Windows Server
Netwrix Auditor relies on native logs for collecting audit data. Therefore, successful change and access auditing requires a certain configuration of native audit settings in the audited environment and on the Auditor console computer. Configuring your IT infrastructure may also include enabling certain built-in Windows services, etc. Proper audit configuration is required to ensure audit data integrity, otherwise your change reports may contain warnings, errors or incomplete audit data.
CAUTION: Folder associated with Netwrix Auditor must be excluded from antivirus scanning. See the Antivirus Exclusions for Netwrix Auditor knowledge base article for additional information.
You can configure your IT Infrastructure for monitoring in one of the following ways:
-
Automatically through a monitoring plan – This is a recommended method. If you select to automatically configure audit in the target environment, your current audit settings will be checked on each data collection and adjusted if necessary.
-
Manually – Native audit settings must be adjusted manually to ensure collecting comprehensive and reliable audit data. You can enable Auditor to continually enforce the relevant audit policies or configure them manually:
-
The Remote Registry and the Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) service must be started. See the Enable Remote Registry and Windows Management Instrumentation Services topic and the Configure Windows Registry Audit Settings topic for additional information.
-
The following advanced audit policy settings must be configured:
- The Audit: Force audit policy subcategory settings (Windows 7 or later) security option must be enabled.
- For Windows Server 2008—The Object Access, Account Management, and Policy Change categories must be disabled while the Security Group Management, User Account Management, Handle Manipulation, Other Object Access Events, Registry, File Share, and Audit Policy Change subcategories must be enabled for "Success".
- For Windows Server 2008 R2 / Windows 7 and above—Audit Security Group Management, Audit User Account Management, Audit Handle Manipulation, Audit Other Object Access Events, Audit Registry, Audit File Share, and Audit Audit Policy Changeadvanced audit policies must be set to "Success".
- See the Configure Local Audit Policies topic and the Configure Advanced Audit Policies topic for additional information.
-
The following legacy audit policies can be configured instead of advanced: Audit object access, Audit policy change, and Audit account management must be set to "Success".
-
The Enable Persistent Time Stamp local group policy must be enabled. This policy should be configured manually since Auditor does not enable it automatically. See the Configure Enable Persistent Time Stamp Policy topic for additional information.
-
The Application, Security, and System event log maximum size must be set to 4 GB. The retention method must be set to “Overwrite events as needed”. See the Adjusting Event Log Size and Retention Settings topic for additional information.
-
For auditing scheduled tasks, the Microsoft-Windows-TaskScheduler/Operational event log must be enabled and its maximum size must be set to 4 GB. The retention method of the log must be set to “Overwrite events as needed”.
-
For auditing DHCP, the Microsoft-Windows-Dhcp-Server/Operational event log must be enabled and its maximum size must be set to 4 GB. The retention method of the log must be set to “Overwrite events as needed”. See the Adjust DHCP Server Operational Log Settings topic for additional information.
-
For auditing DNS, the Microsoft-Windows-DNS-Server/Audit event log must be enabled and its maximum size must be set to 4 GB. The retention method of the log must be set to “Overwrite events as needed”.
-
The following inbound Firewall rules must be enabled:
- Remote Event Log Management (NP-In)
- Remote Event Log Management (RPC)
- Remote Event Log Management (RPC-EPMAP)
- Windows Management Instrumentation (ASync-In)
- Windows Management Instrumentation (DCOM-In)
- Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI-In)
- Network Discovery (NB-Name-In)
- File and Printer Sharing (NB-Name-In)
- Remote Service Management (NP-In)
- Remote Service Management (RPC)
- Remote Service Management (RPC-EPMAP)
- Performance Logs and Alerts (DCOM-In)
- Performance Logs and Alerts (TCP-In)
-
If the audited servers are behind the Firewall, review the list of protocols and ports required for Netwrix Auditor and make sure that these ports are opened. See the Windows Server Ports topic for additional information.
-
For auditing removable storage media, two Event Trace Session objects must be created. See the Configure Removable Storage Media for Monitoring topic for additional information.
-
If you want to use Network traffic compression, make sure that the Auditor console computer is accessible by its FQDN name.
-
For auditing IIS:
- The Remote Registry service must be running and its Startup Type must be set to "Automatic".
- The Microsoft-IIS-Configuration/Operational log must be enabled and its maximum size must be set to 4 GB. The retention method of the log must be set to “Overwrite events as needed”.
-
Whatever method you choose to configure Windows Server for auditing (manual or automated), also remember to do the following:
- Configure Data Collecting Account, as described in the Data Collecting Account topic.
- Configure required protocols and ports, as described in the Windows Server Ports topic.
Exclude Monitored Objects
You can fine-tune Netwrix Auditor by specifying data that you want to exclude from the Windows Server monitoring scope.
Follow the steps to exclude data from the Windows Server monitoring scope:
Step 1 – Navigate to the %Netwrix Auditor installation folder%\Windows Server Auditing folder.
Step 2 – Edit the *.txt files, based on the following guidelines:
- Each entry must be a separate line.
- Wildcards (* and ?) are supported. A backslash () must be put in front of (*), (?), (,), and () if they are a part of an entry value.
- Lines that start with the # sign are treated as comments and are ignored.
| File | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| omitcollectlist.txt | Contains a list of objects and their properties to be excluded from being monitored. If you want to restart monitoring these objects, remove them from the omitcollectlist.txt and run data collection at least twice. | monitoring plan name,server name,class name,property name,property value class name is a mandatory parameter, it cannot be replaced with a wildcard. property name and property value are optional, but cannot be replaced with wildcards either. For example: #*,server,MicrosoftDNS_Server `````` #*,*,StdServerRegProv |
| omiterrors.txt | Contains a list of errors/warnings to be omitted from logging to the Netwrix Auditor System Health event log. | monitoring plan name,server name,error text For example: *,productionserver1.corp.local,*Access is denied* |
| omitreportlist.txt | Contains a list of objects to be excluded from reports and Activity Summary emails. In this case audit data is still being collected. | monitoring plan name,who,where,object type,what,property name For example: *,CORP\\jsmith,*,*,*,* |
| omitsitcollectlist.txt | Contains a list of objects to be excluded from State-in-time reports. | monitoring planname,server name,class name,property name,property value class name is a mandatory parameter, it cannot be replaced with a wildcard. property name and property value are optional, but cannot be replaced with wildcards either. For example: *,server,MicrosoftDNS_Server *,*,StdServerRegProv |
| omitstorelist.txt | Contains a list of objects to be excluded from being stored to the Audit Archive and showing up in reports. In this case audit data is still being collected. | monitoring plan name,who,where,object type,what,property name For example: *,*,*,Scheduled task,Scheduled Tasks\\User_Feed_Synchronization*,* |
Monitored Objects
This section lists Windows Server components and settings whose changes Netwrix Auditor can monitor.
When monitoring a Windows Server, Netwrix Auditor needs to audit some registry settings. See the Windows Server Registry Keys section for additional information. If you want Netwrix Auditor to audit custom registry keys, see the Monitoring Custom Registry KeysMonitoring Custom Registry Keystopic for additional information.
In the table below, double asterisks (**) indicates the components and settings for which the Who value is reported as “Not Applicable”.
| Object type | Attributes |
|---|---|
| General Computer Settings | |
| Computer |
|
| Computer Name |
|
| Environment Variables |
|
| Event Log |
|
| General |
|
| Remote |
|
| Startup and Recovery |
|
| System Time |
|
| Add / Remove Programs | |
| Add or Remove Programs |
|
| Services | |
| System Service |
|
| Audit Policies | |
| Local Audit Policy |
|
| Per-User Local Audit Policy |
|
| Hardware | |
| Base Board** |
|
| BIOS** |
|
| Bus** |
|
| Cache Memory** |
|
| CD-ROM Drive** |
|
| Disk Partition** |
|
| Display Adapter** |
|
| DMA** |
|
| Floppy Drive** |
|
| Hard Drive** |
|
| IDE** |
|
| Infrared** |
|
| Keyboard** |
|
| Logical Disk** |
|
| Monitor** |
|
| Network Adapter |
|
| Network Protocol** |
|
| Parallel Ports** |
|
| PCMCIA Controller** |
|
| Physical Memory** |
|
| Pointing Device** |
|
| Printing |
|
| Processor** |
|
| SCSI** |
|
| Serial Ports** |
|
| Sound Device** |
|
| System Slot** |
|
| USB Controller** |
|
| USB Hub** |
|
| DHCP configuration | |
| If the DHCP server runs on Windows Server 2008 (or below), then the Who value for DHCP server configuration events is reported as “Not Applicable”. | |
| Server role |
|
| Server settings |
|
| DHCP scope |
|
| DHCP Reservation |
|
| DHCP Policy |
|
| Removable media | |
| Removable Storage Media** | Netwrix Auditor does not report on floppy/optical disk and memory card storage medias. For removable storages, the When value reports actual time when a change was made and/or a target server was started.
|
| Scheduled Tasks | |
| Scheduled Task |
|
| Local Users and Groups | |
| Local Group |
|
| Local User |
|
| DNS Configuration | |
| The Who value will be reported for DNS configuration settings only if the DNS server runs on Windows Server 2012 R2. See the following Microsoft article for additional information: Update adds query logging and change auditing to Windows DNS servers. | |
| DNS Server |
|
| DNS Zone |
|
| DNS Resource Records | |
| The Who value will be reported for DNS Resource Records only if the DNS server runs Windows Server 2012 R2. See the following Microsoft article for additional information: Update adds query logging and change auditing to Windows DNS servers. | |
| DNS AAAA |
|
| DNS AFSDB |
|
| DNS ATM A |
|
| DNS A |
|
| DNS CNAME |
|
| DNS DHCID |
|
| DNS DNAME |
|
| DNS DNSKEY |
|
| DNS DS |
|
| DNS HINFO |
|
| DNS ISDN |
|
| DNS KEY |
|
| DNS MB*** |
|
| DNS MD |
|
| DNS MF |
|
| DNS MG |
|
| DNS MINFO |
|
| DNS MR |
|
| DNS MX |
|
| DNS NAPTR |
|
| DNS NS |
|
| DNS NXT |
|
| DNS PTR |
|
| DNS RP |
|
| DNS RRSIG |
|
| DNS RT |
|
| DNS SIG |
|
| DNS SRV |
|
| DNS TEXT |
|
| DNS WINS |
|
| DNS WKS |
|
| DNS X25 |
|
| File Shares | |
| Share |
|
Windows Server Registry Keys
If you want to monitor changes to system components on a Windows Server, make sure that Windows Registry audit settings are configured on that Windows server.
This refers to the following keys:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM
- HKEY_USERS.DEFAULT
For these keys and subkeys, the following advanced permissions must be audited ("Successful" audit type required):
- Set Value
- Create Subkey
- Delete
- Write DAC
- Write Owner
The below is the full list of keys (and subkeys) involved in Windows Server auditing.
| Category | Registry Keys |
|---|---|
| Hardware | - HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters\Interfaces* |
| - HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Network{4D36E972-E325-11CE-BFC1-08002BE10318}* | |
| - HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Class{4D36E972-E325-11CE-BFC1-08002BE10318}* | |
| - HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services* | |
| General | - HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\CrashControl* |
| - HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\CrashControl* | |
| - HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet002\Control\CrashControl* | |
| - HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\WOW6432NODE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion* | |
| - HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion* | |
| Software | - HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\WOW6432NODE\MICROSOFT\WINDOWS\CURRENTVERSION\UNINSTALL* |
| - HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MICROSOFT\WINDOWS\CURRENTVERSION\UNINSTALL* | |
| Services | - HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services* |
| - HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services* | |
| - HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet002\Services* | |
| RemovableMedia | - SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Enum* |
Consider that audit data for the registry keys themselves will not appear in Netwrix Auditor reports, alerts or search results, as it is only used as one of the sources for the Activity Records formation.
- You can configure these settings automatically using Netwrix Auditor, as described in the Settings for Data Collection topic. Corresponding audit settings will be also applied automatically after you select a checkbox under Monitor changes to system components on the General tab in the Windows Server data source properties.
Audit settings will be automatically adjusted only for the keys/subkeys involved in the monitoring of selected components (granular adjustment). For example, if you selected Services, the program will adjust the audit settings for the following subkeys:
-
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services(|\.*)
-
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services(|\.*)
-
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet002\Services(|\.*)
-
To configure the audit settings manually, refer to the Configure Windows Registry Audit Settings topic for additional information.
Monitoring Custom Registry Keys
Follow the steps to monitor custom registry keys.
Step 1 – On the computer where Auditor Server resides, navigate to %Netwrix Auditor installation folder%\Windows Server Auditing.

Step 2 – Edit the following parameters of the customregistrykeys.txt file:
monitoring plan name,server name,registry key name
For example:
#*,productionserver1.corp.local,HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\\SYSTEM\\RNG
Step 3 – Consider the following:
- Each entry must be a separate line.
- Wildcards (* and ?) are supported (except for the
registry key namefield). A backslash () must be put in front of (*), (?), (,), and () if they are a part of an entry value. - Lines that start with the # sign are treated as comments and are ignored.
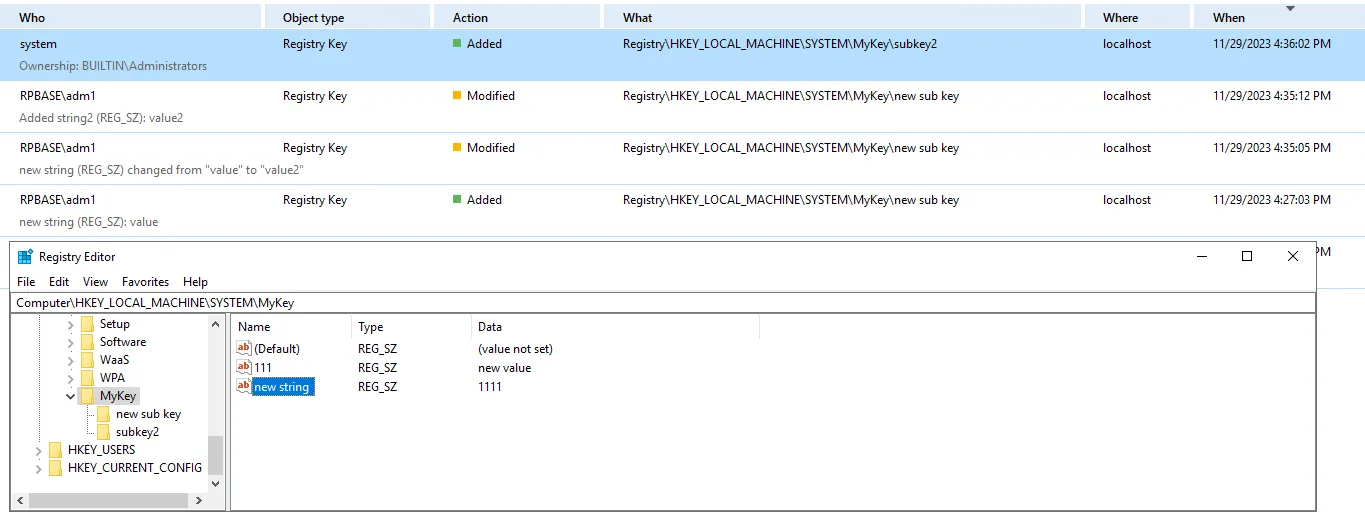
NOTE: In some cases, Who will be the system and When will be collection time, because there is no necessary event in the Security log with this path.
VM Template Cloning
While VM cloning is supported by Netwrix Auditor, an additional setup process should be taken into consideration before the deployment process.
Every monitored VM instance gets a unique ID assigned for monitoring and data collection purposes. To ensure proper operation, the VM template must be excluded from the monitoring scope beforehand. Omitting the VM template will allow Netwrix Auditor to assign unique IDs correctly and collect data as intended.
Follow the steps to add the template server to exclusions.
Step 1 – In main Netwrix Auditor menu, select Monitoring plans.
Step 2 – Select your Windows Server monitoring plan and click Edit.
Step 3 – Choose the AD Container containing the template VM and click Edit data source in the right pane.
Step 4 – In the left pane, select Containers and Computers.
Step 5 – Check the Exclude these objects checkbox and add the template VM by clicking Add Computer.
VM template server is added to exclusions and ready to use.