Enterprise Auditor Initial Configuration
Once the Enterprise Auditor installation process is complete, and before performing actions within Enterprise Auditor, the initial settings for the Enterprise Auditor Console must be configured.
Step 1 – Launch the Enterprise Auditor application. The installation wizard places the Enterprise Auditor icon on the desktop.
Step 2 – On the Welcome page of the Enterprise Auditor Configuration Wizard, click Next to continue.
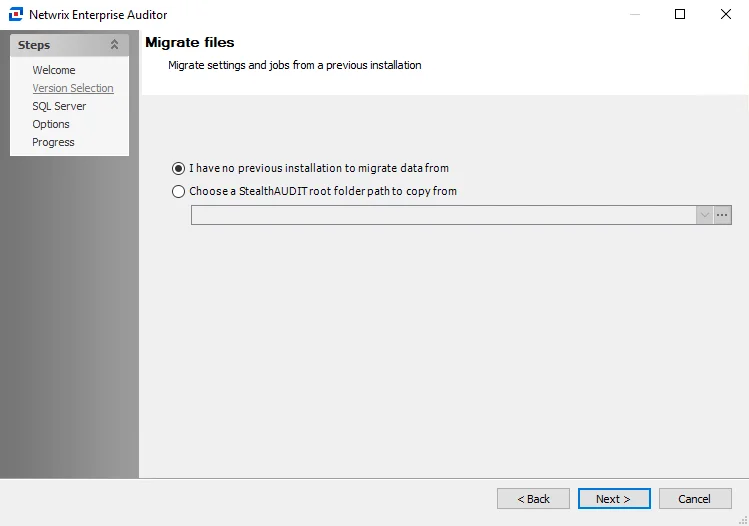
Step 3 – On the Version Selection page, select the I have no previous versions to migrate data from and click Next to continue.
NOTE: If you are upgrading from a previous version of Enterprise Auditor, select Choose a StealthAUDIT root folder path to copy from. See the Enterprise Auditor Console Upgrade topic for additional information.
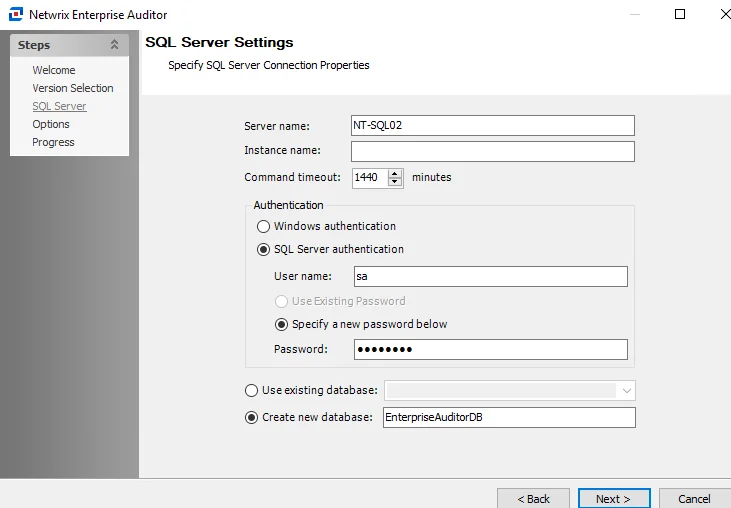
Step 4 – Configure the options on the SQL Server Settings page.
-
Server name – Enter the database server host name (NetBIOS name, FQDN, or IP Address)
-
Instance name – If the SQL Server is configured to use an instance name, provide the instance name in the text box. If not, leave this text box blank.
- To change the instance port number, provide the instance name in the format
<Instance name>,<Port>. For example, if using the default MSSQLSERVER instance and port 12345, the instance name should be entered asMSSQLSERVER,12345.
- To change the instance port number, provide the instance name in the format
-
Command timeout [number] minutes – Number of minutes before Enterprise Auditor halts any SQL queries running for that amount of time. This prevents SQL queries from running excessively long. The default is 1440 minutes.
-
Windows authentication – Leverages the account used to open the Enterprise Auditor Console. This option will use Windows NT Authentication to authenticate to the SQL Server. It also requires the Schedule Service Account to have proper permissions on the SQL database.
-
SQL Server authentication – Leverages an account created within the SQL Server.
- User name and password – If SQL Server authentication is selected, provide the User name and Password for the SQL account.
- Specify a new password below – Specify a new password for the SQL server.
-
Use existing database – Confirm the SQL Server connection has been established by selecting the radio button for Use existing database and clicking the drop-down arrow. If a listing of databases appears, then the connection has been established. Select this option to use a pre-existing database. Then select a database from the drop-down menu of available databases.
-
Create new database – Select this option to create a new database during the configuration of the storage profile. Enter a unique, descriptive name for the new database. If multiple databases might exist for Enterprise Auditor, then the default name of Enterprise Auditor is not recommended.
See the Securing the Enterprise Auditor Database topic for additional information on creating a SQL Server database for Enterprise Auditor.
Step 5 – Click Next.
- If SQL Server authentication is used, the Options page is displayed next. Skip to Step 7.
- If Windows Server authentication is used, the Schedule Account page is enabled for configuration. Continue to Step 6.
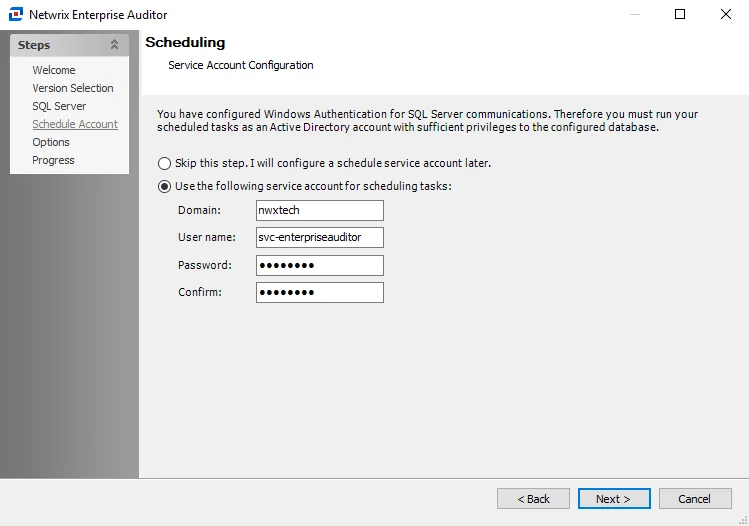
Step 6 – (Windows Authentication Only) Configure the schedule service account on the Scheduling page. The account configured here must be an Active Directory account and must have rights to the Enterprise Auditor Console server’s local Task folders as well as sufficient rights to the Enterprise Auditor database.
There are two options that can be selected:
-
Skip this step, I will configure a schedule service account later – Select this radio button to skip this step and configure the schedule service account later
-
Use the following service for account – Select this radio button to configure the schedule service account and enter the following information:
- Domain – The domain for the service account
- User name – The user name for the service account
- Password – The password for the service account
- Confirm – Re-enter the password for the service account
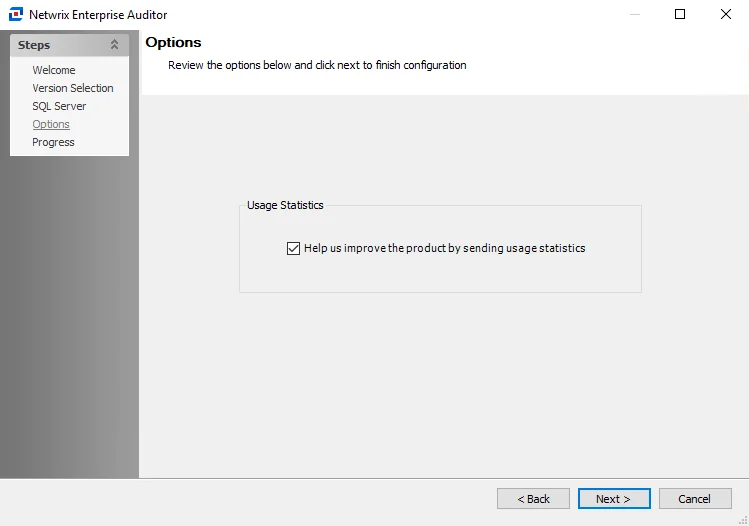
Step 7 – On the Options page, select whether to send usage statistics to Netwrix to help us improve our product. After the Usage Statistics option is set as desired, click Next to continue.
-
If selected, usage statistics are collected and sent to Netwrix
- Upon startup of the Enterprise Auditor console, the system checks if usage statistics have been sent in the last 7 days. If they have not been, stored procedures run against the Enterprise Auditor database and gather data about job runs, access times, and environmental details like resource counts, users counts, number of exceptions, and so on. This data is then sent back to Netwrix to help us identify usage trends and common pain points, so that we can use this information to improve the product.
- Only anonymous statistic-level data is included. No private company or personal data is collected or sent to Netwrix.
-
If cleared, no usage statistics are collected or sent to Netwrix
Step 8 – After the Enterprise Auditor Configuration Wizard finishes configuring your installation, click Finish to open the Enterprise Auditor Console.
NOTE: To view the log for the setup process, click View Log to open it. If you need to view
the log after exiting the wizard, it is located in the installation directory at
..\STEALTHbits\StealthAUDIT\SADatabase\Logs. See the
Troubleshooting
topic for more information about logs.
The Enterprise Auditor Console is now ready for custom configuration and use. There are a few additional steps to complete in order to begin collecting data, such as configuring a Connection Profile and a Schedule Service account as well as discovering hosts and setting up host lists. See the Getting Started topic for additional information.