Scan
- Db2LUW Permissions Scan – Collect permissions from the targeted instances
-
-
Utilities
- Remove Storage Data – Removes stored data for specific instances on a specific host
SQL Custom Connection Profile & Default Dynamic Host List
The SQL Data Collector requires a custom Connection Profile and Host List. The SQL SERVERS default host list can be used with this data collector for the SQL Solution. The host inventory option during host list creation makes it necessary to configure the Connection Profile first.
Connection Profile
Create a Connection Profile and set the following information on the User Credentials window.
-
For an Active Directory account:
-
Select Account Type – Active Directory Account
-
Domain – Drop-down menu with available trusted domains will appear. Either type the short domain name in the textbox or select a domain from the menu.
-
User name – Type the user name
-
Password Storage – Choose the desired option for credential password storage:
- Application – Uses the configured Profile Security setting as selected at the Settings > Application node. See the Application topic for additional information.
- CyberArk – Uses the CyberArk Enterprise Password Vault. See the CyberArk Integration topic for additional information. The password fields do not apply for CyberArk password storage.
-
Password – Type the password
-
Confirm – Re-type the password
-
-
For a SQL account:
- Select Account Type – SQL Authentication
- User name – Enter user name
- Password Storage – Application (Uses the configured Profile Security setting as selected at the Settings > Application node. See the Application topic for additional information.)
- Password – Type the password
- Confirm – Re-type the password
See the Connection topic for additional information.
Host List
The required host list depends on the database that the SQL data collector is being used for.
Default Dynamic Host List (SQL)
Jobs using the SQL Data Collector can use the SQL Servers default host list. This is a dynamic host
list that is populated from hosts in the Host Master Table which meet the host inventory criteria
for the list, IsSQLServer = True. Since the SQL Servers host list is default, it is available to
jobs and job groups for host assignment. See the
Host Management
topic for additional information.
Oracle / MySQL / PostgreSQL / Db2
Jobs in the Oracle, MySQL, Postgre SQL, or Db2 solution using the SQL Data Collector must be configured to query a host list with the servers containing the target databases. Setup the list of hosts that needs to be monitored. Be sure to use a specific host name (if forcing the connection to a secondary host) or just the server name if connecting to the server. See the Host Management topic for additional information.
Additionally, the database instances must be added to the Filter page in the query configuration. See the SQL: Filter topic for additional information.
SQL: Criteria
The Criteria page is where criteria to be used for discovering sensitive data are configured. It is a wizard page for the Sensitive Data Collection category.
This page requires the Sensitive Data Discovery Add-On to be installed on the Enterprise Auditor Console to define the criteria and enable the Criteria Editor. See the Sensitive Data Discovery Add-On Installation topic for additional information.
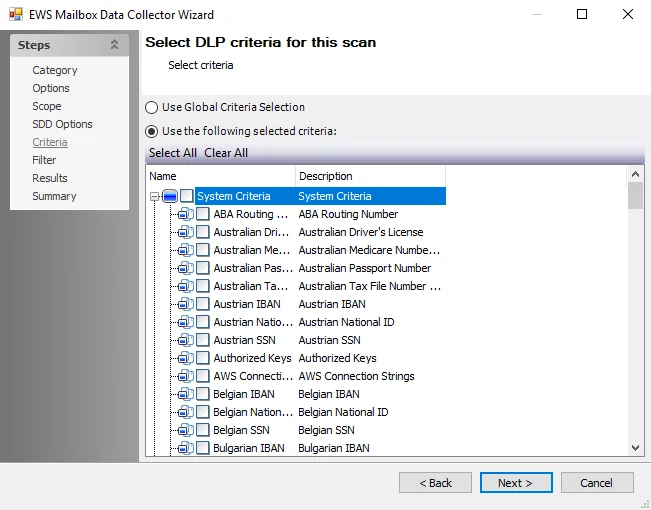
The options on the Criteria page are:
-
Use Global Criterion Selection – Select this option to inherit sensitive data criteria settings from the Settings > Sensitive Data node. See the Sensitive Data topic for additional information.
-
Use the following selected criteria – Select this option to use the table to select which sensitive data criteria to scan for
- Select All– Click Select All to enable all sensitive data criteria for scanning
- Clear All – Click Clear All to remove all selections from the table
- Select the checkboxes next to the sensitive data criteria options to enable it to be scanned for during job execution
The table contains the following types of criteria:
NOTE: Until the Sensitive Data Discovery Add-On is installed, only the headers for the System Criteria and User Criteria nodes are visible in the table.
-
System Criteria – Lists pre-defined criteria
-
User Criteria – Lists user-defined criteria
Use the Sensitive Data Criteria Editor in the Settings > Sensitive Data to create and edit user-defined criteria. See the Sensitive Data Criteria Editor topic for additional information.
NOTE: Adding unnecessary criteria can adversely impact the scanner performance and can cause the scanning job to take a long time. If performance is adversely affected, revisit the sensitive data scanning criteria and remove criteria that is not required.
SQL: Custom Oracle Query
The Custom Query page for a Custom Oracle Query contains the same options as the Custom Query page for a custom SQL query, with the addition of the Convert CDB to DBA on non-container databases checkbox. It is a wizard page for the Custom Oracle Query category.
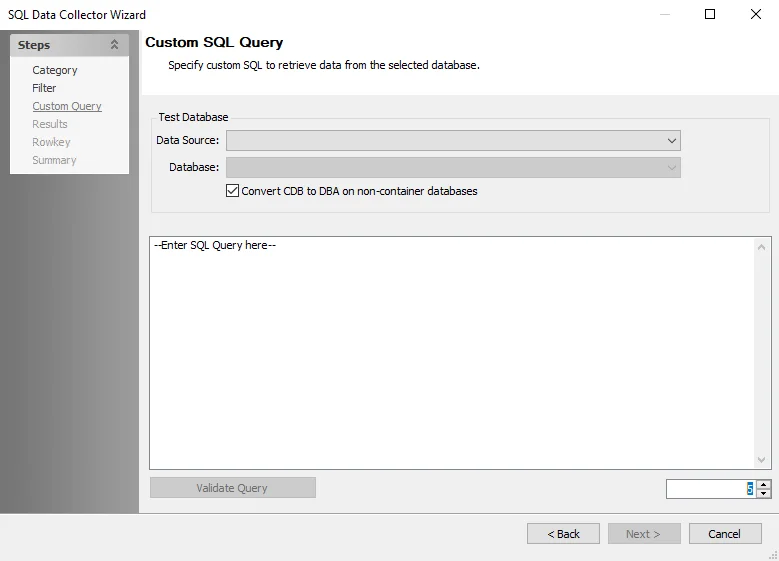
The configurable options are:
-
Test Database:
-
Data Source – Select the host\instance from the drop-down menu
-
Database – Select the database from the drop-down menu
- Convert CDB to DBA on non-container databases
-
-
SQL Query textbox – Enter the custom SQL script
-
Validate Query – Click to test the query, results display in the box
-
Row limit – Enter a number to limit the rows the query is tested on
SQL: Custom SQL Query
The Custom Query page for a Custom SQL Query contains the following configuration options. It is a wizard page for the following categories:
- Custom MySQL Query
- Custom PostgreSQL Query
- Custom SQL Query
- Custom Db2LUW Query
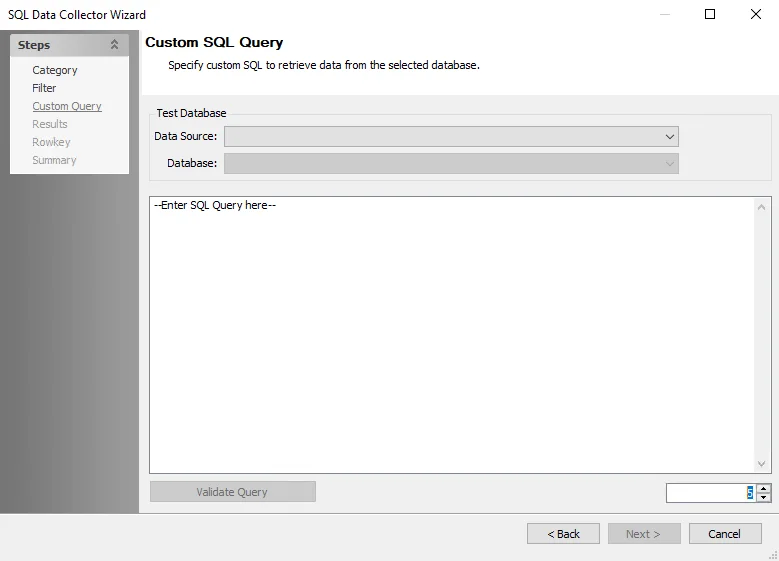
The configurable options are:
-
Test Database:
- Data Source – Select the host\instance from the drop-down menu
- Database – Select the database from the drop-down menu
-
SQL Query textbox – Enter the custom SQL script
-
Validate Query – Click to test the query, results display in the box
-
Row limit – Enter a number to limit the rows the query is tested on
SQL: Filter
The Filter page is where the query can be scoped to target specific databases or instances. It is a wizard page for the categories of:
-
Permissions > Permissions Collection
-
Server Audits > Server Audit Events Collection
-
Sensitive Data > Sensitive Data Collection
-
Microsoft SQL Server:
- Discovery
- Custom SQL Query
- Infrastructure
- Operations
- Utilities > Remove Storage Tables
- Legacy Queries
-
Oracle:
- Custom Oracle Query
- Infrastructure
- Operations
- Utilities > Remove Storage Tables
-
MySQL:
- Custom MySQL Query
- Utilities > Remove Storage Tables
-
PostgreSQL:
- Custom PostgreSQL Query
- Utilities > Remove Storage Tables
-
Db2LUW:
- Custom Db2LUW Query
- Utilities > Remove Storage Tables
- Db2LUW Permissions Scan
-
Utilities – Remove Storage Data
It is necessary for the SA_SQL_Instances table to be populated before available databases/instances can populate the Available Server audits list. For Oracle and SQL, the SA_SQL_Instances table is populated through an instance discovery query. See the 0-SQL_InstanceDiscovery Job topic for additional information. For PostgreSQL and MySQL Scans, the SA_SQL_Instances table is populated manually in the Manage Connections window. See the Manage Connections Window topic for additional information. Once the table has been populated, a query can be scoped.
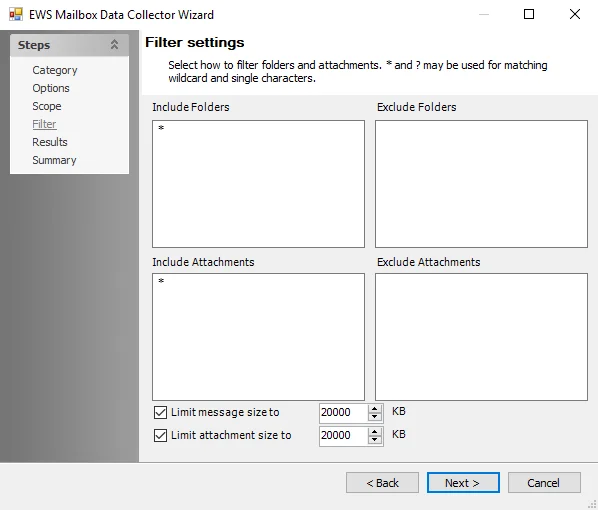
The configurable filter options are:
-
Connections — Opens the Manage Connections window to add or modify database instances. See the Manage Connections Window topic for additional information.
-
Filter options
-
All database objects — No scoping
-
Only select database objects — Scope to specific databases
- Click Retrieve to display available server audits
-
-
Available database objects — Displays known databases and instances for query scoping
- Select from the available list and click Add
-
Selected databases or instances — Displays selected database objects for which the query has been scoped. Additional options include:
- Remove — Removes the selected database/instance from the query
- Include — Reverts an exclusion. By default, all sub tables are included.
- Exclude — Excludes selected databases/instances and displays them in red
- Add Custom Filter — Opens the Add custom filter window to build a custom filter to be applied to the selected databases/instances. See the Add Custom Filter Window topic for additional information.
- Import CSV — Import a list of databases/instances from a CSV file
- Export CSV — Exports the list of databases/instance to a CSV file through the Save As window
Manage Connections Window
The Manage Connections window enables you to add database instances to search. Click the Connections button to open it.
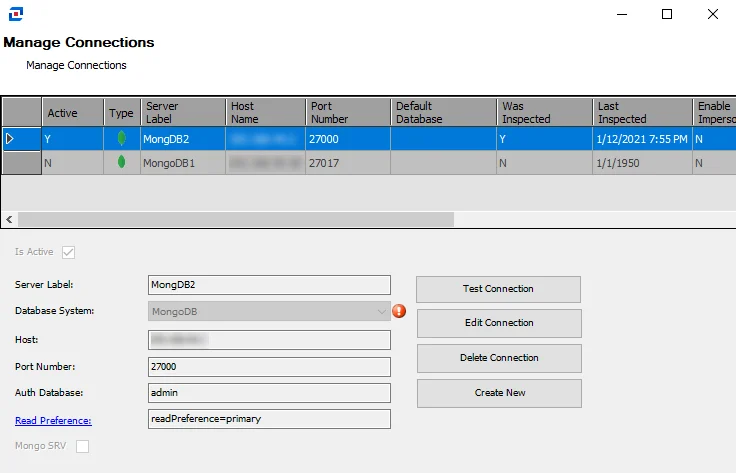
The Manage Connections table lists the previously added database instances and their attributes. Select a row in the table to edit that instance, or create a new instance to add to the table:
- Is Active — Select the checkbox to include the database on the Servers Pane on the Filter page
- Instance Label — The name of the server
- Database System — Select from a list of available databases
- Service Name — Name of the service
- Host — Name or IP address of the host where the database is located
- Port Number — Port number for the database. If a non-default port is being used, it should be specified in the Port Number section.
- Default Database — Account used to access the database. Admin is recommended.
- Enable impersonation — Select to enable impersonation
- Service Type— If applicable, select whether the service type is Service or SID
In the Manage Connections Table, the following information is also listed:
- Was Inspected — Indicates whether information for a connection was validated. Y indicates the information has been validated. N indicates the information has not been validated.
- Last Inspected — Indicates the date and time of when the connection information was last inspected. If blank, the connection information has not yet been validated.
The Manage Connections window has the following buttons:
- Test Connection — Click to verify the connection to the database with the connection profile applied to the job group
- Edit Connection — Click to edit information for the selected connection
- Delete Connection — Click to delete the selected connection
- Create New — Click to create a new connection
Add Custom Filter Window
The Add custom filter window opens from the Filter page of the SQL Data Collector Wizard. It enables you to apply a custom scoping filter to the query.
Type the filter in the window and click Save. The following characters can be used in the filter:
- Forward slash (/) – Path separator
- Asterisk (*) – Wild card for any combination of characters
- Question mark (?) – Wild card for a single character
Use the following format to add a custom filter for a server:
-
SQL:
[SQL Server Name]/[Host or IP Address]/[Database Name]/[TableName]
-
Oracle:
[Oracle Server Name]/[Host or IP Address]/[Container Name]/[Schema]/[Table Name]
-
Azure SQL:
[Azure SQL Server Name]/[Host or IP Address]/[Database Name]/[Table Name]
-
MySQL:
[MySQL Server Name]/[Host or IP Address]/[DastabaseName]/[TableName]
-
PostgreSQL:
[PostgreSQL Server Name]/[Host or IP Address]/[DastabaseName]/[Schema]/[TableName]
-
Db2:
[Db2LUW Server Name]/[Host or IP Address]/[DastabaseName]/[TableName]
SQL: Options
Use the Options page to configure additional settings. The contents of the page vary according to the category selected. The Options page is a wizard page for the categories of:
- Server Audits
- Sensitive Data
Server Audits
Use the Options page to specify collection options to use when gathering server audits. This is a page for the Server Audits Events Collection category.
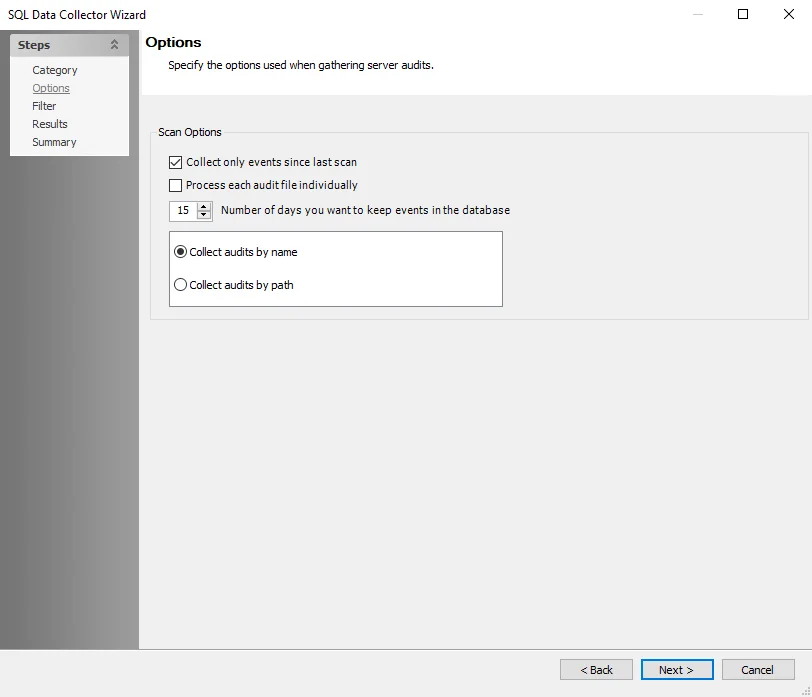
The scan options are:
-
Collect only events since last scan – Differential scanning
-
Process each audit file individually
-
Number of days you want to keep events in the database – Data retention period, set to 15 days by default
-
Collection Method – Choose a collection method:
- Collect audits by name
- Collect audits by path
Sensitive Data
Use the Sensitive Data Scan Settings (Options) page to specify collection options to use when gathering server audits. This is a page for the Sensitive Data Collection category.
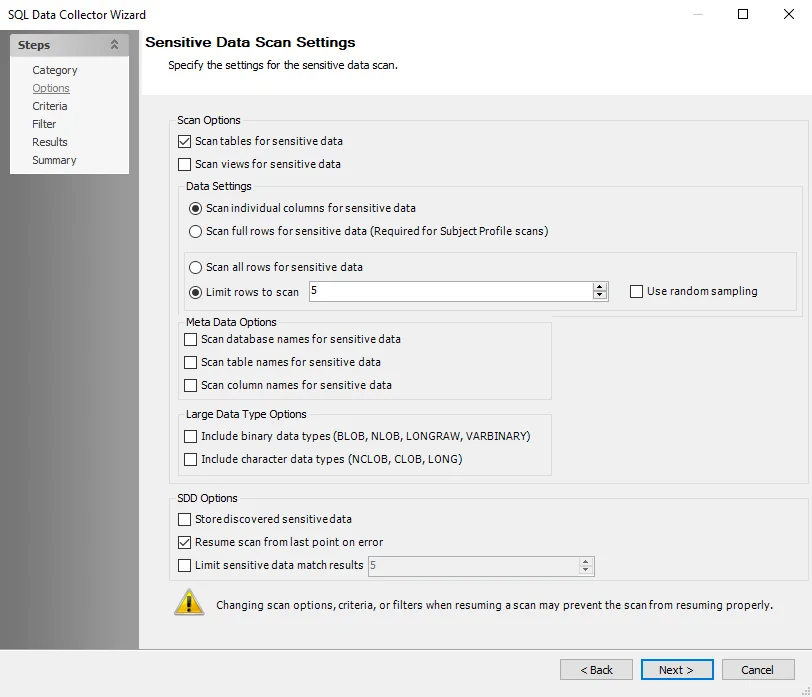
The sensitive data scan settings are:
Scan Options
-
Scan tables for sensitive data – Scans the tables within the database for sensitive data
- The Oracle default is set for optimal performance for a high-level scan of only tables
-
Scan views for sensitive data – Scans views for sensitive data
Data Settings
- Scan individual columns for sensitive data – Scans individual columns within the database for sensitive data
- Scan full rows for sensitive data – Scans full rows within the database for sensitive data
- Scan all rows for sensitive data – Scans all rows within the database for sensitive data
- Limit rows to scan – Select the number of rows to scan for sensitive data. Select the Use random sampling checkbox to enable random sampling for checking for sensitive data.
Meta Data Options
- Scan database names for sensitive data – Scans database names for sensitive data if the database names are included as part of the keyword list in the scanning criteria
- Scan table names for sensitive data – Scans table names within the database for sensitive data if the table names are included as part of the keyword list in the scanning criteria
- Scan column names for sensitive data – Scans column names within the database for sensitive data. This scans all column names of every table for sensitive data if the column names are included as part of the keyword list in the scanning criteria.
Large Data Type Options
- Included binary data types (BLOB, NLOB, LONGRAW, VARBINARY) – Select to include the listed binary data types
- Include character data types (NCLOB, CLOB, LONG) – Select to include the listed character data types
SDD Options
-
Store discovered sensitive data – Stores potentially sensitive data in the Enterprise Auditor database. Any sampled sensitive data discovered based on the matched criteria is stored in the Enterprise Auditor database. This functionality can be disabled by clearing this option.
NOTE: The Store discovered sensitive data option is required to view Content Audit reports in the Access Information Center for SQL data.
CAUTION: Changing scan options, criteria, or filters when resuming a scan may prevent the can from resuming properly.
-
Resume scan from last point on error – Resumes scan from where the previous scan left off when the previous scan was stopped as a result of an error
Remember, the Sensitive Data Discovery Add-on is required to use the sensitive data collection option.
SQL Data Collector
The SQL Data Collector provides information on database configuration, permissions, data extraction, application name of the application responsible for activity events, an IP Address or Host name of the client server, and sensitive data reports. This data collector also provides information on Oracle databases including infrastructure and operations.
The SQL Data Collector has been preconfigured within the Database data collection jobs for Db2, MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, Redshift, and SQL Server databases. Both this data collector and the Database Solution are available with a special Enterprise Auditor license. See the following topics for additional information:
Protocols
TCP
Ports
For Db2:
- Specified by Instances table (default is 5000)
For MySQL:
- Specified by Instances table (default is 3306)
For Oracle:
- Specified by Instances table (default is 1521)
For PostgreSQL:
- Specified by Instances table (default is 5432)
For SQL:
- Specified by Instances table (default is 1433)
Permissions
For MySQL:
- Read access to MySQL instance to include all databases contained within each instance
- Windows Only — Domain Admin or Local Admin privilege
For Oracle:
- User with SYSDBA role
- Local Administrator on the target servers – Only applies to Windows Servers and not on Linux or Unix operating systems
For PostgreSQL:
- Read access to all the databases in PostgreSQL cluster or instance
- Windows Only — Domain Admin or Local Admin privilege
For Redshift:
-
Read-access to the following tables:
- pg_tables
- pg_user
For SQL:
-
For Instance Discovery, local rights on the target SQL Servers:
- Local group membership to Remote Management Users
- Permissions on the following WMI NameSpaces:
root\Microsoft\SQLServer, root\interop
-
For permissions for data collection:
- Read access to SQL instance
- Requires SQL Full-Text and Semantic Extractions for Search feature to be installed on the target SQL instance(s) when using the Scan full rows for sensitive data option on the Options wizard page
- Grant Authenticate Server to [DOMAIN\USER]
- Grant Connect SQL to [DOMAIN\USER]
- Grant View any database to [DOMAIN\USER]
- Grant View any definition to [DOMAIN\USER]
- Grant View server state to [DOMAIN\USER]
- Grant Control Server to [DOMAIN\USER] (specifically required for the Weak Passwords Job)
See the Azure SQL Auditing Configuration topic and the AzureSQL Target Least Privilege Model topic for additional information.
Sensitive Data Discovery Considerations
The Sensitive Data Discovery Add-On must be installed on the Enterprise Auditor Console server, which enables Sensitive Data criteria for scans. If running Sensitive Data Discovery (SDD) scans, it will be necessary to increase the minimum amount of RAM. Each thread requires a minimum of 2 additional GB of RAM per host. For example, if the job is configured to scan 8 hosts at a time , then an extra 16 GB of RAM are required (8x2=16).
SQL Query Configuration
The SQL Data Collector is configured through the SQL Data Collector Wizard. The wizard contains the following pages, which change based upon the query category selected:
NOTE: The SQL Data Collector is used in multiple Enterprise Auditor Solutions, and the query categories used are dependent on the solution.
- SQL: Category
- SQL: Options
- SQL: Criteria
- SQL: Filter
- SQL: Settings
- SQL: Custom SQL Query
- SQL: Custom Oracle Query
- SQL: Results
- SQL: Rowkey
- SQL: Summary
SQL: Results
The Results page is where the properties that will be gathered are selected. It is a wizard page for all of the categories.
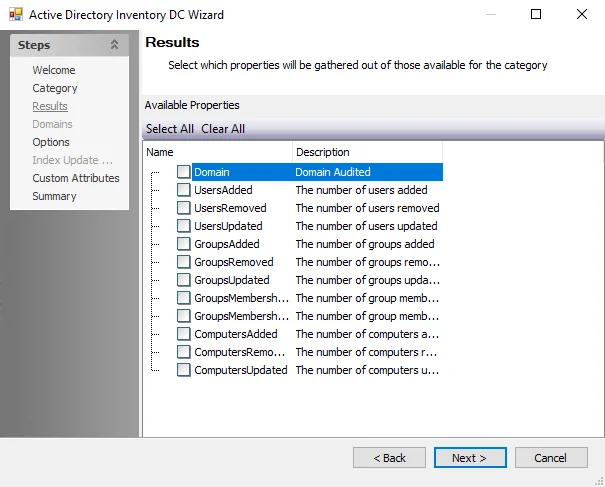
Properties can be selected individually, or the Select All and Clear All buttons can be used. All selected properties are gathered. Available properties vary based on the category selected.
SQL: Rowkey
The Rowkey page configures the Rowkey for the SQL query. It is a wizard page for the Custom Query categories.
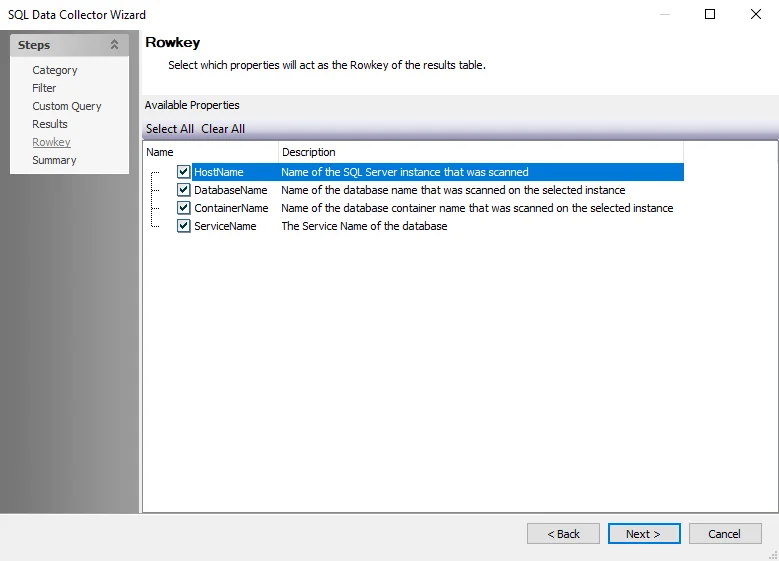
Properties selected on the Results page are listed. Select the property or properties to act as the Rowkey. Properties can be selected individually, or the Select All and Clear All buttons can be used.
SQL: Settings
The Settings page configures the removal of data from the Enterprise Auditor database for specific instances. It is a wizard page for the category of Utilities.
Data from the selected categories will be removed from the Enterprise Auditor database:
- Permissions
- Audits
- Sensitive Data
- Orphaned Rows
SQL: Summary
The Summary page is where the configuration settings are summarized. It is a wizard page for all of the categories.
Click Finish to save configuration changes. If no changes were made, it is a best practice to click Cancel to close the SQL Data Collector Wizard ensuring that no accidental clicks are saved.