Google Drive Source
The Google Drive source configuration screen allows you to enable the crawling and classification of content stored in both G-Suite repositories and Google Drive personal accounts.
IMPORTANT! Make sure you created App for GDrive crawling prior to start adding the source. See Configure G Suite and Google Drive for Crawling for more information.
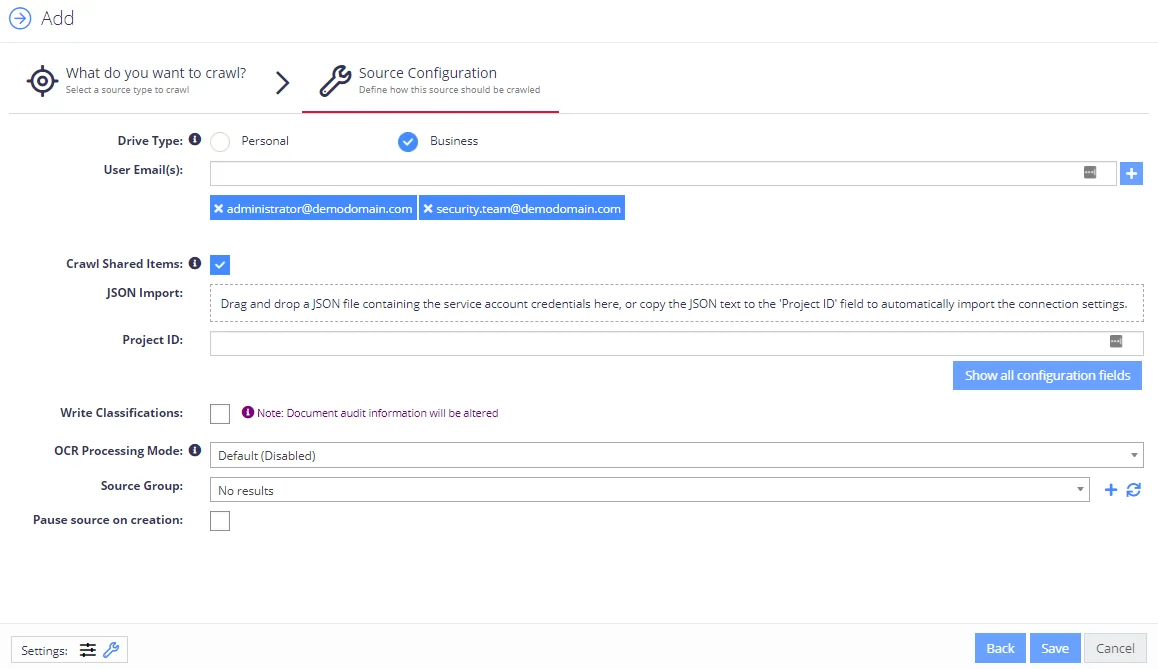
Complete the following fields:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Basic settings | |
| Drive Type | Select Business. |
| User Email(s) | When adding a G-Suite source, enter the email address of the user's drive that you wish to crawl (via impersonation). |
| Crawl Shared Items | Select to crawl all files shared with the specified user in addition to any team drives shared with the user. |
| Crawl Shared Items | Select to enable crawling of any types of documents shared with the specified user. |
| JSON Import | Drag the JSON connection file you downloaded while creating Google service account in the form. |
| Project ID | Open the JSON connection file and copy file contents to Project ID field. |
| Write Classifications | Select to enable the writing of classifications back to the Google Drive repository. NOTE: Any classifications written to Google Drive are stored in custom properties which are not visible to an end user - they are only accessible via the Google Drive APIs. |
| OCR Processing Mode | Select documents' images processing mode: - Disabled – documents' images will not be processed. - Default – defaults to the source settings if configuring a path or the global setting if configured on a source. - Normal – images are processed with normal quality settings. - Enhanced – upscale images further to allow more. |
| Advanced Settings | Click the "wrench" icon in the Settings area ( |
| Source Group | Netwrix recommends creating a dedicated source group for Google Drive. |
| Pause source on creation | Select if you want to make other configuration changes before collection of the source occurs. |
Google Drive
This section contains information on how to configure exclusions and use tagging for a Google Drive source.
Configure Tagging
You can instruct the program to write classification attributes back to to the document properties in the Google Drive repository. Each taxonomy can be mapped to a single property.
NOTE: Custom properties are not exposed to end users and are only available to other applications using the API.
By design, Google Drive supports custom properties with the following limitations:
- Maximum of 100 custom properties per file, totalled from all sources
- Maximum of 30 public properties per file, totalled from all sources
- Maximum 124 characters for both the property name and the list of classifications
NOTE: See this article for details.
To overcome these limitations, Google Drive tagging implemented in the solution supports appending a counter to the field name. So, it is possible to split classifications across multiple fields if a text limit is hit within the source system. For example, you may have classifications written to the fields “Agriculture” and “Agriculture_1”.
NOTE: Due to the way Google Drive manages document audit information, writing classifications to a document (i.e. tagging) in this source will affect additional document metadata such as modified date and/or modified user:
- modified date information will be changed to the time of tagging
- modified user will be changed to the account that was configured for crawling this source
Related content source settings can be configured at a global level (default), or at a source level.
To configure tagging on a global level
- In the management console, click Sources →Google Drive, then in the left pane click Write Configuration.
- Select the taxonomy you need and click the Edit link for it.
- In the taxonomy properties, enable writing classification attributes (tags) and specify other settings:
| Setting | Description | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Enabled | Use to enable / disables the writing of classifications for the selected taxonomy. | Cleared by default |
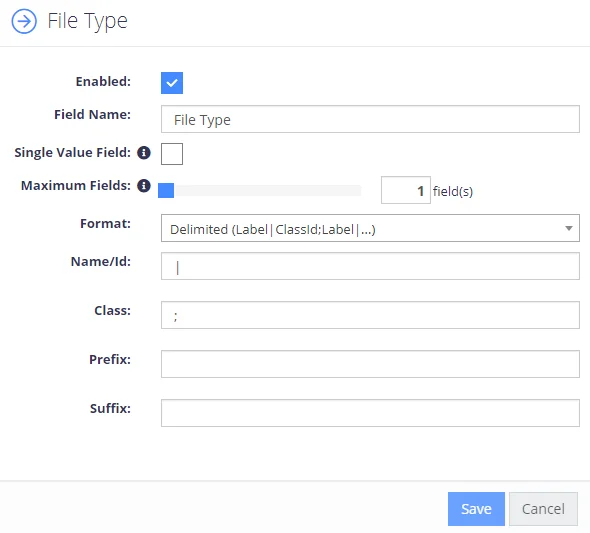
| Field Name | Defines the attribute name to be used when persisting the classifications (metadata property name). | |
| Single Value Field | If selected, this option will cause only the highest scoring classification to be written to the field. | |
| Maximum Field | Specifies the maximum number of properties which can be used to write classifications. Property names will be in the format 'FieldName_X' | This allows more classifications to be written for sources where there is a limit on field length, by writing classifications across multiple properties. |
| Format | How the classifications should be formatted. | You can create a custom delimited combination of the labels / GUIDs. |
| Name/ID or Class | Depending on the format, take the term labels, IDs or a combination of both | The corresponding Delimiter must be a string or array type with a maximum length of 3. |
| Prefix/ Suffix | Will be appended to the formatted string of classifications. |
Configure Exclusions
In the Collection Exclusions window you can set up the following:
- List of file locations that will be ignored when indexing files from Google Drive source
- Excluding conditions based on the metadata of a document
In the management console, click Sources →Google Drive, then in the left pane click Collection Exclusions.
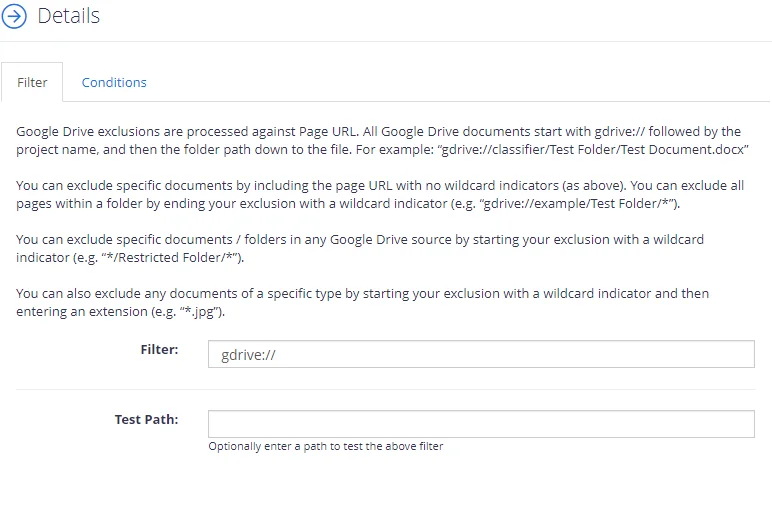
- Click Filter tab and in the Filter field specify the file locations to exclude from crawling.
- Wildcards can be used anywhere in the exclusion pattern definition as follows:
- The asterisk character (*) - matches any sequence of characters
- The question mark character (?) - matches any single character
NOTE: Exclusions are case-insensitive.
For example, to exclude all Excel files stored in the corp/Year2020 folder, enter gdrive://corp/Year2020/*.xlsx
-
To verify exclusion location, enter its path in the Test Path field and click Test.
-
If needed, you can use metadata conditions to restrict when an exclusion filter should be applied. For that, click Condition tab and click Add. Then select how the exclusion conditions will work: it can check if metadata field of the document has any value, is not specified, or matches a specific metadata value.
Criteria Condition Comparison Compare a value in the document metadata field with the value set by condition. With this criteria selected, you will then need to specify: - Field name — document metadata field to check - Comparison — operator to use (for example, "does not contain") - Value — value to compare against For example, to exclude documents tagged with year 2018, set the condition as follows: - Field Name — DocYear - Comparison — equals - Value — 2018 Has any value Exclude the document if its metadata field has any value. With this criteria selected, specify Field Name. Has no values Exclude the document if metadata field value is not specified. With this criteria selected, specify Field Name. When finished, click Add.
-
To verify the settings, click Test.
-
Finally, click Save and close the window.
Any item that matches the excluding filter will be ignored.