Database Configuration Wizard
For the database sources, you can enable security-based crawling, that is, finding sensitive data (which logically will either be stored in text or binary-based columns). It is possible to create an intelligent content mapping, crawling certain fields as unstructured index text, and other fields — as mapped metadata.
This section explains how to use the Database Configuration Wizard for configuring the crawling process. You can run this wizard when adding the data source, or you can later open the Source tab, select your database source and click Launch Wizard.
IMPORTANT! If you want to crawl a target database in your MS SQL replication model, you must backup your database before running the configuration wizard.
See next:
Introduction
On this step, provide matching rules to search in the database for data that match exactly or are similar to a specific pattern. You can indicate both: exact or partial matches over the database strings.
Tables
On this step, review the grid of the tables in the database that are not currently enabled for crawling (if already enabled then don't show in this grid) and have at least one text/binary column. Configure your crawling scope considering the following:
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Table | Contains the list of all tables in the database, followed by alphabetically. |
| Text Columns | Contains the number of text/binary columns for each table. Click the number link to review the full list. |
| Metadata Columns | Contains the number of non-text/binary columns for each table. Click the number link to review the full list. |
| Primary Key | Contains the primary key for each table. Review the following Microsoft article for more information on SQL Server primary keys: Primary Keys Constraints. |
| Modified Filter | To improve performance the product performs automatic re-indexing against a field in each table that indicates the last modified date of the row. Where possible, the product will automatically map this based upon the exact match or inclusion of one of the below values within the field name. Additional values can be added below in order to support other naming conventions for modified fields (different language or internal convention). |
| Include? | Select if you want to disable crawling for this table. NOTE: You can disable crawling for all listed tables using the Include none option in the upper right corner of the wizard or enable crawling accordingly with the Include all. |
| View Sample | Shows a table of the top 15 rows allowing to view if the table is one to exclude. |
Exceptions
On this step, review tables with missing primary keys and/or missing modified filters.
- Missing primary keys – only shows if users have tables that are missing primary keys where the user can select the primary key from a dropdown of all the columns. This step does not show if there are no missing primary keys.
- Missing modified filters – only shows if there are tables missing modified filters. Here tables are shown that are missing a modified and that have a datetime (or equivalent) typed column to select. If there are none this stage is skipped.
Summary
At this step, review your database configuration.
- Overview – review a high-level overview of the number of configured tables and excluded tables with their details.
- Configured Tables – double-check the configuration of tables to be crawled.
- Excluded Tables – review the full list of the tables to be excluded from classification scope with exclusion reason.
When the database configuration has been completed you will be redirected to the Advanced Source Configuration, this allows you to define how the database will be crawled. It is possible to crawl either specific tables, or crawl custom queries (defined select statements, which may use JOIN statements across multiple tables). See Database for more information.
Add Database Source
The Database source configuration screen allows you to enable the crawling and classification of content stored in your Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, and Oracle databases.
Content must either be configured / crawled using the configured service accounts (IIS Application Pool User, Windows Services) or by using specific connection details.
Once connected it is possible to create an intelligent content mapping, crawling certain fields as unstructured index text, and other fields as mapped metadata. For more information please see the Database Configuration Wizard section.
If you wish to make other configuration changes before collection of the source occurs ensure you tick the checkbox "Pause source on creation".
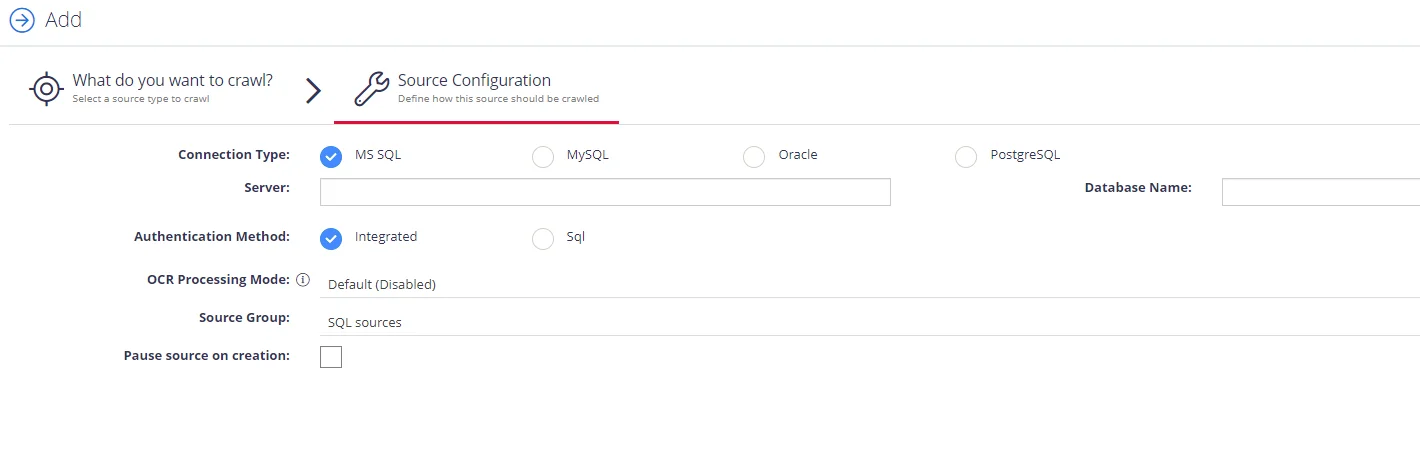
Complete the following fields:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Connection Type | Select your connection type: MS SQL, MySQL, or Oracle. |
| Server | Specify the server name of the database system to be crawled ("." can be used to indicate the local server). |
| Database Name | Specify the database that will be crawled. It is possible to configure multiple databases from the same server. |
| Authentication Method | Select authentication method: Integrated or SQL. - With Integration option selected, database will be accessed under the account currently logged on. - With SQL option selected, specify user name and password to be used when accessing the database. |
| OCR Processing Mode | Select processing mode for images in the documents: - Disabled – documents' images will not be processed. - Default – defaults to the source settings if configuring a path or the global setting if configured on a source. - Normal – images are processed with normal quality settings. - Enhanced – upscale images further to allow more accurate results. This will provide better accuracy but can lead to longer processing time if the images do not contain text. |
| Source Group | If you want to add database to a source group, select existing, or create a new one. |
| Pause source on creation | Select to make other configuration changes before the initial data collection starts. |
After the source configuration is completed, you will be prompted to lauch SQL crawling configuration wizard. See Database Configuration Wizard for more information.
Database
This section describes how to specify configuration settings for the Database source. You can specify which tables / views / queries will be crawled, or set up table configuration. Also, you can use Write Configuration options to configure tagging.
Configure tagging
Tagging allows you to write classification taxonomy attributes back to the source database.
Each registered taxonomy can be mapped to a property in the database table’s metadata. The program will update a specific column per taxonomy within the source repository with the associated classifications for a record. You can specify how the classifications should be mapped to the table:
- Which table should be updated
- Which column should be updated
- How to filter the table to ensure that at most only one row will be updated (each update statement is verified prior to execution in order to ensure that only one row will be updated).
These settings are configured in the Write Configuration window for the selected entity (table or query).
To configure tagging, do the following:
- In the Sources window, select the required source by clicking on the triple cog icon.
- Select the entity that you wish to configure tagging for (table or query) and click Edit.
- Select Write Configuration on the left.
Configure tagging options listed below:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Table Name | Specify the name of the table to be updated (in most cases this will be the same as the table being crawled). |
| Column Name | Specify the name of the column to be updated (text/varchar column). |
| Update Filter | Update filters are the method used to restrict the update at the target destination. If multiple filters are configured then they all must be true. Filters should be created in the format: ColumnName=@Parameter where @Parameter is a correctly configured metadata value from the source table/query. The specified values will result in a query in the following format: UPDATE TABLENAME SET COLUMNNAME=@Classifications WHERE FILTERS |
Other Database Configuration settings
You can also specify the following settings:
Source Configuration
The Source Configuration screen allows you to define which tables / views / queries will be crawled. The following options are available:
- Add Source—Add a new SQL database connection
- Edit Connection—Amend the connection details of the currently selected source
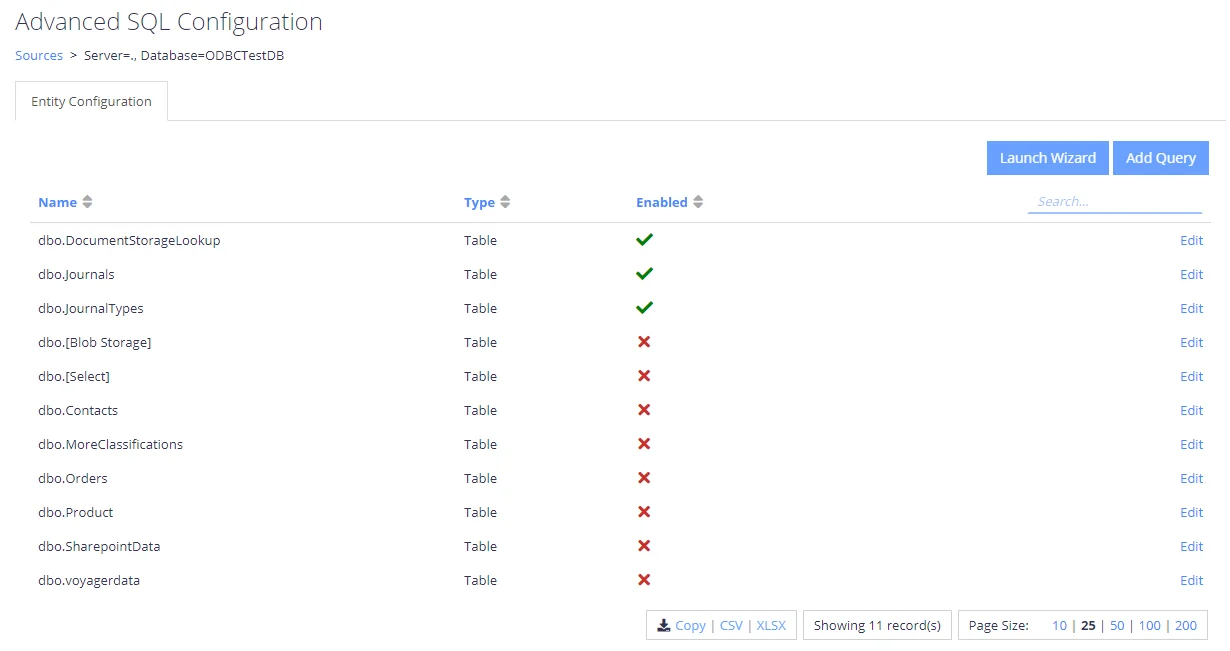
- Add Query—Add a custom method for crawling content (custom SELECT statements), Templates are provided for Hummingbird, Worksite and Documentum.
You can access the Source Configuration screen by selecting the multi-cog (Advanced Configuration)
icon from the sources
grid:.
Selecting Edit for one of the tables / queries on the list will redirect you to the entity level configuration, which identifies how content will be mapped into the core index.
Selecting the Add Query option will present a popup allowing you to select a unique name for the query, as well as the queries to be used for crawling:
Primary Key Query
The primary key query should return a set of values that uniquely identify each row to be crawled, in the event that JOINs are used you should JOIN from the largest dataset to the smallest, to ensure that each row is unique.
Example: SELECT PageID FROM Pages
NOTE: Stored procedures are currently not supported.
Content Query
The content query must return all fields to be indexed/classified on, as well as the fields included in the primary key query.
Example: SELECT * FROM Pages
NOTE: Stored procedures are currently not supported
Adding the query will take you to the custom query configuration. Here you can update the primary key query and the content query, all other configuration options are described in the Table Configuration section:
Table Configuration
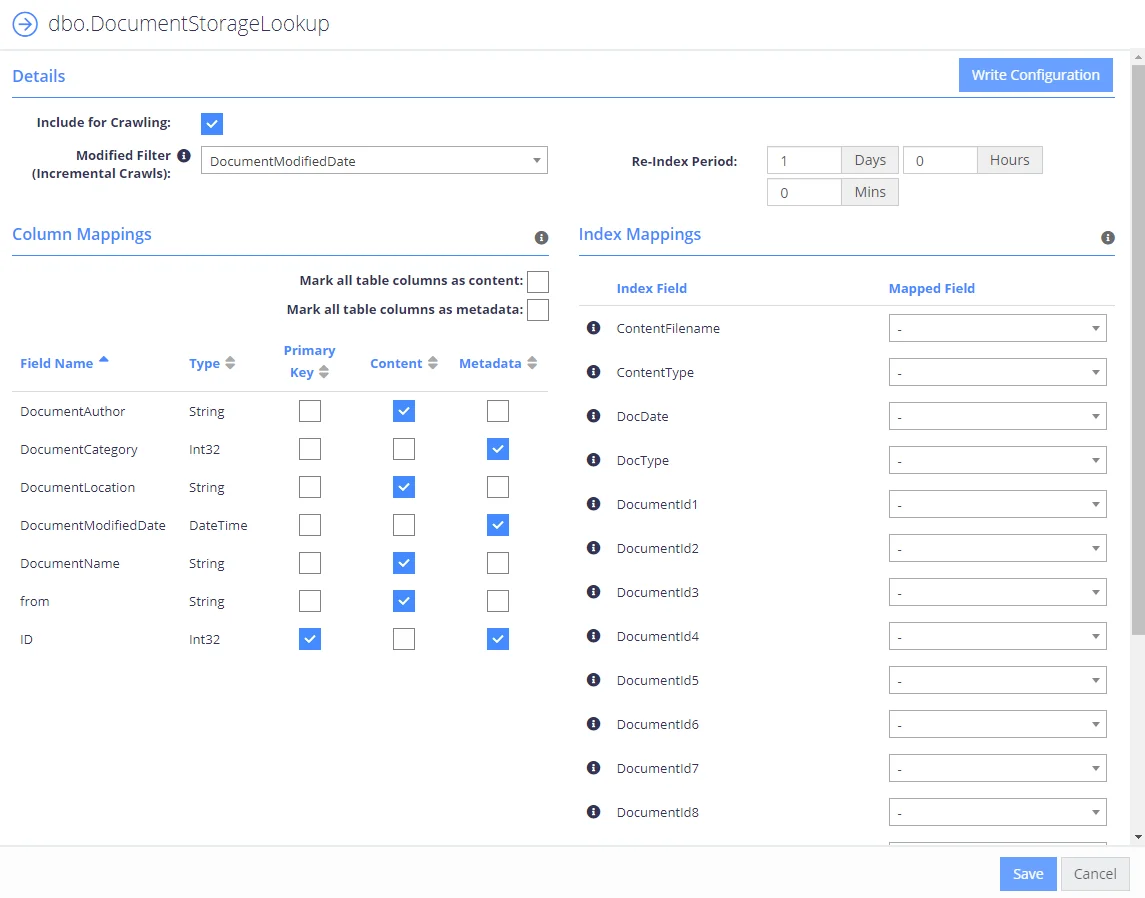
The table configuration allows you to choose how each specific entity will be crawled:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Include for Crawling | When checked the table/entity will be enabled in the collection schema. |
| Upload Content | When checked the Content fields will be uploaded into the SQL database. Uploaded content can be retrieved after collection by passing the PageId for the record to the QS API call "GetDownload". |
| PK - Primary Key | Please select the fields which uniquely identify the row to be crawled, in the event that multiple rows are returned by the Primary Key, the query will be aborted. Custom queries will not require the primary key to be defined, this will be set automatically from the primary key query. |
| Content | Identifies the fields that will be crawled as searchable text in the core search index. Multiple fields can be mapped to Content, each will be appended with a line break. It is also possible to configure a single binary field type that contains a document, the collection process will load the binary and attempt to convert and extract text from the document. When this functionality is used we recommend setting the ContentFilename or ContentType index mapping to aid the process of text extraction. |
| Metadata | Identifies the fields that will be mapped as metadata values. |
| Index Mappings | Index mappings identifies mappings between the entities fields and the internal core database. Each row also contains an information icon identifying its purpose within the crawling process. |
| Modified Filter (Incremental Crawls) | This should be set to a field that defines when a row has changed (the modified date for the row). When set the collection process will automatically filter the re-indexing process to rows that have a modified date that is larger than the last crawl time. |
| Re-Index Period | This value is the number of days/hours/minutes that will pass between Re-Indexing. The Re-Indexing process involves querying the table(s) to find new and changed records. |