Sync Service Administration
For most use cases of the Sync Service, installation is all the configuration and administration required. For advanced setups, there is a set of options available in the configuration file which are listed at the end of this document.
ServiceNow Features
The ServiceNow integration has additional features due to it's popularity.
Configure Device Discovery
Instead of maintaining a list of all your servers, desktops and switches in ServiceNow and Change Tracker, it is possible to synchronize configuration items from ServiceNow to Change Tracker as devices. Not only does this give you a single place to maintain that list (ServiceNow), it also speeds up initial setup of Change Tracker.
When devices are created via Device Discovery from ServiceNow, the configuration items from RFCs are matched to devices in Change Tracker on their ServiceNow Id, ensuring a perfect match.
Agentless monitoring (via a proxy agent or Splunk) has always required the manual creation of devices for change events to be linked to. Device discovery removes this manual configuration.
Follow the steps to configure Device Discovery.
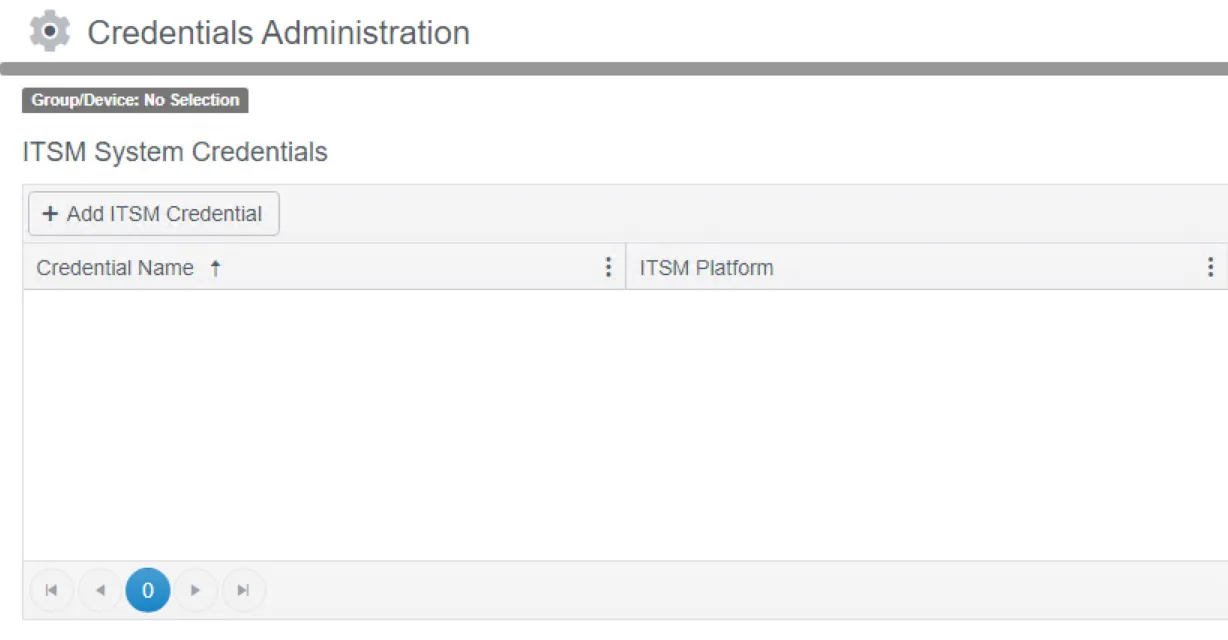
Step 1 – From the Settings menu, select Credentials, scroll to the ITSM System Credentials section and click Add ITSM Credential.
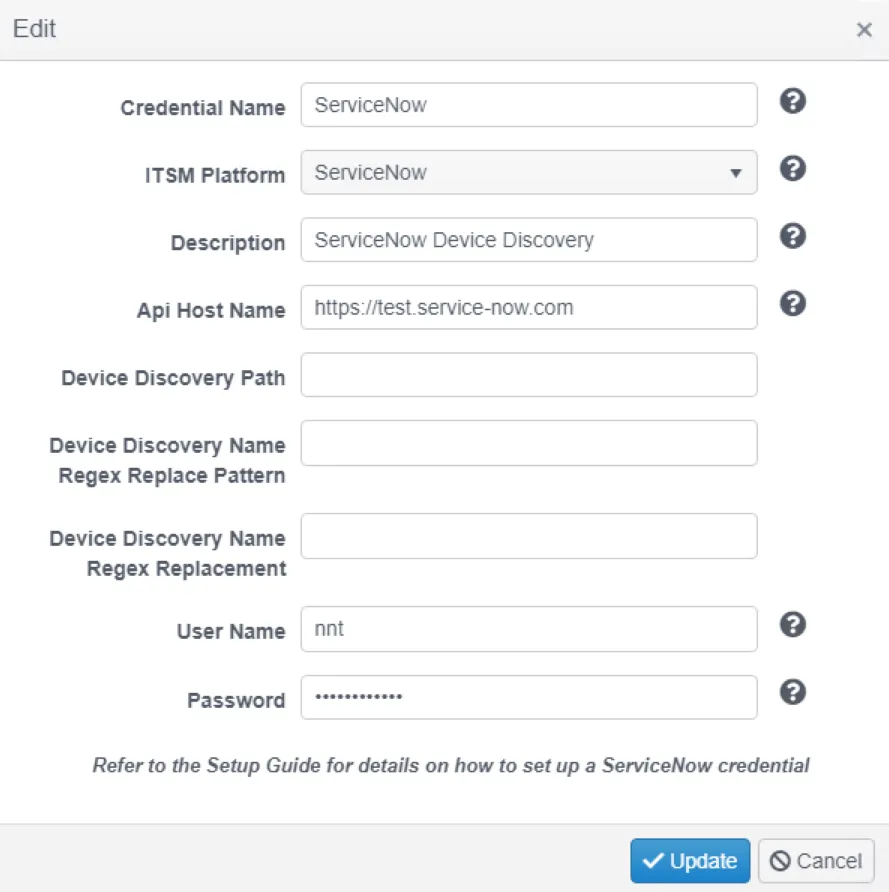
Step 2 – Select ServiceNow from the initial drop down and enter the details of the ServiceNow instance to connect to.
By default Change Tracker will look for devices in the cmdb_ci_computer table in ServiceNow's CMDB. The Device Discovery Path field can be used to specify a different table to pull devices from.
The Device Discovery Name Regex Replace Pattern field is used to define a piece of regex that can identify a pattern in device names that the user would like to not include or to replace with something else when the devices are created in Change Tracker. This can be useful when there is not an exact match between device names in the change events and device names in ServiceNow.
The Device Discovery Name Regex Replacement fields defines the value to replace the pattern defined in the field above. Leaving this empty will cause the pattern matched by the regex above to be trimmed from device names created in Change Tracker.
Step 3 – Select a device to act as the proxy for the calls made to ServiceNow. The agent on the same host as the Hub is often a good choice here.
Step 4 – Select the credentials created earlier.
Step 5 – Select the group to put the discovered devices into.
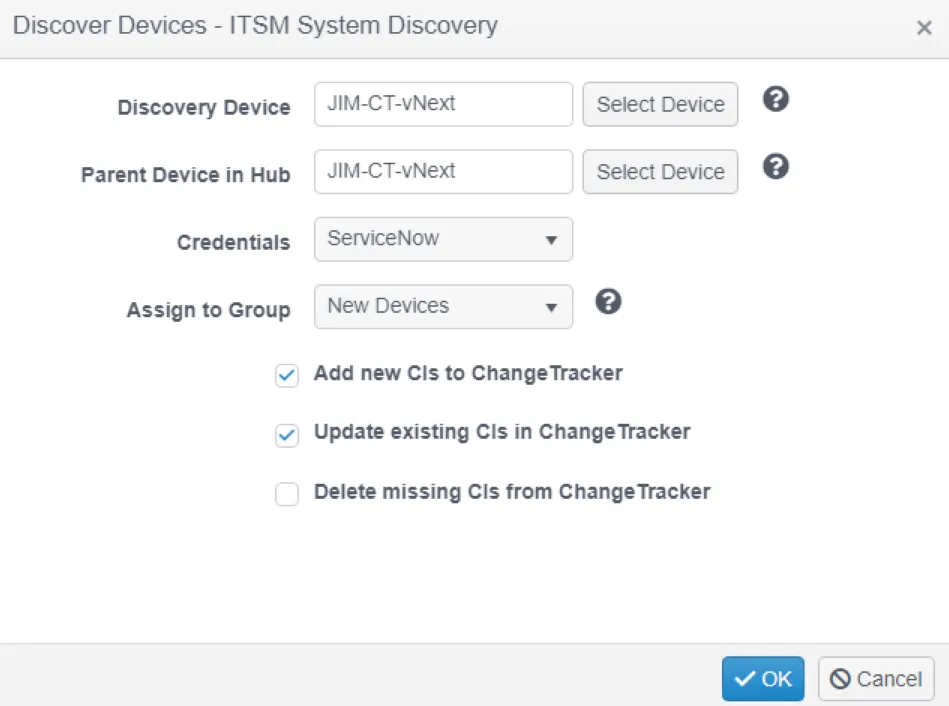
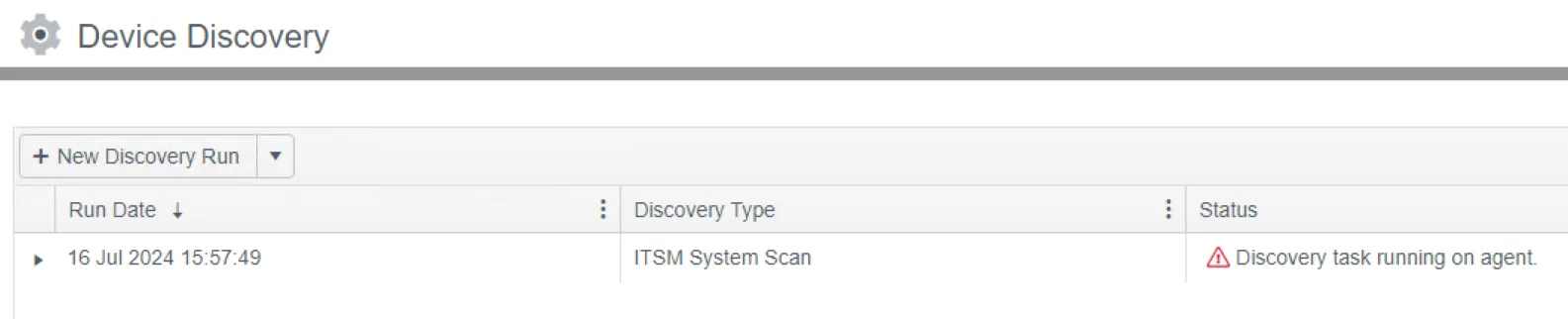
Step 6 – Click OK. A discovery task will start and create the devices.
Raise a ServiceNow Incident
To close the loop of change management someone who can act must be alerted of unplanned changes so they can be investigated and resolved appropriately. A great option for unplanned change alerts is to raise an incident in ServiceNow which will alert the owner of the matching configuration item and provide a work flow to resolve the situation.
Follow the steps to raise a ServiceNow incident.
Step 1 – From the Settings menu, select System Settings and scroll to the ServiceNow Integration section. Insert the URL and credentials of the ServiceNow instance to raise incidents to. The test button will raise a test incident to prove connectivity.
Step 2 – Select the device group you want to raise incidents for (All devices is the common choice), select the Un-planned Change Notification Type and select ServiceNow as the notification Method.
Configuration Options
| Key | Notes |
|---|---|
| restSyncProvider.retryTimes | Byte (default: 3, max: 255) Determines how many times a failed REST request is retried before being abandoned. |
| restSyncProvider.retryMilliseconds | Integer (default: 250) Determines the delay in milliseconds between retries of failed REST requests. |
| restSyncProvider.startSyncTimeUtc | DateTime (default: current UTC date / time written by installer e.g., “2023-03-27T17:56:30”) Typically used by SyncAdapters as a chronological start point when first requesting incremental changes. |
| changeTracker.getEventsStartTimeSpan | TimeSpan (default: 7.00:00:00, equivalent to 7 days) When submitting / re-submitting events for a Planned Change whose Start Time is set to continuous, this determines the actual Start Time used |
| changeTrackerPlannedChangeRestSyncAdapter.usePlannedChangeRulesetName | String (e.g., “MyRuleSet”) Nominates a planned change ruleset to be used as the criteria when matching events to planned changes. By default events would be matched by date and device. This setting allows events to be matched on any field. An example would be to match the event's Who Made The Change (WMTC) to the planned change's Assigned To field to ensure the change was done by the person expected. |
| changeTrackerPlannedChangeInstanceRestSyncAdapter.requireMembers | Boolean (default: false) Determines whether linked members (Devices or Groups) are a requirement for a Planned Change to be created. Default setting (false) is recommended while establishing that the service is working correctly. Note: production systems should have this setting set to true, since a Planned Change which has no linked members will never capture any events, hence is redundant. |
| changeTrackerRestSyncProvider.baseUrl | String (e.g., “https://localhost:5001/api”) The base URL for the REST API endpoint. All REST requests will be made relative to this URL. |
| changeTrackerRestSyncProvider.userName | String (e.g., “itsm”) The username of the account used to connect to Change Tracker. Note: While an “itsm” role is created in Change Tracker which has the appropriate permissions, no user is assigned to this role by default. |
| changeTrackerRestSyncProvider.password | String (e.g., “password”) The password of the account used to connect to Change Tracker. Note: This setting is encrypted by the service and written back to the config file under the key “E. changeTrackerRestSyncProvider.password” |
| serviceNow.deviceClassNames | String (e.g., “cmdb_ci_win_server,cmdb_ci_linux_server”, default: “”) Optional comma-separated whitelist of Configuration Item class names (sourced from the cmdb_ci.sys_class_name property) which restricts which CIs can be mapped to a Device in Change Tracker. |
| serviceNow.groupClassNames | String (default: “”) Optional comma-separated whitelist of Configuration Item class names (sourced from the cmdb_ci.sys_class_name property) which restricts which CIs can be mapped to a Group in Change Tracker. A value of DO_NOT_MATCH disables the group lookup if the device name is not found. |
| serviceNow.timeZone | String (e.g., “Eastern Standard Time”, default: “”) Optional time zone taken from this list, which should match the time zone of the account used to connect to ServiceNow. Note: this should be used where it’s not possible to set the account to use GMT. |
| serviceNowChangeRequest.createplannedchangepertask | Boolean (default: false) When true, any RFC in ServiceNow that has tasks against it will result in a planned change for each task. If start or end times are missing on the tasks they will be taken from the parent RFC. |
| serviceNowChangeRequestRestSyncAdapter.changesUrl | String (e.g., “https://site.service-now.com/api/now/table/change_request”, default: “”) Optional absolute URL for the REST API endpoint from which to retrieve Change Requests. |
| serviceNowChangeRequestRestSyncAdapter.taskCiUrl | String (e.g., “https://site.service-now.com/api/now/table/task_ci”, default: “”) Optional absolute URL for the REST API endpoint from which to retrieve Configuration Items linked to Change Requests. |
| serviceNowChangeRequestRestSyncAdapter.getIncrementalChangesFilter | String (e.g., “approvalINapproved,withdrawn,reverted”, default: “”) Optional filter which can be used to restrict the Change Requests retrieved from ServiceNow during the periodic polling for modified entries. |
| serviceNowImportJob.intervalMilliseconds | Integer (default: 30000, equivalent to 30 seconds) Optional setting which can be used to determine the frequency of the periodic polling for modified entries. |
| serviceNowRestSyncProvider.baseUrl | String (e.g., “https://site.service-now.com/api”) The base URL for the REST API endpoint. All REST requests will be made relative to this URL, unless “serviceNowChangeRequestRestSyncAdapter.changesUrl”, “serviceNowChangeRequestRestSyncAdapter.taskCiUrl” or “serviceNowRestSyncProvider.accessTokenUrl” are specified (which take precedence as absolute URLs) |
| serviceNowRestSyncProvider.authType | Integer, Enum (default: 0) Determines which type of authentication is used when connecting to ServiceNow: · 0 = Basic Authentication (requires userName and password) · 1 = OAuth2 Password Grant (requires userName, password, clientId and clientSecret) · 2 = OAuth2 Client Credentials Grant (requires clientId and clientSecret) |
| serviceNowRestSyncProvider.userName | String (e.g., “itsm”) Optional, depending on “authType”. The username of the account used to connect to ServiceNow. |
| serviceNowRestSyncProvider.password | String (e.g., “password”) Optional, depending on “authType”. The password of the account used to connect to ServiceNow. Note: This setting is encrypted by the service and written back to the config file under the key “E.serviceNowRestSyncProvider.password” |
| serviceNowRestSyncProvider.accessTokenUrl | String (e.g., “https://site.service-now.com/oauth_token.do”) Optional, depending on “authType”. Absolute URL for the REST API endpoint from which to retrieve OAuth2 tokens. |
| serviceNowRestSyncProvider.clientId | String (e.g., “8b466c8147bd21609527f6e9a0ef4301”) Optional, depending on “authType”. The client ID of the OAuth application, defined in ServiceNow. |
| serviceNowRestSyncProvider.clientSecret | String (e.g., “0aZbfubF7A”) Optional, depending on “authType”. The client secret of the OAuth application, defined in ServiceNow. Note: This setting is encrypted by the service and written back to the config file under the key “E.serviceNowRestSyncProvider.clientSecret” |
| serviceNowRestSyncProvider.origin | String (e.g., “ServiceNow”) Optional. Used to tag any entities created by the service |