NetApp Data ONTAP Cluster-Mode Access & Sensitive Data Auditing Configuration
This topic provides instructions for configuring NetApp Data ONTAP Cluster-Mode devices.
CIFS Method 1 Credential Configuration
Configuring access to CIFS shares using FPolicy and ONTAP API for Access Analyzer requires the following:
- Configure Data LIF to Allow HTTPS Traffic
- Configure Empty FPolicy
See the CIFS Method 2 Credential Configuration topic for an alternative method.
Configure Data LIF to Allow HTTPS Traffic
As of NetApp Clustered ONTAP 9.6, users can assign service policies (instead of LIF roles) to LIFs that determine the kind of traffic that is supported for the LIFs.
- Starting with ONTAP 9.5, ONTAP supports service policies
- Starting with ONTAP 9.6, LIF roles are deprecated and service policies are supported for all types of services
For users running ONTAP 9.6+, data LIFs used for HTTPS communication with Access Analyzer are
required to use a LIF service policy that includes the management-https service. Without this
service applied to a data LIF’s service policy, HTTPS communication will not be possible.
The following examples offer guidance for managing service policies, but may vary depending on the NetApp environment’s specific configuration and needs.
Use the following command to display available services:
network interface service show
Use the following command to create a service policy (example includes NFS, CIFS, and HTTPS traffic):
network interface service-policy create -vserver [SVM_NAME] -policy [SERVICE_POLICY_NAME] -services [LIST_OF_SERVICES_COMMA-SEPARARTED] -allowed-addresses [IP_CIDR_NOTATION]
Example with the NFS, CIFS, and HTTPS protocols being allowed:
network interface service-policy create -vserver testserver -policy new_service_policy -services data-nfx,data-cifs,management-https,data-core -allowed-addresses 0.0.0.0/0
Use the following command to verify if the service policy was properly created:
network interface service-policy show
Use the following command to add the created service policy to an existing data LIF:
network interface modify -vserver [SVM_NAME] -lif [LIF_NAME] -service-policy [SERVICE_POLICY_NAME]
Example:
network interface modify -vserver testserver -lif lif_1 -service-policy new_service_policy
A service policy can only be used by LIFs in the same SVM that is specified when creating the service policy.
CIFS Method 2 Credential Configuration
Configuring access to CIFS shares using the special C$ share is an alternative least privileged access option for NetApp Data ONTAP Cluster-Mode devices v9.0+. See the CIFS Method 1 Credential Configuration topic for an alternative method.
The following permissions are required:
-
Group membership in the Backup Operators group on either the file system proxy server for Proxy Mode scans or the Access Analyzer server for Local Mode scans (to get a high integrity token)
-
Group membership in the NetApp SVM's Power Users group (to enumerate shares)
-
Use the following command to add the Service Account to BUILTIN\Power Users:
cifs users-and-groups local-group add-members ‑group-name "BUILTIN\Power Users" ‑member-names [DOMAIN_USER] ‑vserver [SVM_NAME]
-
-
Group membership in the NetApp SVM's Backup Operators group (to bypass NTFS permissions)
-
NetApp SVM's SeBackupPrivilege needs to be applied to this group
-
This group must have read-only access to the SVM's C$ share
-
Use the following command to add the Service Account to BUILTIN\Backup Operators:
cifs users-and-groups local-group add-members ‑group-name "BUILTIN\Backup Operators" ‑member-names [DOMAIN_USER] ‑vserver [SVM_NAME]
-
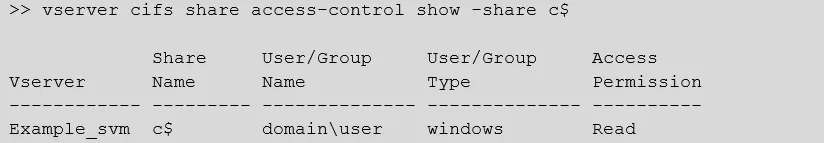
If an ACE does not already exist for a specific user/group on an SVM's c$ share, then it needs to be added with the desired rights (No_access, Read, Change, or Full_Control). To check the current ACE for a user or group on each SVM's c$ share, the following ONTAP CLI command should be used at the cluster management level.
vserver cifs share access-control show -share c$
The output will list each SVM's ACL for its c$ share. For example:
If the desired ACE does not exist on an SVM's c$ share, then one can be created with the following command:
vserver cifs share access-control create -share c$ -user-or-group [USER_OR_GROUP_NAME] -permission Read -vserver [SVM_NAME]
If an existing ACE needs to be modified, the following command should be used:
CAUTION: The following command will overwrite an existing ACE. For example, it is possible to downgrade a user with Full_Control to Read, or vice versa.
vserver cifs share access-control modify -share c$ -user-or-group [USER_OR_GROUP_NAME] -permission Read -vserver [SVM_NAME]
NOTE: If users would prefer to avoid permissioning C$, then there is an alternative. Users can instead give the SVM's Backup Operators group read-only access to each share to be scanned.
In order to utilize Access Analyzer’s LAT Preservation (Last Access Time) feature during sensitive data scans and metadata tag collection, applying ONTAP’s SeRestorePrivilege to the service account is also required.
As an alternative to membership in BUILTIN\Backup Operators, SeBackupPrivilege can be directly applied to a user via the NetApp command line.
The following commands can be used to grant these permissions to the service account to be used for scanning by Access Analyzer.
Use the following commands to add SeBackupPrivilege to the Service Account (or a BUILTIN Group):
cifs users-and-groups privilege add-privilege ‑user-or-group-name [USER_OR_GROUP_NAME] ‑privileges SeBackupPrivilege ‑vserver [SVM_NAME]
Use the following commands to add the Service Account to BUILTIN\Power Users:
cifs users-and-groups local-group add-members ‑group-name "BUILTIN\Power Users" ‑member-names [DOMAIN_USER] ‑vserver [SVM_NAME]
Use the following commands to add the Service Account to BUILTIN\Backup Operators:
cifs users-and-groups local-group add-members ‑group-name "BUILTIN\Backup Operators" ‑member-names [DOMAIN_USER] ‑vserver [SVM_NAME]
Use the following commands to verify the results from the previous commands:
cifs users-and-groups privilege show ‑vserver [SVM_NAME] ‑user-or-group-name [USER_OR_GROUP_NAME]
Use the following commands to give the Service Account Read-only Access to NetApp SVM's c$ Share:
cifs share access-control create ‑vserver [SVM_NAME] ‑share c$ ‑user-or-group [USER_OR_GROUP_NAME] ‑permission Read
NOTE: In the previous command, "create" needs to be replaced with "modify" if the CIFS share ACE already exists for the share/user combination.
Use the following commands to verify the results from the previous command:
cifs share access-control show ‑vserver [SVM_NAME] ‑share c$
NFSv3 Credential Configuration
The following is a list of example commands that can be used to configure a NetApp export policy to scan a volume via NFSv3 using the Access Analyzer File System Solution.
CAUTION: The export policy for a volume's parent (ex. the SVM's root volume), or the export policy for a qtree's parent, must have access rights that are equal or wider in scope to the export policy for the target volume/qtree. If Access Analyzer cannot access all segments of a target volume/qtree's junction path, then NFS access will be denied.
Use the following command to create an export policy:
vserver export-policy create ‑vserver [SVM_NAME] ‑policyname [EXPORT_POLICY_NAME]
Example:
vserver export-policy create ‑vserver testserver ‑policyname testNFS
Use the following command to add a rule to the previous export policy, using the nfsv3, auth_sys (aka auth_unix), and superuser properties:
vserver export-policy rule create ‑vserver [SVM_NAME] ‑policyname [EXPORT_POLICY_NAME] ‑clientmatch [IP_CIDR_NOTATION] ‑rorule sys ‑rwrule sys ‑superuser sys -protocol nfs3
Example:
vserver export-policy rule create ‑vserver testserver ‑policyname testNFS ‑clientmatch 0.0.0.0/0 ‑rorule sys ‑rwrule sys ‑superuser sys -protocol nfs3
Use the following command to show each volume’s export policy:
volume show ‑vserver [SVM_NAME] ‑fields policy
Example:
volume show ‑vserver testserver ‑fields policy
Use the following command to change a volume’s export policy:
volume modify ‑vserver [SVM_NAME] ‑volume [VOLUME_NAME] ‑policy [EXPORT_POLICY_NAME]
Example:
volume modify ‑vserver testserver ‑volume testVolume ‑policy testNFS
Troubleshooting NFSv3 Export Access
If Access Analyzeris not discovering the expected NFS export, it is possible that the export policy is not properly configured to allow the Access Analyzer server or proxy server IP Address to mount the NFS export. One step in troubleshooting this issue is to confirm a Unix client (or WSL for Windows) in the same IP range as the Access Analyzer server or proxy server can mount the NFS export.
Run the following command from a Unix host to verify the NFS mount is available:
showmount ‑e [NFS_HOSTNAME_OR_IP]
If the NFS export is returned as a result of the previous command, then Access Analyzer should also
be able to mount it. If not, it may be necessary to run the following command on the NetApp SVM to
get the NFS export to be returned by the showmount command:
vserver nfs modify ‑vserver [SVM_NAME] ‑showmount enabled