File System Proxy as a Service Overview
The File System Solution can be enabled to use proxy servers for scanning targeted file systems in very large or widely dispersed environments.
When File System scans are run in proxy mode as a service, there are two methods available for deploying the service:
- Pre-Installed File System Proxy Service – File System Proxy Service installation package must be installed on the Windows proxy servers prior to executing the scans. This is the recommended method.
- Ad Hoc File System Proxy Service Deployment – File System Proxy Service is installed on the Windows proxy server when the job is executed
The data collection processing is conducted by the proxy server where the service is running and leverages a local mode-type scan to each of the target hosts. The final step in data collection is to compress and transfer the data collected in the SQLite databases, or Tier 2 databases, back to the Access Analyzer Console server.
Communication between the Access Analyzer Console Server and the proxy server is secure by default using HTTPS requests.
The version of the proxy service must match the major version of Access Analyzer.
See the File System Solution topic for information on the required prerequisites.
Supported Platforms
The File System Proxy Service for the Access Analyzer File System Solution can be installed on the following Windows operating systems:
- Windows Server 2022
- Windows Server 2019
- Windows Server 2016
Proxy Scanning Architecture
Access Analyzer is configured by default to process data collection against ten target hosts simultaneously. When File System scans are run in local mode ten hosts process simultaneously, and processing against the eleventh host begins after the processing against the first host is completed. Proxy scanning architecture supports large deployments or widely dispersed environments.
A proxy server is any server that can be leveraged to process data collection against target hosts.
CAUTION: The File System Proxy Service cannot be installed on the same server as Access Analyzer.
Two options are available for implementing the proxy scanning architecture:
- Proxy mode with applet
- Proxy mode as a service
Proxy Mode with Applet
When File System scans are run in proxy mode with applet, it means the File System applet is deployed to the Windows proxy server when the job is executed to conduct data collection. The data collection processing is initiated by the proxy server where the applet is deployed and leverages a local mode-type scan to each of the target hosts. The final step in data collection is to compress and transfer the data collected in the SQLite databases, or Tier 2 databases, back to the Access Analyzer Console server.
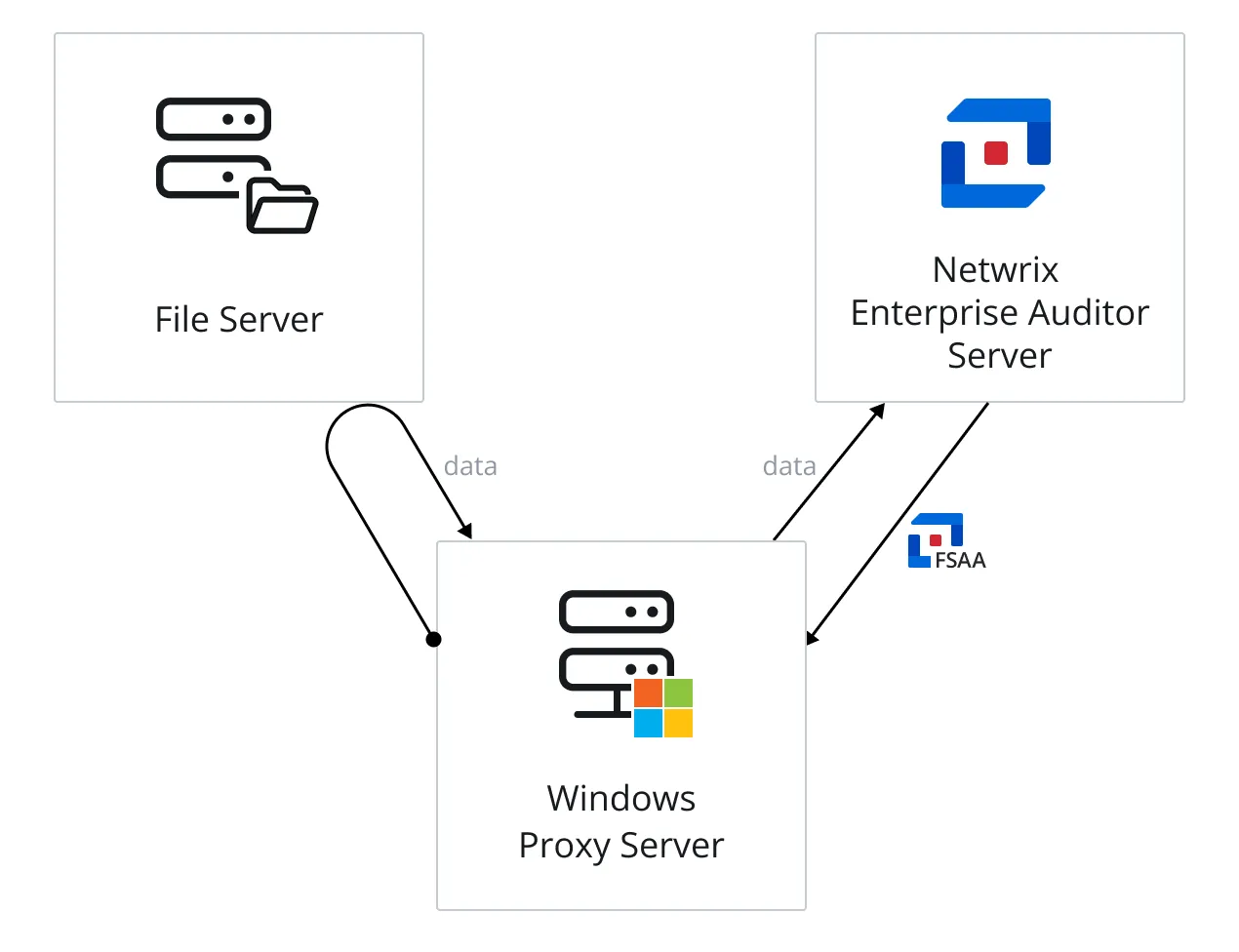
The diagram illustrates the Access Analyzer server sending an FSAA applet to a proxy server, which runs the scan against a file server, and then returns data to the Access Analyzer server.
Proxy Mode as a Service
When File System scans are run in proxy mode as a service, there are two methods available for deploying the service:
- Pre-Installed File System Proxy Service – File System Proxy Service installation package must be installed on the Windows proxy servers prior to executing the scans. This is the recommended method.
- Ad Hoc File System Proxy Service Deployment – File System Proxy Service is installed on the Windows proxy server when the job is executed
The data collection processing is conducted by the proxy server where the service is running and leverages a local mode-type scan to each of the target hosts. The final step in data collection is to compress and transfer the data collected in the SQLite databases, or Tier 2 databases, back to the Access Analyzer Console server.
The proxy communication is configured during the installation of the service on the proxy server and certificate exchange options are configured via the Applet Settings page of the File System Access Auditing Data Collector Wizard. The credential provided for the secure communications in the installation wizard is also added to the Access Analyzer Connection Profile assigned to the File System Solution.
See the File System Proxy Service Installation topic for additional information.
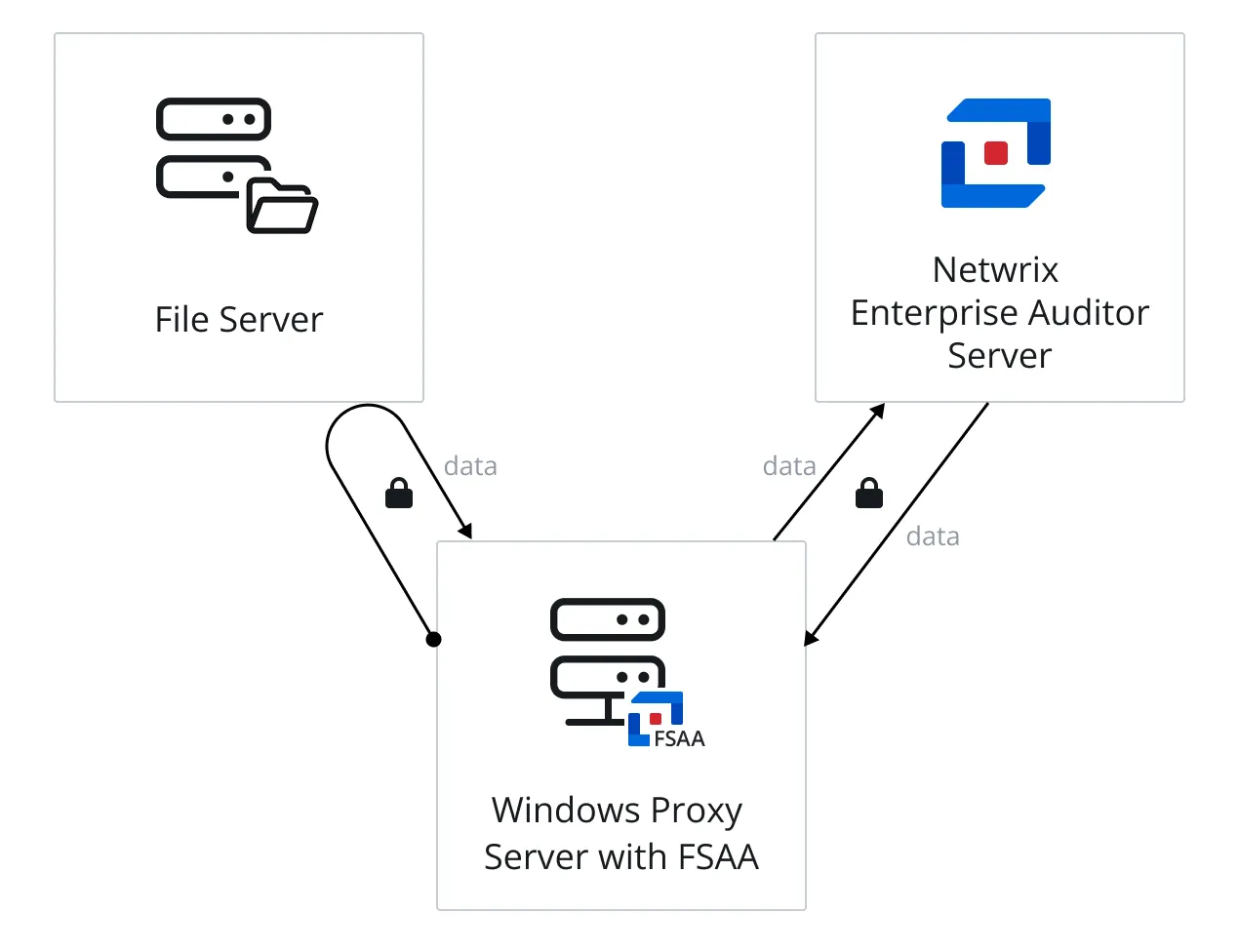
The diagram illustrates the Access Analyzer server communicating securely with the proxy service on a proxy server, which runs the scan against a file server, collecting the data locally and securely. Then the proxy service returns data securely to the Access Analyzer server.
When a proxy mode scan is initiated from the Access Analyzer Console, it will distribute hosts to be scanned across all proxy hosts. Access Analyzer monitors the scans from the central console. Once all proxy hosts have completed scanning, all results and SQLite databases are returned to the Access Analyzer Console server.
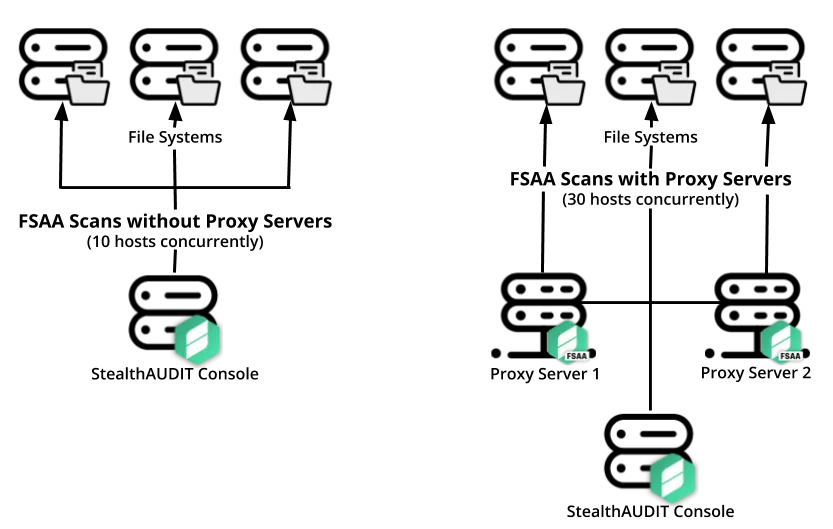
The diagram shows the difference between an implementation of Access Analyzer without proxy servers (on the left) and with proxy servers (on the right). On the right side of the diagram, the scans have been configured to use the local host and two additional proxy servers to perform the FSAA Data Collector scans. This allows it to execute three times as many concurrent hosts than would be possible without proxy servers. This provides a clear benefit in scalability and scan times.
The proxy functionality for the FSAA Data Collector provides security and reliability.
Remember, It is recommended that the File System Proxy Service is installed on the proxy server before running File System scans in proxy mode as a service. Once installed, the FileSystemAccess (FSAA) Data Collector must be configured to use the service. See the File System Data Collection Configuration for Proxy as a Service topic for additional information.
Sensitive Data Discovery Auditing Consideration
If running Sensitive Data Discovery (SDD) scans, it will be necessary to increase the minimum amount of RAM. Each thread requires a minimum of 2 additional GB of RAM per host. By default, SDD scans are configured to run two concurrent threads. For example, if the job is configured to scan 8 hosts at a time with two concurrent SDD threads, then an extra 32 GB of RAM are required (8x2x2=32).