SQL: Filter
The Filter page is where the query can be scoped to target specific databases or instances. It is a wizard page for the categories of:
-
Permissions > Permissions Collection
-
Server Audits > Server Audit Events Collection
-
Sensitive Data > Sensitive Data Collection
-
Microsoft SQL Server:
- Discovery
- Custom SQL Query
- Infrastructure
- Operations
- Utilities > Remove Storage Tables
- Legacy Queries
-
Oracle:
- Custom Oracle Query
- Infrastructure
- Operations
- Utilities > Remove Storage Tables
-
MySQL:
- Custom MySQL Query
- Utilities > Remove Storage Tables
-
PostgreSQL:
- Custom PostgreSQL Query
- Utilities > Remove Storage Tables
-
Db2LUW:
- Custom Db2LUW Query
- Utilities > Remove Storage Tables
- Db2LUW Permissions Scan
-
Utilities – Remove Storage Data
It is necessary for the SA_SQL_Instances table to be populated before available databases/instances can populate the Available Server audits list. For Oracle and SQL, the SA_SQL_Instances table is populated through an instance discovery query. See the 0-SQL_InstanceDiscovery Job topic for additional information. For PostgreSQL and MySQL Scans, the SA_SQL_Instances table is populated manually in the Manage Connections window. See the Manage Connections Window topic for additional information. Once the table has been populated, a query can be scoped.
The configurable filter options are:
-
Connections — Opens the Manage Connections window to add or modify database instances. See the Manage Connections Window topic for additional information.
-
Filter options
-
All database objects — No scoping
-
Only select database objects — Scope to specific databases
- Click Retrieve to display available server audits
-
-
Available database objects — Displays known databases and instances for query scoping
- Select from the available list and click Add
-
Selected databases or instances — Displays selected database objects for which the query has been scoped. Additional options include:
- Remove — Removes the selected database/instance from the query
- Include — Reverts an exclusion. By default, all sub tables are included.
- Exclude — Excludes selected databases/instances and displays them in red
- Add Custom Filter — Opens the Add custom filter window to build a custom filter to be applied to the selected databases/instances. See the Add Custom Filter Window topic for additional information.
- Import CSV — Import a list of databases/instances from a CSV file
- Export CSV — Exports the list of databases/instance to a CSV file through the Save As window
Manage Connections Window
The Manage Connections window enables you to add database instances to search. Click the Connections button to open it.
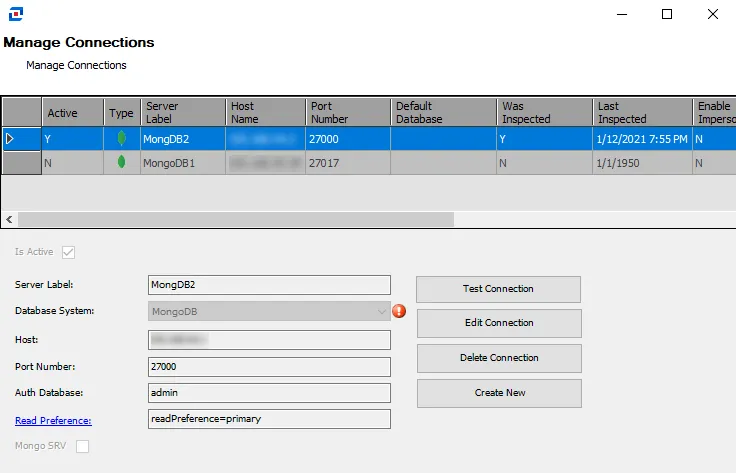
The Manage Connections table lists the previously added database instances and their attributes. Select a row in the table to edit that instance, or create a new instance to add to the table:
- Is Active — Select the checkbox to include the database on the Servers Pane on the Filter page
- Instance Label — The name of the server
- Database System — Select from a list of available databases
- Service Name — Name of the service
- Host — Name or IP address of the host where the database is located
- Port Number — Port number for the database. If a non-default port is being used, it should be specified in the Port Number section.
- Default Database — Account used to access the database. Admin is recommended.
- Enable impersonation — Select to enable impersonation
- Service Type— If applicable, select whether the service type is Service or SID
In the Manage Connections Table, the following information is also listed:
- Was Inspected — Indicates whether information for a connection was validated. Y indicates the information has been validated. N indicates the information has not been validated.
- Last Inspected — Indicates the date and time of when the connection information was last inspected. If blank, the connection information has not yet been validated.
The Manage Connections window has the following buttons:
- Test Connection — Click to verify the connection to the database with the connection profile applied to the job group
- Edit Connection — Click to edit information for the selected connection
- Delete Connection — Click to delete the selected connection
- Create New — Click to create a new connection
Add Custom Filter Window
The Add custom filter window opens from the Filter page of the SQL Data Collector Wizard. It enables you to apply a custom scoping filter to the query.
Type the filter in the window and click Save. The following characters can be used in the filter:
- Forward slash (/) – Path separator
- Asterisk (*) – Wild card for any combination of characters
- Question mark (?) – Wild card for a single character
Use the following format to add a custom filter for a server:
-
SQL:
[SQL Server Name]/[Host or IP Address]/[Database Name]/[TableName]
-
Oracle:
[Oracle Server Name]/[Host or IP Address]/[Container Name]/[Schema]/[Table Name]
-
Azure SQL:
[Azure SQL Server Name]/[Host or IP Address]/[Database Name]/[Table Name]
-
MySQL:
[MySQL Server Name]/[Host or IP Address]/[DastabaseName]/[TableName]
-
PostgreSQL:
[PostgreSQL Server Name]/[Host or IP Address]/[DastabaseName]/[Schema]/[TableName]
-
Db2:
[Db2LUW Server Name]/[Host or IP Address]/[DastabaseName]/[TableName]