Automate Add-On Execution
To ensure you feed the most recent data to your SIEM solution, Netwrix recommends scheduling a daily task for running the add-on.
Perform the following steps to create a scheduled task:
Step 1 – On the computer where you want to execute the add-on, navigate to Task Scheduler.
Step 2 – On the General tab, specify a task name. Make sure the account that runs the task has all necessary rights and permissions.
Step 3 – On the Triggers tab, click New and define the schedule. This option controls how often audit data is exported from Auditor and saved to event log. Netwrixrecommends scheduling a daily task.
Step 4 – On the Actions tab, click New and specify action details. Review the following for additional information:
| Option | Value |
|---|---|
| Action | Set to "Start a program". |
| Program/script | Input "Powershell.exe". |
| Add arguments (optional) | Add a path to the add-on in double quotes and specify add-on parameters. For example: -file "C:\Add-ons\Netwrix_Auditor_Add-on_for_IBM_QRadar.ps1" -NetwrixAuditorHost 172.28.6.15 |
Step 5 – Save the task.
After creating a task, wait for the next scheduled run or navigate to Task Scheduler and run the task manually. To do this, right-click a task and click Run.
Work with Collected Data
Follow the steps to work with collected data:
Step 1 – On the computer where you executed the add-on, navigate to Start > All Programs > Event Viewer.
Step 2 – In the Event Viewer dialog, navigate to Event Viewer (local) > Applications and Services Logs >Netwrix Auditor Integration log.
Step 3 – Review events.
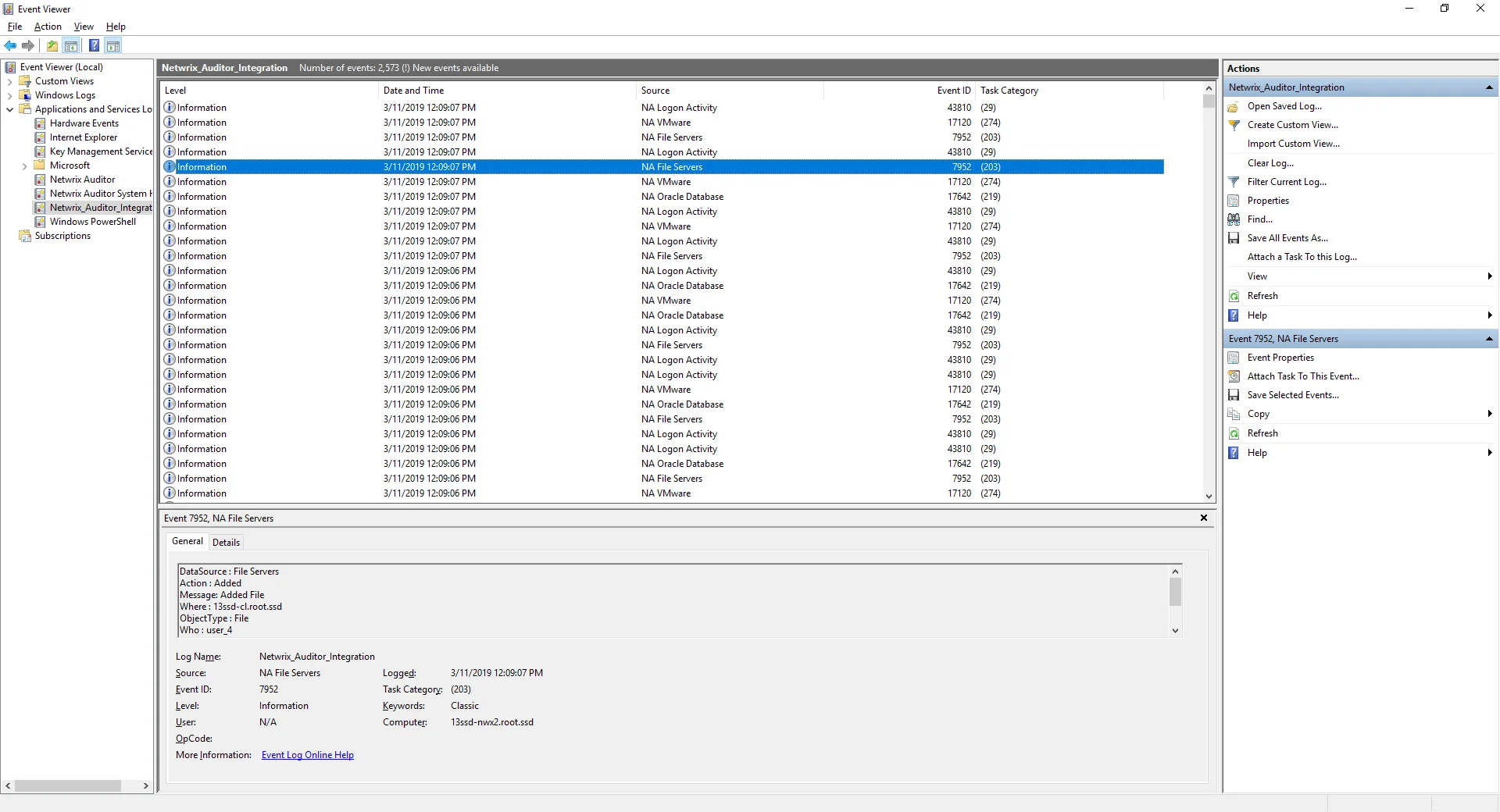
Now you can augment Windows event log with data collected by the Auditor.
Choose Appropriate Execution Scenario
Auditor Add-on for the SIEM solution runs on any computer in your environment. For example, you can run the add-on on the computer where Auditor is installed or on a remote server. Depending on the execution scenario you choose, you have to define a different set of parameters. See the Define Parameters topic for additional information.
Netwrix suggests the following execution scenarios:
| Scenario | Example |
|---|---|
| The add-on runs on the Auditor Server with the current user credentials. Activity Records are exported to a local event log. | C:\Add-ons\Netwrix_Auditor_Add-on_for_IBM_QRadar.ps1 |
| The add-on runs on the Auditor Server with explicitly defined credentials. Activity Records are exported to a local event log. | C:\Add-ons\NetwrixAuditor_Add-on_for_IBM QRadar.ps1 -NetwrixAuditorUserName enterprise\NAuser -NetwrixAuditorPassword NetwrixIsCool |
| The add-on exports Activity Records from a remote Auditor Server using current user credentials and writes data to a local event log. | C:\Add-ons\NetwrixAuditor_Add-on_for_IBM QRadar.ps1 -NetwrixAuditorHost 172.28.6.15 |
| The add-on exports Activity Records from a remote Auditor Server using explicitly defined credentials and writes data to a local event log. | C:\Add-ons\NetwrixAuditor_Add-on_for_IBM QRadar.ps1 -NetwrixAuditorHost 172.28.6.15 -NetwrixAuditorUserName enterprise\NAuser -NetwrixAuditorPassword NetwrixIsCool |
For security reasons, Netwrix recommends running the script with current user credentials (skipping user credentials). Create a special user account with permissions to both Auditor data and event log and use it for running the script.
Integration Event Log Fields
This section describes how the add-on fills in the Netwrix Auditor Integration event log fields with data retrieved from Activity Records.
The Activity Record structure is described in the Reference for Creating Activity Recordstopic.
| Event log field name | Filled in with value | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Source | NA__{Data Source Name}** -OR- **Netwrix _Auditor_Integration_API__ | Depending on SetDataSourceAsEventSource in-script parameter. |
| EventID | {Calculated by add-on} -OR- 0 | Depending on GenerateEventId in-script parameter (calculation result also depends on IncludeDataSourceToMakeEventId parameter — if GenerateEventId = True). |
| Task Category | {DataSource ID} -OR- 1 | Depending on SetDataSourceAsEventCategory in-script parameter. |
See the Define Parameters topic for additional information.
EventData is filled in with data from the Activity Record fields as follows:
| Entry in EventData | Activity Record field |
|---|---|
| DataSource | {DataSource} |
| Action | {Action} |
| Message | {Action ObjectType} |
| Where | {Where} |
| ObjectType | {ObjectType} |
| Who | {Who} |
| What | {What} |
| When | {When} |
| Workstation | {Workstation} |
| Details | {Details} |
Details are filled in only if this Activity Record field is not empty.
IBM QRadar
Netwrix Auditor Add-on for SIEM helps you to get most from your SIEM investment. This topic focuses on the IBM QRadar SIEM solution.
The add-on works in collaboration with Netwrix Auditor, supplying additional data that augments the data collected by the SIEM solution.
The add-on enriches your SIEM data with actionable context in human-readable format, including the before and after values for every change and data access attempt, both failed and successful. Aggregating data into a single audit trail simplifies analysis, makes your SIEM more cost effective, and helps you keep tabs on your IT infrastructure.
Implemented as a PowerShell script, this add-on facilitates the audit data transition from Netwrix Auditor to the SIEM solution. All you have to do is provide connection details and schedule the script for execution.
On a high level, the add-on works as follows:
- The add-on connects to the Netwrix Auditor server and retrieves audit data using the Netwrix Auditor Integration API.
- The add-on processes Netwrix Auditor-compatible data (Activity Records) into log events that work as input for the SIEM solution. Each event contains the user account, action, time, and other details.
- The add-on creates a special Windows event log named Netwrix_Auditor_Integration and stores events there. These events are structured and ready for integration with the SIEM solution.
See the Integration API topic for additional information on the structure of the Activity Record and the capabilities of the Netwrix Auditor Integration API.\
Prerequisites
Before running the add-on, ensure that all the necessary components and policies are configured as follows:
| On... | Ensure that... |
|---|---|
| The Auditor server side | - Auditor version is 10.0 or later. - The Audit Database settings are configured in Auditor Server. See the Prerequisites and Audit Database topics for additional information. - The TCP 9699 port (default Auditor Integration API port) is open for inbound connections. - The user retrieving data from the Audit Database is granted the Global reviewer role in Auditor or is a member of the Netwrix Auditor Client Users group. See the Role-Based Access and Delegation topic for additional information. Alternatively, you can grant the Global administrator role or add the user to the Netwrix Auditor Administrators group. In this case, this user will have the most extended permissions in the product. |
| The computer where the script will be executed | - PowerShell 3.0 or later must be installed. - .NET 4.5 or later must be installed. - Execution policy for powershell scripts is set to "Unrestricted". Run Windows PowerShell as administrator and execute the following command: Set-ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted - The user running the script is granted the write permission on the script folder—the add-on creates a special .bin file with the last exported event. - The user running the script must be a member of the Domain Users group. - At least the first script run should be performed under the account with elevated privileges, as it will be necessary to create event log file and perform other required operations. |
Compatibility Notice
Make sure to check your product version, and then review and update your add-ons and scripts leveraging Netwrix Auditor Integration API. Download the latest add-on version in the Add-on Store.
Define Parameters
Before running or scheduling the add-on, you must define connection details: Auditor Server host, user credentials, etc. Most parameters are optional, the script uses the default values unless parameters are explicitly defined. You can skip or define parameters depending on your execution scenario and security policies. See the Choose Appropriate Execution Scenario topic for additional information.
| Parameter | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Connection to Netwrix Auditor | ||
| NetwrixAuditorHost | localhost:9699 | Assumes that the add-on runs on the computer hosting the Auditor Server and uses default port 9699. If you want to run the add-on on another machine, provide a name of the computer where Auditor Server resides (e.g., 172.28.6.15, EnterpriseNAServer, WKS.enterprise.local). To specify a non-default port, provide a server name followed by the port number (e.g., WKS.enterprise.local:9999). |
| NetwrixAuditorUserName | Current user credentials | Unless specified, the add-on runs with the current user credentials. If you want the add-on to use another account to connect to Auditor Server, specify the account name in the DOMAIN\username format. The account must be assigned the Global reviewer role in Auditor or be a member of the Netwrix Auditor Client Users group on the computer hosting Auditor Server. |
| NetwrixAuditorPassword | Current user credentials | Unless specified, the script runs with the current user credentials. Provide a different password if necessary. |
In-Script Parameters
You may also need to modify the parameters that define how EventIDs should be generated for exported events, though their default values address most popular usage scenarios. In-script parameters are listed in the table below. To modify them, open the script for edit and enter the values you need.
Once set, these parameter values must stay unchanged until the last run of the script — otherwise dynamically calculated EventIDs will be modified and applied incorrectly.
| Parameter | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| EventID generation | ||
| GenerateEventId | True | Defines whether to generated unique EventIDs. Possible parameter values: - True — generate unique EventIDs using Activity Record fields - False — do not generate a unique ID, set EventID=0 for all cases EventID is generated through CRC32 calculation that involves the following Activity Record field values: - ObjectType - Action - DataSource (optional, see below for details) Only the lowest 16 bits of the calculation result are used. See the Activity Records topic for additional information. |
| IncludeDataSourceToMakeEventId* | True | Defines whether the DataSource field of Activity Record should be used in the EventID calculation. This parameter is applied only if GenerateEventId is set to TRUE. |
| SetDataSourceAsEventCategory | True | Defines whether to fill in Event Category event field with a numeric value derived from the DataSource field of Activity Record. Possible parameter values: - True — generate a numeric value for Event Category using Activity Record field - False — do not generate a numeric value, set Event Category=1 for all cases The Event Category field value is generated through CRC32 calculation that involves the DataSource field of Activity Record. Only the lowest 9 bits of the calculation result are used. |
| SetDataSourceAsEventSource | False | Defines whether to fill in the Event Source event field with the value from the DataSource field of Activity Record. Possible parameter values: - True — fill in the Event Source with the value from DataSource field of Activity Record, adding the prefix defined by $EventSourcePrefix. Default prefix is NA, for example:NA Windows Server - False — set Event Source to Netwrix_Auditor_Integration_API for all cases If the script cannot fill in the Event Source for some DataSource, the default value Netwrix_Auditor_Integration_API will be used. If the event source for particular DataSource does not exist in the Netwrix_Auditor_Integration event log, elevated privileges are required for add-on execution. |
* When configuring the IncludeDataSourceToMakeEventId parameter, consider that the Object Type - Action pair may be identical for several data sources (e.g., Object='User' and Action='Added'); thus, excluding DataSource from calculation may lead to the same EventID (duplicates). See the Run the Add-On with PowerShell topic for additional information about duplicates.
Run the Add-On with PowerShell
First, provide a path to your add-on followed by script parameters with their values. Each parameter is preceded with a dash; a space separates a parameter name from its value. You can skip some parameters— the script uses a default value unless a parameter is explicitly defined. If necessary, modify the parameters as required.
Follow the steps to run add-on with PowerShell:
Step 1 – On computer where you want to execute the add-on, start Windows PowerShell.
Step 2 – Type a path to the add-on. Or simply drag and drop the add-on file in the console window.
Step 3 – Add script parameters. The console will look similar to the following:
Windows PowerShell
Copyright (C) 2014 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
PS C:\Users\AddOnUser> C:\Add-ons\Netwrix_Auditor_Add-on_for_IBM_QRadar.ps1 - NetwrixAuditorHost 172.28.6.15
NOTE: If the script path contains spaces (e.g., C:\Netwrix Add-ons), embrace it in double quotes and insert the ampersand (&) symbol in front (e.g., & "C:\Netwrix Add-ons").
Step 4 – Hit Enter.
Depending on the number of Activity Records stored in Netwrix Auditor Audit Database execution may take a while. Ensure the script execution completed successfully. The Netwrix Auditor Integration event log will be created and filled with events.
By default, the Netwrix Auditor Integration event log size is set to 1GB, and retention is set to "Overwrite events as needed". See the Integration Event Log Fields topic for additional information.
NOTE: Event records with more than 30,000 characters length will be trimmed.
At the end of each run, the script creates the Netwrix_Auditor_Event_Log_Export_Add-on_EventIDs.txt file. It defines mapping between the Activity Records and related Event IDs . You can use this file to track possible duplicates of Event IDs created at each script execution. Duplicates, if any, are written to the Netwrix_Auditor_Event_Log_Export_Add-on_EventIDsDuplicates.txt file.
Similarly, the add-on also creates the Netwrix_Auditor_Event_Log_Export_Add-on_CategoriesIDs.txt file that defines mapping between the Data Source and related Category ID.
Applying Filters
Every time you run the script, Auditor makes a timestamp. The next time you run the script, it will start retrieving new Activity Records. Consider the following:
-
By default, the add-on does not apply any filters when exporting Activity Records. If you are running the add-on for the first time (there is no timestamp yet) with no filters, it will export Activity Records for the last month only. This helps to optimize solution performance during the first run. At the end of the first run, the timestamp will be created, and the next run will start export from that timestamp.
-
However, if you have specified a time period for Activity Records to be exported, then this filter will be applied at the add-on first run and the runs that follow.