File System Scan Options
Required permissions on the targeted file system are dependent upon not only the type of environment targeted but also the mode in which the data collection scan is executed. There are three primary types of scan modes: local, applet, or proxy. The proxy mode can be conducted via applet deployment, or via running as a service (installed in advance).
For the purpose of this document, “applet” refers to the runtime deployment of the
FSAAAppletServer.exe to either the target host (applet mode scans) or the proxy host (proxy mode
with applet scans) via Microsoft Task Scheduler. A “proxy” host is any host which can be leveraged
for running File System scans against target hosts.
Local Mode
When File System scans are run in local mode, it means all of the data collection processing is conducted by the Access Analyzer Console server across the network. The data is collected in the SQLite database(s), or Tier 2 database(s), on the Access Analyzer Console server, and then imported into the Access Analyzer database, or Tier 1 database, on the SQL Server.
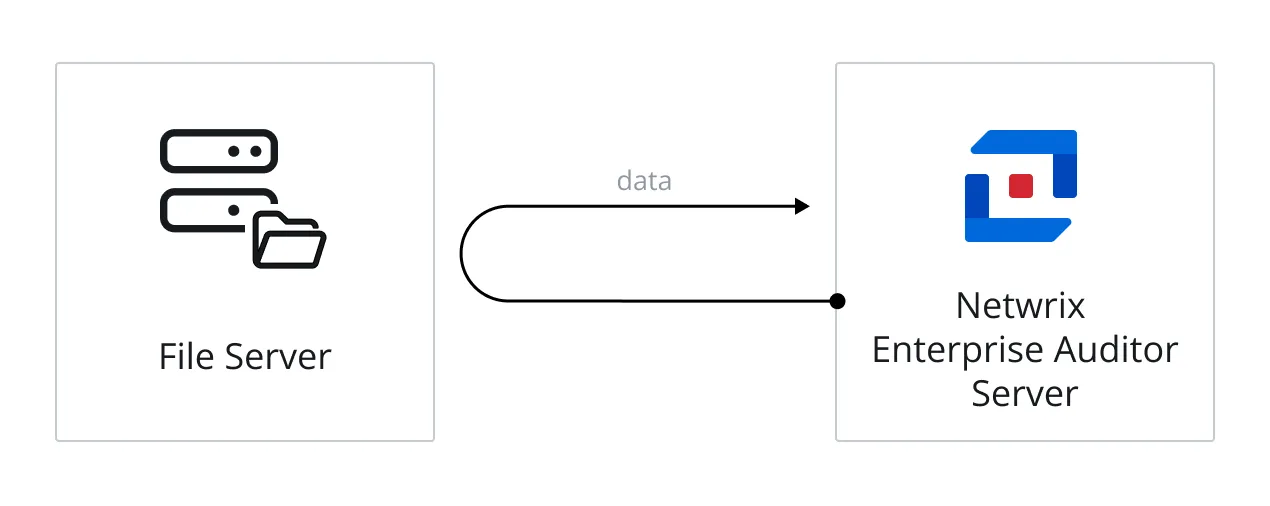
The diagram illustrates the Access Analyzer server running the scan against a file server.
See the following topics for additional information:
Applet Mode
CAUTION: The local policy, “Network access: Do not allow storage of passwords and credentials for network authentication” must be disabled in order for the applet to start.
When File System scans are run in applet mode, it means the File System applet is deployed to the target host when the job is executed to conduct data collection. However, the applet can only be deployed to a server with a Windows operating system. The data is collected on the Windows target host where the applet is deployed. The final step in data collection is to compress and transfer the data collected in the SQLite database(s), or Tier 2 database(s), back to the Access Analyzer Console server. If the target host is a NAS device, the File System scans will default to local mode for that host.
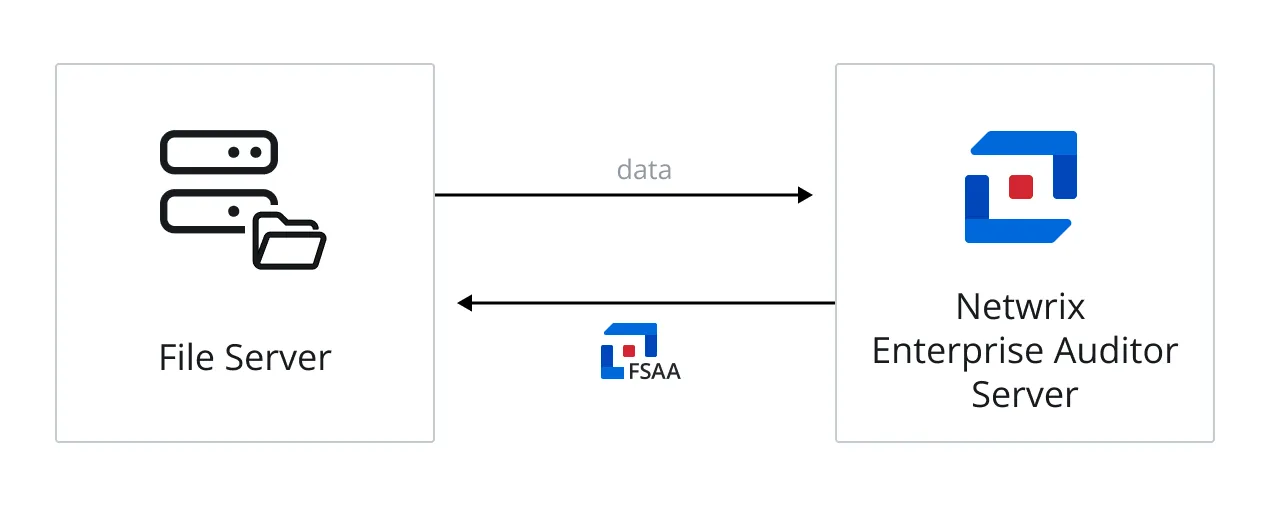
The diagram illustrates the Access Analyzer server sending an FSAA applet to a targeted Windows file server, which runs the scan against locally, and then returns data to the Access Analyzer server.
See the following topics for additional information:
Proxy Mode with Applet
CAUTION: The local policy, “Network access: Do not allow storage of passwords and credentials for network authentication” must be disabled in order for the applet to start.
When File System scans are run in proxy mode with applet, it means the File System applet is deployed to the Windows proxy server when the job is executed to conduct data collection. The data collection processing is initiated by the proxy server where the applet is deployed and leverages a local mode-type scan to each of the target hosts. The final step in data collection is to compress and transfer the data collected in the SQLite databases, or Tier 2 databases, back to the Access Analyzer Console server.
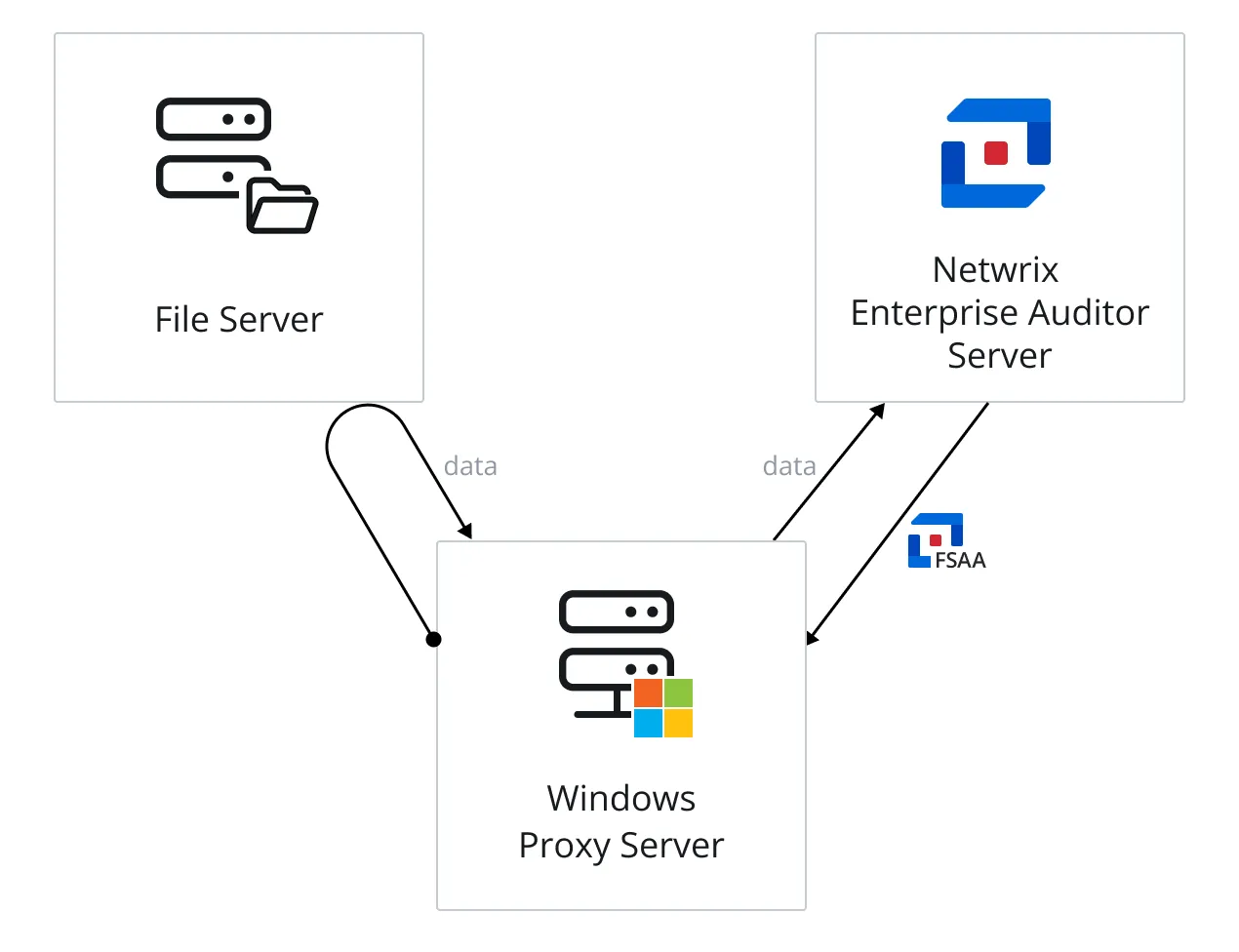
The diagram illustrates the Access Analyzer server sending an FSAA applet to a proxy server, which runs the scan against a file server, and then returns data to the Access Analyzer server.
See the following topics for additional information:
- Proxy Mode Server Requirements
- Proxy Mode with Applet Permissions
- Proxy Mode with Applet Port Requirements
Proxy Mode as a Service
When File System scans are run in proxy mode as a service, there are two methods available for deploying the service:
- Pre-Installed File System Proxy Service – File System Proxy Service installation package must be installed on the Windows proxy servers prior to executing the scans. This is the recommended method.
- Ad Hoc File System Proxy Service Deployment – File System Proxy Service is installed on the Windows proxy server when the job is executed
The data collection processing is conducted by the proxy server where the service is running and leverages a local mode-type scan to each of the target hosts. The final step in data collection is to compress and transfer the data collected in the SQLite databases, or Tier 2 databases, back to the Access Analyzer Console server.
The proxy communication is configured during the installation of the service on the proxy server and certificate exchange options are configured via the Applet Settings page of the File System Access Auditing Data Collector Wizard. The credential provided for the secure communications in the installation wizard is also added to the Access Analyzer Connection Profile assigned to the File System Solution.
See the File System Proxy Service Installation topic for additional information.
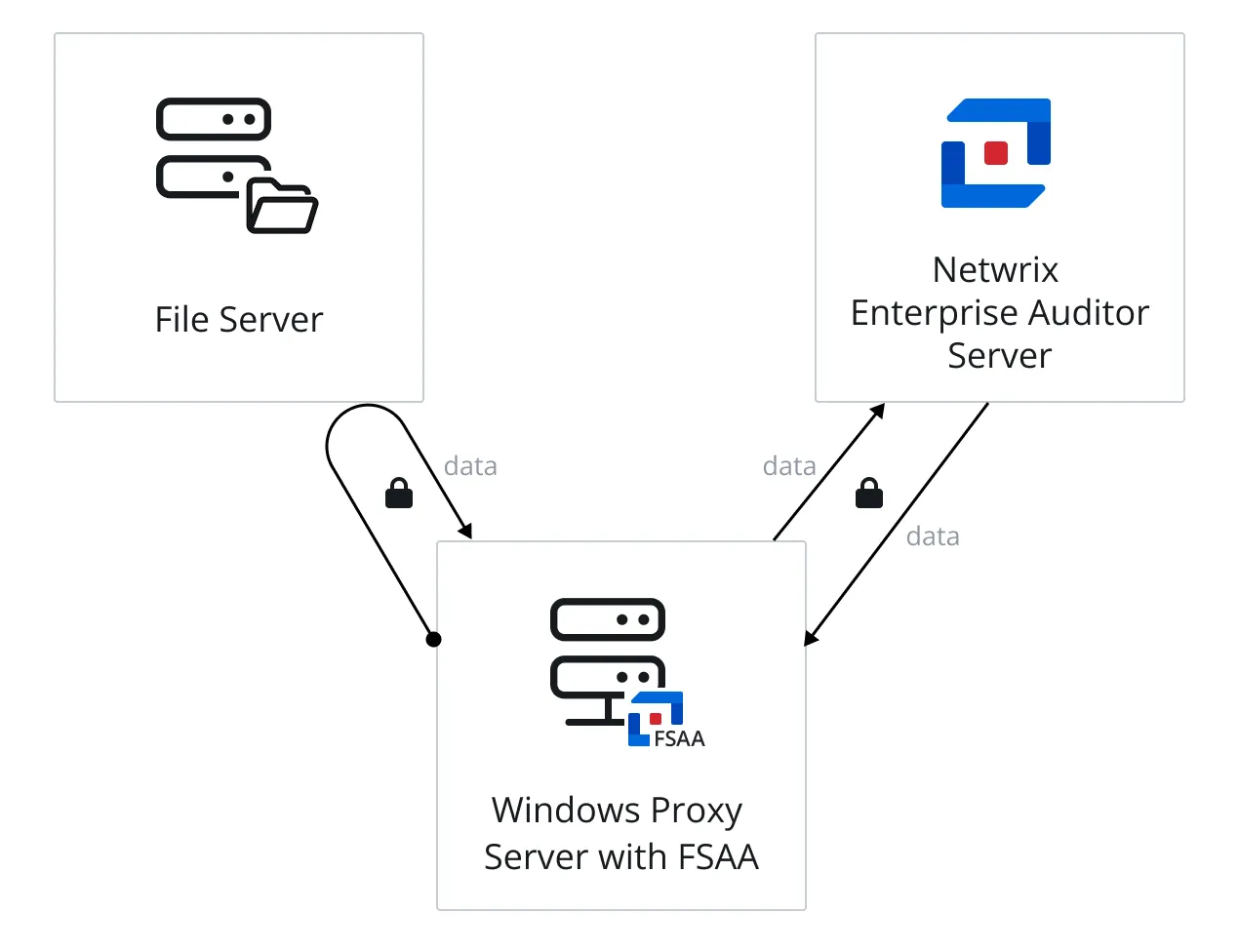
The diagram illustrates the Access Analyzer server communicating securely with the proxy service on a proxy server, which runs the scan against a file server, collecting the data locally and securely. Then the proxy service returns data securely to the Access Analyzer server.
See the following topics for additional information: