Manually Configure Auditing in OneFS
Manual configuration for auditing is optional for newer versions as the Activity Agent can configure the auditing automatically using the OneFS API. Follow the steps through the OneFS Storage Administration Console.
Step 1 – Navigate to the Cluster Management tab, and select Auditing.
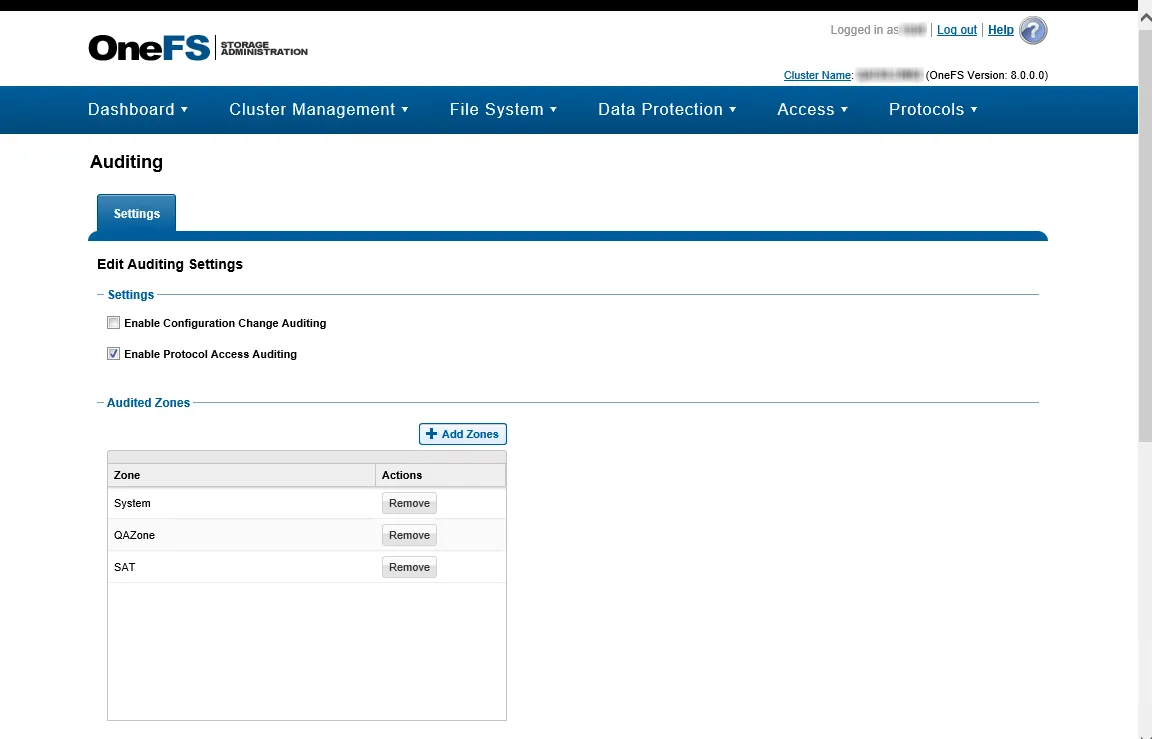
Step 2 – In the Settings section, check the Enable Protocol Access Auditing box.
Step 3 – In the Audited Zones section, add at least one zone to be audited. The System zone is typically used. If the CIFS or NFS shares are accessible through different zones on the OneFS cluster, include all relevant zones.
Ensure that OneFS collects only events you are interested in. By default, OneFS may monitor things like directory reads, which can take up a large amount of space. Configuring the OneFS events that need monitoring is not done through the Activity Monitor console. Configure OneFS event monitoring using OneFS CLI with the isi audit modify command for each access zone. Enabling monitoring for only what is needed for the environment will reduce the data load to the agent.
Activity Monitor monitors the following events: close_file_modified, close_file_unmodified,
create_file, create_directory, delete_file, delete_directory, rename_file,
rename_directory, set_security_file, set_security_directory, and open_directory (if you want
to monitor Directory List/Read events).
For each monitored access zone:
-
Use isi audit settings view
isi --zone ZONENAMEto check current settings. -
Disable reporting of failure and syslog audit events with:
isi audit settings modify --zone ZONENAME --clear-audit-failure --clear-syslog-audit-events
-
Set the success audit events with:
isi audit settings modify --zone ZONENAME --audit-success=close_file_modified,close_file_unmodified,create_file,create_directory,delete_file,delete_directory,rename_file,rename_directory,set_security_file,set_security_directory
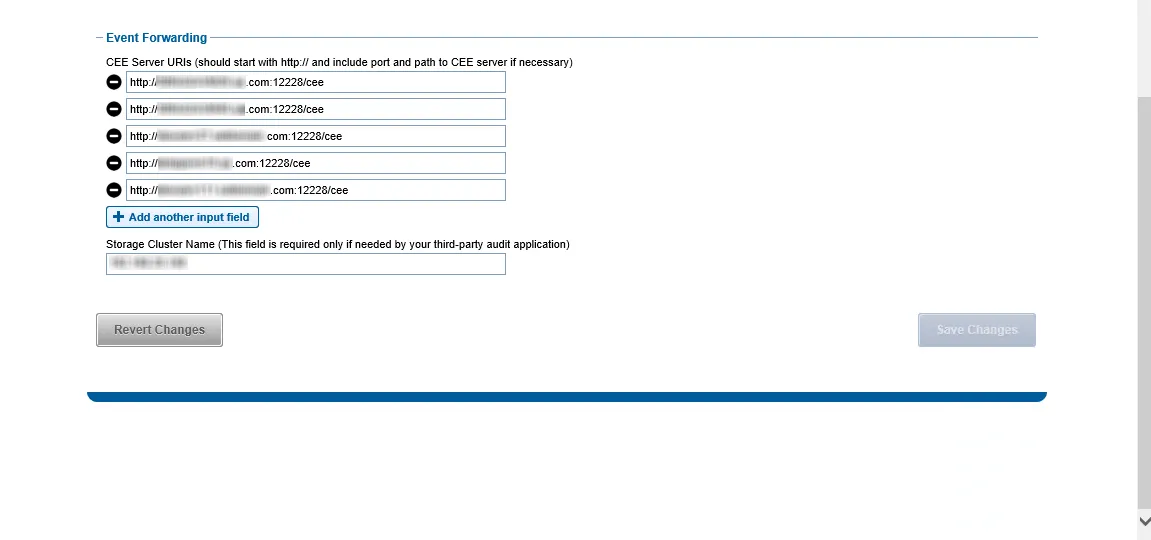
Step 4 – In the Event Forwarding section, add the CEE Server URI value for the Windows or Linux server hosting CEE. Use either of the following format:
http://[IP ADDRESS]:[PORT]/cee
http://[SERVER Name]:[PORT]/cee
RECOMMENDED: When deploying multiple Dell CEE instances at scale, it is recommended that an accommodating agent must be configured with each CEE instance. If multiple CEE instances send events to just one agent, it may create an overflow of data and overload the agent. Distributing the activity stream into pairs will be the most efficient way of monitoring large data sets at scale.
Step 5 – Also in the Event Forwarding section, set the Storage Cluster Name value. It must be an exact match to the name which is entered in the Activity Monitor for the Monitored Host list.
This name is used as a ‘tag’ on all events coming through the CEE. This name must exactly match what is in the Activity Monitor or it does not recognize the events.
RECOMMENDED: Use the CIFS DNS name for Dell OneFS.
NOTE: To use the Activity Monitor with Access Analyzer for Activity Auditing (FSAC) scans, the name entered here must exactly match what is used for Access Analyzer as a target host.
If the Storage Cluster Name cannot be modified (for example, another third-party depends on it), you need to set the Host Aliases parameter in the Activity Monitor Console:
- If the Storage Cluster Name is not empty, set the Host Aliases parameter to its value
- If the Storage Cluster Name is empty, set the Host Aliases to a semicolon-separated list of OneFS node names
Next, it is time to configure the monitoring agent on the Windows server to monitor the Isilon/PowerScale device.