Get-Contact
Use the Get-Contact cmdlet to retrieve basic information about a contact.
Syntax
Get-Contact
[[-Identity] <string[]>]
[-SearchContainer <string[]>]
[-SearchContainersScopeList <string>]
[-ShouldReturnCollection]
[-MaxItemsToDisplay <int>]
[-ObjectType <string[]>]
[-LdapFilter <string>]
[-SmartFilter <string>]
[-ServerFilter <string>]
[-AttributesToLoad <string[]>]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- None
Example:
The following command retrieves a contact from the specified container of the identity store.
Get-Contact -SearchContainer "OU=osamamu,DC=naveed,DC=local"
See Also
New-Contact
Use the New-Contact cmdlet to create a new contact in the directory. Most contact properties can be directly added by using the parameters supported by this cmdlet.
Syntax
New-Contact
-Name <string>
-OrganizationalUnit <string>
-FirstName <string>
-LastName <string>
-DisplayName <string>
[-UPNSuffix <string>]
[-Title <string>]
[-City <string>]
[-State <string>]
[-Zip <string>]
[-Country <string>]
[-Initials <string>]
[-Address <string>]
[-Office <string>]
[-Business <string>]
[-Business2 <string>]
[-Alias <string>]
[-EmailAddress <string>]
[-Department <string>]
[-Company <string>]
[-Mobile <string>]
[-Home <string>]
[-Manager <string[]>]
[-HomePage <string>]
[-Assistant <string>]
[-Notes <string>]
[-MailEnabled <string>]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameters
- Name
- OrganizationalUnit
- FirstName
- LastName
- DisplayName
Example:
The following command creates a new contact in the container specified by the OrganizationalUnit parameter. The command also specifies the logon name, first name, last name and display name of the new contact.
New-Contact -Name "OsamaContact" -OrganizationalUnit "OU=osamamu,DC=naveed,DC=local" -FirstName "OsamaContact" -LastName "OsamaContact" -DisplayName "OsamaContact"
See Also
Contact Commands
GroupID provides the following cmdlets to perform contact-related tasks, such as:
- Get-Contact: retrieves a contact that matches the given criteria.
- New-Contact: creates a new contact.
- Remove-Contact: removes a contact from the directory.
- Set-Contact: modifies a contact in the directory.
See Also
Remove-Contact
Use the Remove-Contact cmdlet to delete a contact from the directory.
Syntax
Remove-Contact
-Identity <string[]>
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- Identity
Example:
The following command deletes the specified contact from the identity store.
Remove-Contact -Identity "OsamaContact"
See Also
Set-Contact
The Set-User cmdlet modifies a user in the directory. Most user properties can be directly modified by using the parameters supported by this cmdlet.
Syntax
Set-Contact
-Identity <string>
[-FirstName <string>]
[-LastName <string>]
[-Title <string>]
[-City <string>]
[-State <string>]
[-Zip <string>]
[-Country <string>]
[-Initials <string>]
[-Address <string>]
[-Office <string>]
[-Business <string>]
[-Add <hashtable[]>]
[-Remove <hashtable[]>]
[-Replace <hashtable[]>]
[-Clear <string[]>]
[-Department <string>]
[-Company <string>]
[-Assistant <string>]
[-HomePage <string>]
[-Alias <string>]
[-EmailAddress <string>]
[-Description <string>]
[-Notes <string>]
[-AdministrativeNotes <string>]
[-DisplayName <string>]
[-SimpleDisplayName <string>]
[-CustomAttribute1 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute2 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute3 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute4 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute5 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute6 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute7 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute8 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute9 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute10 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute11 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute12 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute13 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute14 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute15 <string>]
[-Delimiter <string>]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- Identity
Example:
The following command modifies the city of the specified contact.
Set-Contact -Identity "OsamaContact" -City "Islamabad"
See Also
New-Dynasty
The New-Dynasty cmdlet creates a new Dynasty in Directory. A Dynasty is a Smart Group that can create and maintain the membership of other Smart Groups. A Dynasty retrieves data from Directory in the same manner as a Smart Group, but it divides the result set into child groups based on group-by field values.
You can specify multiple group-by fields. For instance, with the group-by fields Country, State, and City, this commandlet creates a group for every distinct country value, then for each state within a country, and finally for each city in that state. All created child groups inherit those attributes of the parent that are set in the InheritedAttrs option.
You can view events related to this commandlet in GroupID portal, against the History node in the left panel.
Syntax
New-Dynasty
-TopManager <string>
-SamAccountName <string>
-Name <string>
-OrganizationalUnit <string>
-GroupScope <string>
-Type <string>
-SecurityType <string>
[-ChildContainer <string[]>]
[-Filters <string[]>]
[-Separator <string[]>]
[-ExcludeNestedLists <string>]
[-CreateFlatManagerialList <string>]
[-IncludeManagerAsMember <string>]
[-ChildPath <string>]
[-DynastyInheritance <bool>]
[-SearchContainers <string[]>]
[-SearchContainersScopeList <string[]>]
[-ObjectTypes <string[]>]
[-LdapFilter <string>]
[-IncludeRecipients <string[]>]
[-ExcludeRecipients <string[]>]
[-Storage <string>]
[-DataSourceType <string>]
[-SystemDSN <string>]
[-TableorView <string>]
[-DataSourceUserName <string>]
[-DataSourcePassword <string>]
[-FilePath <string>]
[-Server <string>]
[-Port <int>]
[-LDAPSearchContainer <string>]
[-DataSourceName <string>]
[-DataSourceConnection <string>]
[-DataSourceQuery <string>]
[-KeyMapDB <string>]
[-KeyMapAD <string>]
[-WindowsAthentication]
[-IsPasswordExpiryGroup]
[-DomainExpiration <int>]
[-ExpirationRange <int>]
[-IncludeDisabledUsers <string>]
[-IncludePasswordNeverExpireUsers <string>]
[-Script <string>]
[-ScriptFilePath <string>]
[-Sun_Container <string>]
[-GroupAlias <string>]
[-ManagedBy <string[]>]
[-DisplayName <string>]
[-MailEnabled <string>]
[-Description <string>]
[-AdditionalOwners <string[]>]
[-NotifyOptOutAdditionalOwners <string[]>]
[-Members <string[]>]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameters
- TopManager
- SamAccountName
- Name
- OrganizationalUnit
- GroupScope
- Type
- SecurityType
Example 1:
The following command creates a new mail-enabled, universal, distribution Dynasty and constructs its child groups for every distinct department value in the container specified by the OrganizationalUnit parameter using the credentials of current user logged-on to the identity store.
New-Dynasty -OrganizationalUnit "OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -Name "Departmental" -SamAccountName "Departmental" -Type "Distribution" -GroupScope "Universal Group" -MailEnable True -GroupAlias "Departmental" -GroupBy "Department"
Example 2:
The following command creates a new mail-enabled, universal, distribution, multi-level Dynasty with the group-by attributes Country, State and City based on the specified filters and separator, using the credentials set in the $Credentials environment variable. See the Set the $Credentials Environment Variable topic for setting credentials in an environment variable.
New-Dynasty -OrganizationalUnit "OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -Name "Geographical" -GroupAlias "Geographical" -MailEnable True -SamAccountName "Geographical" -GroupScope "Universal Group" -Type "Distribution" -GroupBy "co","st","l" -Filters "Left 3","Left 3","%GROUPBY%\*" -Separator "_","_","_" -Credential $Cred
Example 3:
The following command creates a new universal, distribution Managerial Dynasty in the container specified by the OrganizationalUnit parameter, searches the direct reports of the top manager in the containers specified in the SearchContainers parameter including sub containers and creates them in the same container where the Top Manager resides.
New-Dynasty -OrganizationalUnit "OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -Name "Managerial" -SamAccountName "Managerial" -GroupScope "Universal Group" -Type "Distribution" -SearchContainers "OU=Recruiting,OU=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US","OU=Outsourcing,OU=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -SearchContainersScopeList "2","2" -TopManager "CN=BrianRegan,CN=Users,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -ExcludeNestedLists False -ChildContainer ""
See Also
Dynasty Commands
This section covers the following cmdlets for managing Dynasties.
- New-Dynasty: creates a new Dynasty.
- Set-Dynasty: modifies a Dynasty or its children.
See Also
Set-Dynasty
The Set-Dynasty commandlet lets you to modify a Dynasty or its children in Directory.
GroupID maintains a history for this commandlet, which you can view against the History node in the left panel.
Syntax
Set-Dynasty
-Identity <string>
[-GroupBy <string[]>]
[-AliasTemplate <string>]
[-DisplayNameTemplate <string>]
[-InheritanceBehaviour
{InheritSelectedAttributeOnCreation |
AlwaysInheritSelectedAttributes |
NeverInheritSelectedAttributes}]
[-TopManager <string>]
[-ChildContainer <string[]>]
[-ExcludeNestedLists <string>]
[-CreateFlatManagerialList <string>]
[-IncludeManagerAsMember <string>]
[-Filters <string[]>]
[-Separator <string[]>]
[-SearchContainers <string[]>]
[-SearchContainersScopeList <string[]>]
[-ObjectTypes <string[]>]
[-LdapFilter <string>]
[-IncludeRecipients <string[]>]
[-ExcludeRecipients <string[]>]
[-Storage <string>]
[-DataSourceType <string>]
[-SystemDSN <string>]
[-TableOrView <string>]
[-DataSourceUserName <string>]
[-DataSourcePassword <string>]
[-FilePath <string>]
[-Server <string>]
[-Port <int>]
[-LDAPSearchContainer <string>]
[-DataSourceName <string>]
[-DataSourceQuery <string>]
[-WindowsAuthentication]
[-EnableUpdate <string>]
[-IsPasswordExpirySmartDL]
[-ExpirationRange <int>]
[-DomainExpiration <int>]
[-MaximumPasswordAge <int>]
[-MinimumPasswordAge <int>]
[-IncludeDisabledUsers <string>]
[-IncludePasswordNeverExpireUsers <string>]
[-SendEmail <string>]
[-EmailTemplatePath <string>]
[-Script <string>]
[-ScriptFilePath <string>]
[-Provider_Container <string>]
[-PowerTools <ArrayList>]
[-KeyMapAD <string>]
[-KeyMapDB <string>]
[-ExtendGroupLife]
[-ExpirationPolicy <int>]
[-MsExchCoManagedByLink <string[]>]
[-IsExpired <string>]
[-GroupScope <string>]
[-Type <string>]
[-Prefix <string>]
[-SecurityType <string>]
[-ManagedBy <string[]>]
[-MaxSendSize <int>]
[-AcceptMessagesOnlyFrom <string[]>]
[-RejectMessagesFrom <string[]>]
[-AcceptMessagesOnlyFromGroups <string[]>]
[-RejectMessagesFromGroup <string[]>]
[-AdditionalOwners <string[]>]
[-NotifyOptOutAdditionalOwners <string[]>]
[-ExpansionServer <string>]
[-BypassOwnersPolicy <string>]
[-MsExchRequireAuthToSendTo <string>]
[-HiddenFromAddressListEnabled <string>]
[-SendOofMessageToOriginatorEnabled <string>]
[-HideMembershipFromAddressListEnabled <string>]
[-ReportToManagerEnabled <string>]
[-ReportToOriginatorEnabled <string>]
[-UpdateMembershipByManagerEnabled <string>]
[-Add <hashtable[]>]
[-Remove <hashtable[]>]
[-Replace <hashtable[]>]
[-Clear <string[]>]
[-Department <string>]
[-Company <string>]
[-Assistant <string>]
[-HomePage <string>]
[-Alias <string>]
[-EmailAddress <string>]
[-Description <string>]
[-Notes <string>]
[-AdministrativeNotes <string>]
[-DisplayName <string>]
[-SimpleDisplayName <string>]
[-CustomAttribute1 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute2 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute3 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute4 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute5 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute6 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute7 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute8 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute9 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute10 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute11 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute12 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute13 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute14 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute15 <string>]
[-Delimiter <string>]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- Identity
Example 1:
The following command modifies the Departmental Dynasty by changing the Group-by attributes list using the credentials of current user logged-on to the identity store.
Set-Dynasty -Identity "CN=DepartmentalOU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -GroupBy "Department","Company","Title"
Example 2:
The command below modifies the Top Manager of a Managerial Dynasty, changes the alias name and display name templates for the Dynasty children, sets the scope to search Dynasty children in the containers specified in the Add parameter excluding sub-containers using the credentials set in the $Credentials environment variable. See the Set the $Credentials Environment Variable topic for setting credentials in an environment variable.
Set-Dynasty -Identity "CN=Managerial,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -TopManager "CN=Administrator,CN=Users,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -Add @{ SearchContainers="OU=Recruiting,OU=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US#1","OU=Outsourcing,OU=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US#1"}-ExcludeNestedLists False -ChildContainer "" -AliasTemplate "%Manager% -DirectReports" -DisplayNameTemplate "Direct reports of %Manager%" -Credential $Cred
Example 3:
The following command modifies the search criteria for the Managerial Dynasty to retrieve all mail-enabled objects who are the member of the Training group.
Set-Dynasty -Identity "CN=Managerial,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -ObjectTypes "ExchangeUsers","ExternalUsers","ExternalContacts","EmailGroups" -LdapFilter "(MemberOf=Training)"
Example 4:
The following command adds three group-by levels to an Organizational Dynasty.
Set-Dynasty -Identity "CN=Organizational,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -Add @{GroupBy="Company#OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US#Left 3#-","Department#OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US#Right 5#-","OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US#With %GROUPBY%\*#^"}
Example 5:
The following command modifies additional owners, Includes and Excludes lists and replaces Search Scope of a Managerial Dynasty.
Set- Dynasty -Identity "CN=Managerial,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -Add @{AdditionalOwners="CN=Roger Manson,OU=Recruiting,OU=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US","Robin Soto"; Includes="USWing","PKWing"; Excludes="UAEWing"} -Replace @{SearchContainers="OU=Recruiting,OU=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US#1","OU=Outsourcing,OU=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US#1"}
Example 6:
The following command clears the groups specified in the Includes list of a Managerial Dynasty.
Set-Dynasty -Identity "CN=Managerial,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -Clear "Includes"
See Also
Get-Computer
The Get-Computer commandlet retrieves the information about a computer object from the connected identity store. The computer can be a domain controller or an exchange server or just a simple client connected to the domain.
Syntax
Get-Computer
[-Identity <string>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- None
Example 1:
This example retrieves a computer with a name arsalanahmadsvm.
Get-computer -Identity arslanahmadsvm
See Also
Get-ConnectedStoreInformation
The Get-ConnectedStoreInformation commandlet retrieves information about the identity store connected to the current instance of the Management Shell.
Syntax
Get-ConnectedStoreInformation
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- None
Example 1:
The example displays name of the connected identity store, the last replication time to Elasticsearch, and messaging servers configured in the connected identity store.
Get-ConnectedStoreInformation
See Also
Get-ConnectedUser
The Get-ConnectedUser commandlet retrieves the general information about the user connected to the current instance of Management Shell.
Syntax
Get-ConnectedUser
[-IdentityStoreId <Int32>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <PSCredential>]
[-WarningAction <ActionPreference>]
[-InformationAction <ActionPreference>]
[-WarningVariable <String>]
[-InformationVariable <String>]
[-PipelineVariable <String>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- None
Example 1:
The example displays the logon name of the connected user, account locked information, identity store name, role name(s), and ObjectGuid.
Get-ConnectedUser
See Also
Get-GroupIdInformation
The Get-GroupIdInformation commandlet retrieves general information about GroupID.
Syntax
Get-GroupIdInformation
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- None
Example 1:
This example displays the name of the database and name of the SQL server being used by GroupID, GroupID version and the installation path of GroupID.
Get-GroupIdInformation
See Also
Get-ImanamiCommand
Use the Get-ImanamiCommand cmdlet to retrieve basic information about GroupID Management Shell commandlets and command elements.
Syntax
Get-ImanamiCommand
[-Name <string[]>]
[-Verb <string>]
[-Noun <string>]
[-AttributesToLoad <string[]>]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- None
Example 1:
The following command shows information about all commandlets.
Get-ImanamiCommand
Example 2:
The following command gets all commandlets and command elements with the word Set in their name.
Get-ImanamiCommand -Name Set*
Example 3:
The following command gets all commandlets and command elements with the letter Y anywhere in the verb of their name.
Get-ImanamiCommand -Verb *Y*
See Also
Get-ReplicationStatus
The Get-ReplicationStatus commandlet retrieves the replication status of the connected identity store. The commandlet provides replication status of each object (such as users, groups, contact, computer, public folders and OUs) in the provider.
Syntax
Get-ReplicationStatus
[-IdentityStoreName] <string>
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- IdentityStoreName
Example 1:
The following commandlet provides date and time information when the objects of an identity store are replicated to Elasticsearch and the time elapsed since last replication.
Get-ReplicationStatus -IdentityStoreName AdStore8
See Also
Get-TombStoneObject
When you delete an object from Directory, the object is not physically removed from the database. Instead, Directory marks the object as deleted, strips most of the properties from the object and moves it to a special container. The object becomes invisible to normal directory operations and is referred to as a tombstone object.
The Get-TomStoneObject commandlet let you view the information of these tombstone objects.
Syntax
Get-TombstoneObject
[[-Identity] <string[]>]
[-SearchContainer <string[]>]
[-SearchContainersScopeList <string>]
[-ShouldReturnCollection]
[-MaxItemsToDisplay <int>]
[-ObjectType <string[]>]
[-LdapFilter <string>]
[-SmartFilter <string>]
[-ServerFilter <string>]
[-AttributesToLoad <string[]>]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- None
Example 1:
The following command retrieves all tombstone objects from Directory, using the credentials of current user logged-on to the identity store.
Get-TombStoneObject
Example 2:
The following command retrieves the tombstone group Event Management, using the credentials set in the $Credentials environment variable. For information about setting credentials, see Appendix A.
Get-TombStoneObject -identity "Event Management" -Credential $Cred
Example 3:
The following command retrieves all tombstone objects with display names starting with the letter S.
Get-TombStoneObject -LdapFilter "(CN = S*)"
See Also
Invoke-Replication
The Invoke-Replication commandlet starts replication process for all the identity stores or a specific identity store.
Syntax
Invoke-Replication
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-DeletedObjects]
[-RestoreReplication]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- None
Example 1:
The following command replicate identity store with ID 1.
Invoke-Replication -IdentitystoreId 1
Example 2:
The following command replicate deleted objects for identity store with ID 1.
Invoke-Replication -IdentitystoreId 1 -DeletedObjects
Example 3:
The following command will start restoration of replication for identity store with ID 1.
Invoke-Replication -IdentitystoreId 1 -RestoreReplication
See Also
New-Container
The New-Container commandlet creates a new organizational unit in Directory. You can also use it to create nested organizational units by repeatedly executing the commandlet and changing the value of the ParentContainer parameter.
Syntax
New-Container
-ContainerName <string[]>
-OrganizationalUnit <string>
[-AccidentalDeletion]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameters
- ContainerName
- OrganizationalUnit
Example 1:
The following command creates the organizational unit Recruiting at the root level in Directory, using the credentials of current user logged-on to the identity store.
New-Container -OrganizationalUnit "DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -ContainerName "Recruiting"
Example 2:
The following command creates the organizational unit Local Recruiting inside the Recruiting container in Directory using the credentials set in the $Credentials environment variable. See the Set the $Credentials Environment Variable topic for setting credentials.
New-Container - OrganizationalUnit "OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -ContainerName "Local Recruiting" -Credential $Cred
See Also
General Commands
You can use the following Management Shell cmdlets to perform tasks such as:
- Get-Computer: provides information about a computer object.
- Get-ConnectedStoreInformation: provides information about the connected identity store.
- Get-ConnectedUser: provides information about the connected user.
- Get-GroupIdInformation: provides information about GroupID.
- Get-ImanamiCommand: provides basic information about GroupID Management Shell cmdlets.
- Get-ReplicationStatus: provides the replication status of objects in an identity store.
- Get-TombStoneObject: displays information about tombstone objects.
- Invoke-Replication: starts the replication process for all the identity stores or for a specific identity store.
- New-Container: creates a new organizational unit.
- Remove-Container: removes an empty organizational unit.
- Restore-TombStoneObject: restores tombstone objects from the directory.
- Send-Notification: sends notifications to a group or a user.
See Also
Remove-Container
Use the Remove-Container commandlet to delete organizational units from Directory. The commandlet only supports deletion of containers at leaf level, having no objects. If the container contains objects or sub-containers, the commandlet does not process the request and throws an exception.
Syntax
Remove-Container
-Identity <string>
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- Identity
Example 1:
The following command removes the Miscellaneous container, using the credentials of current user logged-on to the identity store.
Remove-Container -identity "OU=Miscellaneous,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US"
Example 2:
The following command first shows the changes that result from executing the command. The command uses the credentials set in the $Credentials environment variable to perform the deletion. See the Set the $Credentials Environment Variable topic for setting credentials in the environment variable.
Remove-Container -identity "OU=Miscellaneous,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -Credential $Cred
See Also
Restore-TombStoneObject
The Restore-TombStoneObject commandlet restores tombstone objects from Directory. A tombstone object is restored as an unmanaged group with all supported attributes to its original container. If the parent container has been deleted, the commandlet also reinstates the container for the group.
Syntax
Restore-TombstoneObject
[-Identity] <string>
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- None
Example:
The following command restores the tombstone group Event Management, using the credentials set in the $Creds environment variable. See the Set the $Credentials Environment Variable topic for setting credentials in an environment variable.
Restore-TombStoneObject -identity "Event Management" -Credential $Cred
See Also
Send-Notification
Use the Send-Notification commandlet to send notifications to a group or a user. GroupID modules automatically generate e-mail notifications upon the occurrence of certain events; for example, expiry of groups, execution of a job, and generation of workflow requests. The modules use template files for generating the contents of the notification e-mails. These template files are located at:
X:\Program Files\Imanami\GroupID 8.0\Automate\Templates\Notifications
Where X is the drive where the GroupID installation directory resides.
The Send-Notification commandlet also requires a template file for generating an e-mail notification. You can utilize one from the available templates or create your own. The commandlet also requires an SMTP server and a From e-mail address that you can configure using the Set-Options commandlet.
Syntax
Send-Notification
-Identity <string>
-Subject <string>
-TemplateFile <string>
[-InlineImageFile <string>]
[-QueueEmail]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameters
- Identity
- Subject
- TemplateFile
Example 1:
The following commands first configure the SMTP Server, then set a From e-mail address, and finally send a group expiry notification to UserA using the credentials of current user logged-on to the identity store.
Set-Options -SmtpServer "HR.Imanami.US"
Set-Options -FromAddress "Administrator@HR.Imanami.US"
Send-Notification -Identity "CN=UserA,CN=Users,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -Subject "Expiry Notification" -TemplateFile "C:\Program Files\Imanami\GroupID
8.0\Automate\Templates\Notifications\ExpiringTemplate.html" -QueueEmail
Example 2:
The following command sends a notification to the New Arrivals group. It uses a custom template with an in-line image and uses the credentials of the user set in the $Credentials environment variable. See the Set the $Credentials Environment Variable topic for setting credentials in an environment variable.
Send-Notification -Identity "CN=New Arrivals,CN=Users,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -Subject "Welcome to Imanami" -TemplateFile "C:\Welcome.html" -InlineImageFile "C:\WelcomeNote.jpg" -QueueEmail
See Also
Convert-Group
The Convert-Group commandlet converts an unmanaged group to a Smart Group.
GroupID Management Shell prompts for the identity of the unmanaged group you want to convert into a Smart Group. After executing, the commandlet displays the status that update is successful as shown in the following snapshot:
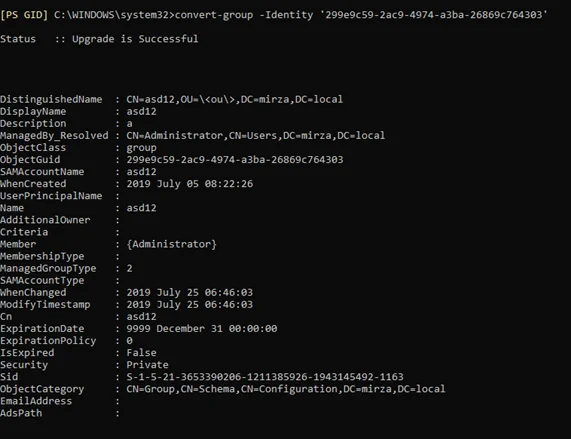
The converted Smart Group will not have an LDAP query attached to it. You have to define it manually.
Syntax
Convert-Group
-Identity <string>
[-SearchContainers <string[]>]
[-SearchContainersScopeList <string[]>]
[-ObjectTypes <string[]>]
[-LdapFilter <string>]
[-IncludeRecipients <string[]>]
[-ExcludeRecipients <string[]>]
[-Storage <string>]
[-DataSourceType <string>]
[-SystemDSN <string>]
[-TableOrView <string>]
[-DataSourceUserName <string>]
[-DataSourcePassword <string>]
[-FilePath <string>]
[-Server <string>]
[-Port <int>]
[-LDAPSearchContainer <string>]
[-DataSourceName <string>]
[-DataSourceQuery <string>]
[-WindowsAuthentication]
[-EnableUpdate <string>]
[-IsPasswordExpirySmartDL]
[-ExpirationRange <int>]
[-DomainExpiration <int>]
[-MaximumPasswordAge <int>]
[-MinimumPasswordAge <int>]
[-IncludeDisabledUsers <string>]
[-IncludePasswordNeverExpireUsers <string>]
[-SendEmail <string>]
[-EmailTemplatePath <string>] [-Script <string>]
[-ScriptFilePath <string>]
[-Provider_Container <string>]
[-PowerTools <ArrayList>]
[-KeyMapAD <string>]
[-KeyMapDB <string>]
[-ExtendGroupLife]
[-ExpirationPolicy <int>]
[-MsExchCoManagedByLink <string[]>]
[-IsExpired <string>]
[-GroupScope <string>]
[-Type <string>]
[-Prefix <string>]
[-SecurityType <string>]
[-ManagedBy <string[]>]
[-MaxSendSize <int>]
[-AcceptMessagesOnlyFrom <string[]>]
[-RejectMessagesFrom <string[]>]
[-AcceptMessagesOnlyFromGroups <string[]>]
[-RejectMessagesFromGroup <string[]>]
[-AdditionalOwners <string[]>]
[-NotifyOptOutAdditionalOwners <string[]>]
[-ExpansionServer <string>]
[-BypassOwnersPolicy <string>]
[-MsExchRequireAuthToSendTo <string>]
[-HiddenFromAddressListEnabled <string>]
[-SendOofMessageToOriginatorEnabled <string>]
[-HideMembershipFromAddressListEnabled <string>]
[-ReportToManagerEnabled <string>]
[-ReportToOriginatorEnabled <string>]
[-UpdateMembershipByManagerEnabled <string>]
[-Add <hashtable[]>]
[-Remove <hashtable[]>]
[-Replace <hashtable[]>]
[-Clear <string[]>]
[-Department <string>]
[-Company <string>]
[-Assistant <string>]
[-HomePage <string>]
[-Alias <string>]
[-EmailAddress <string>]
[-Description <string>]
[-Notes <string>]
[-AdministrativeNotes <string>]
[-DisplayName <string>]
[-SimpleDisplayName <string>]
[-CustomAttribute1 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute2 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute3 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute4 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute5 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute6 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute7 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute8 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute9 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute10 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute11 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute12 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute13 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute14 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute15 <string>]
[-Delimiter <string>]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- Identity
Example:
The following commandlet converts a group Clay2 group to a Smart Group using the credentials of current logged-on user.
Convert-Group -Identity "Clay2" -Credential $Cred
See Also
Get-Group
This Get-Group commandlet retrieves both managed and unmanaged groups that are in one or more containers in the identity store matching the given criteria.
Syntax
Get-Group
[[-Identity] <string[]>]
[-SearchContainer <string[]>]
[-SearchContainersScopeList <string>]
[-ShouldReturnCollection]
[-MaxItemsToDisplay <int>]
[-ObjectType <string[]>]
[-LdapFilter <string>]
[-SmartFilter <string>]
[-ServerFilter <string>]
[-AttributesToLoad <string[]>]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- None
Example 1:
The following command retrieves all groups in the base container specified by the SearchContainer parameter including its sub-containers, using the credentials of logged-in user.
Get-Group -SearchContainer "OU=Recuriting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US"
Example 2:
The following command retrieves all groups with a display name beginning with S in the base containers specified by the SearchContainer parameter including sub-containers of the first base container and excluding sub-containers of the second one using the credentials set in the $Credentials environment variable. See the Set the $Credentials Environment Variable topic for setting credentials in an environment variable.
Get-Group -SearchContainer "OU=Recuriting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US","OU=OutSourcing,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -SearchContainersScopeList "2","1" -LdapFilter "(DisplayName = S*)" -Credential $Cred
Example 3:
The following command retrieves all Smart Groups from the connected identity store with Security Type Private and John Smith as their additional owner. The OUT-NULL commandlet is useful for preventing the retrieved groups' information from appearing on the console.
Get-Group -SmartFilter "(SecurityType = Private)" | Set-Group -AdditionalOwners "CN=JohnSmith,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" | OUT-NULL
See Also
Move-Group
The Move-Group commandlet enables you to move a group to a different container in the same domain or in a different domain within the same forest. Movement of groups across forests is not allowed.
You can view events related to this commandlet in GroupID portal, against the History node in the left panel.
Syntax
Move-Group
-Identity <string>
-DestinationContainer <string>
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameters
- Identity
- DestinationContainer
Example 1:
The following command moves the group Training to the Local Recruiting organizational unit using the credentials of current user logged-on to the identity store.
Move-Group -Identity "CN=Training,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -DestinationContainer "OU=Local Recruiting,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US"
Example 2:
The following command moves the group Training to the OffShore Recruiting organizational unit. The command uses the credentials set in the $Credentials environment variable for moving a group. See the Set the $Credentials Environment Variable topic for setting credentials in an environment variable.
Move-Group -Identity "CN=Training,OU=Local Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -DestinationContainer "OU=OffShore Recruiting,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -Credential $Cred
See Also
New-Group
Use the New-Group commandlet to create a new unmanaged group in a particular container in directory.
You can view events related to this commandlet in GroupID portal, against the History node in the left panel.
Syntax
New-Group
-SamAccountName <string>
-Name <string>
-OrganizationalUnit <string>
-GroupScope <string>
-Type <string>
-SecurityType <string>
[-GroupAlias <string>]
[-ManagedBy <string[]>]
[-DisplayName <string>]
[-MailEnabled <string>]
[-Description <string>]
[-AdditionalOwners <string[]>]
[-NotifyOptOutAdditionalOwners <string[]>]
[-Members <string[]>]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameters
- SamAccountName
- Name
- OrganizationalUnit
- GroupScope
- Type
- SecurityType
Example 1:
The following command creates a new unmanaged, mail-disabled, global, distribution group in the container specified by the OrganizationalUnit parameter, using the credentials of current user logged-on to the identity store.
New-Group -Name "Event Management" -OrganizationalUnit "OU=Local Recruiting,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -GroupAlias "EventManagement" -SamAccountName "Event Management" -GroupScope "Global Group" -Type "Distribution"
Example 2:
The command below creates a new mail-enabled, domain-local, semi-private, security group in the container specified by the OrganizationalUnit parameter, using the credentials set in the $Credentials environment variable. See the Set the $Credentials Environment Variable topic for setting credentials in an environment variable.
New-Group -Name "Enrollment" -OrganizationalUnit "OU=Local Recruiting,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -GroupAlias "Enrollment" -MailEnable True -SamAccountName "Enrollment" -GroupScope "Domain Local" -Type "Security" -SecurityType "Semi_Private"
See Also
Group Commands
This section covers cmdlets for performing tasks related to managed and unmanaged groups.
- Convert-Group: converts an unmanaged group to a Smart Group.
- Expire-Group: expires a group temporarily.
- Get-Group: retrieves groups from one or more containers.
- Move-Group: moves a group to a different container in the same domain or in a different domain.
- New-Group: creates an unmanaged group.
- Remove-Group: deletes a managed group, unmanaged group, or Dynasty in the directory.
- Renew-Group: reactivates an expired group.
- Set-Group: modifies an unmanaged group in the directory.
See Also
Remove-Group
Use this commandlet to delete a group (managed or unmanaged) or Dynasty in directory. Removing a parent Dynasty using this commandlet removes all its children as well.
You can view events related to this commandlet in GroupID portal, against the History node in the left panel.
Syntax
Remove-Group
-Identity <string[]>
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- Identity
Example 1:
The following command removes the Event Management group, using the credentials of current user logged-on to the identity store.
Remove-Group -identity "OU=Event Management,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US"
Example 2:
The following command first shows the changes that will be made by executing the command (a deletion). The command uses the credentials set in the $Credentials environment variable to perform the deletion. See the Set the $Credentials Environment Variable topic for setting credentials in an environment variable.
Remove-Group -identity "OU=Event Management,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -Credential $Cred
See Also
Renew-Group
The Renew-Group re-activates an expired group.
You can view events related to this commandlet in GroupID portal, against the History node in the left panel.
Syntax
Renew-Group
-Identity <string[]>
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- Identity
Example:
The following command renews the specified group in the connected identity store.
Renew-Group -Identity "CN=Training,OU=Local Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US"
See Also
Set-Group
The Set-Group commandlet modifies an unmanaged group in directory. However, you can use this commandlet to modify those parameters of a Smart Group that are native attributes of an unmanaged group in Directory. For modifying Smart Group-specific attributes, you can use the Set-SmartGroup commandlet.
You can view events related to this commandlet in GroupID portal, against the History node in the left panel.
Syntax
Set-Group
-Identity <string>
[-ExtendGroupLife]
[-ExpirationPolicy <int>]
[-MsExchCoManagedByLink <string[]>]
[-IsExpired <string>]
[-GroupScope <string>]
[-Type <string>]
[-Prefix <string>]
[-SecurityType <string>]
[-ManagedBy <string[]>]
[-MaxSendSize <int>]
[-AcceptMessagesOnlyFrom <string[]>]
[-RejectMessagesFrom <string[]>]
[-AcceptMessagesOnlyFromGroups <string[]>]
[-RejectMessagesFromGroup <string[]>]
[-AdditionalOwners <string[]>]
[-NotifyOptOutAdditionalOwners <string[]>]
[-ExpansionServer <string>]
[-BypassOwnersPolicy <string>]
[-MsExchRequireAuthToSendTo <string>]
[-HiddenFromAddressListEnabled <string>]
[-SendOofMessageToOriginatorEnabled <string>]
[-HideMembershipFromAddressListEnabled <string>]
[-ReportToManagerEnabled <string>]
[-ReportToOriginatorEnabled <string>]
[-UpdateMembershipByManagerEnabled <string>]
[-Add <hashtable[]>]
[-Remove <hashtable[]>]
[-Replace <hashtable[]>]
[-Clear <string[]>]
[-Department <string>]
[-Company <string>]
[-Assistant <string>]
[-HomePage <string>]
[-Alias <string>]
[-EmailAddress <string>]
[-Description <string>]
[-Notes <string>]
[-AdministrativeNotes <string>]
[-DisplayName <string>]
[-SimpleDisplayName <string>]
[-CustomAttribute1 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute2 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute3 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute4 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute5 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute6 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute7 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute8 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute9 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute10 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute11 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute12 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute13 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute14 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute15 <string>]
[-Delimiter <string>]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- Identity
Example 1:
The following command changes the expiration policy of the Training group to 60 days and assigns a manager to the group, using the credentials of current user logged-on to the identity store.
Set-Group -Identity "CN=Training,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -ExpirationPolicy "60" -ExtendGroupLife -ManagedBy "CN=John Smith,CN=Users,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US"
Example 2:
The following command expires the group Training, using the credentials set in the $Credentials environment variable. See the Set the $Credentials Environment Variable topic for setting credentials in an environment variable.
Set-Group -Identity "CN=Training,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -IsExpired True -Credential $Cred
Example 3:
The following command gets all groups in the container Recruiting, clears their additional owner lists and sets their expiration policy to Never Expire. The OUT-NULL commandlet has been used to prevent the retrieved groups information from appearing on the console.
Get-Group -searchcontainer "OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" | Set-Group -AdditionalOwners "" -ExpirationPolicy "0" -ExtendGroupLife | OUT-NULL
Example 4:
The following command removes two additional owners from the Training group and adds three new additional owners to the group and excludes an additional owner from receiving e-mail notifications.
Set-Group -Identity "CN=Training,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -Remove @{AdditionalOwners = "CN=Roger_Manson,OU=ResignedStaff,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US","KillenEdward"} -Add @{AdditionalOwners = "RobinSoto","MeganFox","DollyChan"} -NotifyOptOutAdditionalOwners "RobinSoto"
See Also
Get-Mailbox
Use the Get-Mailbox commandlet to retrieve basic information about a mailbox that match your given criteria.
Syntax
Get-MailBox
[[-Identity] <string[]>]
[-SearchContainer <string[]>]
[-SearchContainersScopeList <string>]
[-MailBoxStore <string>]
[-ShouldReturnCollection]
[-MaxItemsToDisplay <int>]
[-ObjectType <string[]>]
[-LdapFilter <string>]
[-SmartFilter <string>]
[-ServerFilter <string>]
[-AttributesToLoad <string[]>]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- None
Example:
The following command retrieves the specified mailbox from the connected identity store.
Get-MailBox -Identity "OsamaMailBox"
See Also
New-Mailbox
Use the New-Mailbox commandlet to create a new mailbox in Directory. Most mailbox properties can be directly added by using the parameters of this commandlet.
Syntax
New-MailBox
-MailBoxStore <string>
-Alias <string>
-Name <string>
-OrganizationalUnit <string>
-SAMAccountName <string>
-Password <string>
-FirstName <string>
-LastName <string>
-DisplayName <string>
[-UPNSuffix <string>]
[-Title <string>]
[-City <string>]
[-State <string>]
[-Zip <string>]
[-Country <string>]
[-Initials <string>]
[-Address <string>]
[-Office <string>]
[-Business <string>]
[-Business2 <string>]
[-EmailAddress <string>]
[-Department <string>]
[-Company <string>]
[-Mobile <string>]
[-Home <string>]
[-AccountDisabled <string>]
[-PasswordNeverExpires <string>]
[-PasswordForceChange <string>]
[-Manager <string[]>]
[-HomePage <string>]
[-Assistant <string>]
[-Notes <string>]
[-MailEnabled <string>]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameters
- MailBoxStore
- Alias
- Name
- OrganizationalUnit
- SAMAccountName
- Password
- FirstName
- LastName
- DisplayName
Example:
The following command creates a new mailbox in the container specified by the OrganizationalUnit parameter of specified mailbox store. The command also specifies the logon name, password, first name, last name and display name of the new mailbox.
New-MailBox -MailBoxStore "OsamaMailBoxDb120435" -Name "OsamaMailBox" -OrganizationalUnit "OU=osamamu,DC=naveed,DC=local" -SAMAccountName "OsamaMailBoxUser" -Password "webdir123R" -FirstName "OsamaMailBox" -LastName "MailBoxuser" -DisplayName "OsamaMailBox" -Alias "OsamaMailBox
See Also
Mailbox Commands
This section covers cmdlets for performing mailbox-specific tasks such as:
- Get-Mailbox: retrieves a mailbox.
- New-Mailbox: creates a new mailbox.
- Remove-Mailbox: deletes a mailbox.
- Set-Mailbox: modifies a mailbox.
See Also
Remove-Mailbox
Use the Remove-Mailbox commandlet to delete mailbox from the connected identifty store.
Syntax
Remove-MailBox
-Identity <string[]>
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameters
- Identity
Example:
The following command deletes the specified mailbox from the connected identity store.
Remove-MailBox -Identity "OsamaMailBox"
See Also
Set-Mailbox
The Set-Mailbox commandlet modifies a mailbox in Directory. Most mailbox properties can be directly modified by using the parameters of this commandlet.
Syntax
Set-MailBox
-Identity <string>
[-FirstName <string>]
[-LastName <string>]
[-Title <string>]
[-City <string>]
[-State <string>]
[-Zip <string>]
[-Country <string>]
[-Initials <string>]
[-Address <string>]
[-Office <string>]
[-Business <string>]
[-Add <hashtable[]>]
[-Remove <hashtable[]>]
[-Replace <hashtable[]>]
[-Clear <string[]>]
[-Department <string>]
[-Company <string>]
[-Assistant <string>]
[-HomePage <string>]
[-Alias <string>]
[-EmailAddress <string>]
[-Description <string>]
[-Notes <string>]
[-AdministrativeNotes <string>]
[-DisplayName <string>]
[-SimpleDisplayName <string>]
[-CustomAttribute1 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute2 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute3 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute4 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute5 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute6 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute7 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute8 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute9 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute10 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute11 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute12 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute13 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute14 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute15 <string>]
[-Delimiter <string>]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- Identity
Example:
The following commandlet modifies the country value of the specified mailbox in the connected identity store.
Set-MailBox -Identity "OsamaMailBox" -Country "Pakistan"
See Also
Disable-DistributionGroup
Use this commandlet to disable the mailing capabilities for a distribution group in Directory.
GroupID maintains a history for this commandlet, which you can view in GroupID Management Console using the History tab of the object's properties dialog box.
Syntax
Disable-DistributionGroup
-Identity <string>
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- Identity
Example:
The following command mail-disables a distribution group specified by the Identity parameter, using the credentials of current user logged-on to the identity store.
Disable-DistributionGroup -Identity "CN=Smart_Training,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US"
See Also
Enable-DistributionGroup
This commandlet makes a distribution group in directory mail-enabled.
GroupID maintains a history for this commandlet, which you can view in GroupID portal, against the History node in the left panel.
Syntax
Enable-DistributionGroup
-Identity <string>
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- Identity
Example:
The following command mail-enables a distribution group specified by the Identity parameter, using the credentials of current user logged-on to the identity store.
Enable-DistributionGroup -Identity "CN=Smart_Training,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US"
See Also
Mail-Enable/Disable Groups Commands
This section covers cmdlets for enabling and disabling groups for email.
- Disable-DistributionGroup: disables a group's email capability.
- Enable-DistributionGroup: enable a group's email capability.
See Also
Add-GroupMember
The Add-GroupMember commandlet helps you to add one or more objects to the membership of a group in Directory. Two types of membership can exist in GroupID.
- Perpetual membership
- Temporary membership
Modifying the membership of a Smart Group or Dynasty using this commandlet is not recommended, since your changes will be discarded the next time the group is updated.
GroupID maintains a history for this commandlet, which you can view in GroupID portal, against the History node in the left panel.
Syntax
Add-GroupMember
-GroupIdentity <string>
-Identity <string>
[-Type <string>]
[-StartDate <datetime>]
[-EndDate <datetime>]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameters
- GroupIdentity
- Identity
Example 1:
The following command adds the user Brian Regan to the membership of the Event Management group using the credentials set in the $Credentials environment variable. See the Set the $Credentials Environment Variable topic for setting credentials in an environment variable.
Add-GroupMember -GroupIdentity "CN=Event Management,OU=Local Recruiting,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -Identity "CN=BrianRegan,CN=User,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -Credential $Cred
Example 2:
The following command gets all users from the Local Recruiting container and adds them to the membership of the Event Management group. For detailed information about the Get-Object commandlet, see Get-Object. The OUT-NULL commandlet is used here to restrict the retrieved users information from appearing on the console.
Get-Object -SearchContainer "OU=Local Recruiting,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -ObjectType "User" | Add-GroupMember -GroupIdentity "CN=Event Management,OU=Local Recruiting,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US"
See Also
Get-GroupMember
Use this commandlet to retrieve members of a particular group from directory. You can apply filters to the results returned by the commandlet.
Syntax
Get-GroupMember
[-Identity] <string>
[[-LdapFilter] <string>]
[-AttributesToLoad <string[]>]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- None
Example 1:
The following command retrieves all members of the Password_Expiry group using the credentials set in the $Credentials environment variable. See the Set the $Credentials Environment Variable topic for setting credentials in an environment variable.
Get-GroupMember -Identity "CN=Password_Expiry,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -Credential $Cred
Example 2:
The command below retrieves all members from the Enrollment group display name of which starts with the character S using the credentials of current user logged-on to the identity store.
Get-GroupMember -Identity "CN=Enrollment,OU=Local Recruiting,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -LdapFilter "(displayname=S*)"
See Also
Get-Object
Use this commandlet to retrieve objects from one or more containers in a domain that match the given criteria.
Syntax
Get-Object
[[-Identity] <string[]>]
[-ShouldReturnCollection]
[-MaxItemsToDisplay <int>]
[-ObjectType <string[]>]
[-SearchContainer <string[]>]
[-SearchContainersScopeList <string>]
[-LdapFilter <string>]
[-SmartFilter <string>]
[-ServerFilter <string>]
[-AttributesToLoad <string[]>]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- None
Example 1:
The following command retrieves all objects from the domain you are connected to.
Get-Object
Example 2:
The command below retrieves the object Event Management starting from the container Recruiting excluding its sub-containers using the credentials set in the $Credentials environment variable. See the Set the $Credentials Environment Variable topic for setting credentials in an environment variable.
Get-Object -Identity "HR.Imanami.US\Event Management" -SearchContainer "OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -SearchContainersScopeList "1" -Credential $Cred
Example 3:
The following command searches all objects in the specified containers including sub-containers with display names starting with the letter S .
Get-Object -SearchContainer "OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US","OU=OutSourcing,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -LdapFilter "(DisplayName = S*)"
See Also
Membership Commands
This section covers cmdlets for managing the memberships of both managed and unmanaged groups.
- Add-GroupMember: adds objects to the membership of a group.
- Get-GroupMember: retrieves members of a group.
- Get-Object: retrieves objects.
- Remove-GroupMember: removes recipients from a group's membership.
- Set-Object: modifies an object.
See Also
Remove-GroupMember
Use this commandlet to remove one or more members from a group membership.
GroupID maintains a history for this commandlet, which you can view in GroupID portal, against the History node in the left panel.
Syntax
Remove-GroupMember
-GroupIdentity <string>
-Identity <string>
[-Type <string>]
[-StartDate <datetime>]
[-EndDate <datetime>]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameters
- GroupIdentity
- Identity
Example:
The following command removes the user Brian Regan from the membership of the group Event Management using the credentials set in the $Credentials environment variable. See the Set the $Credentials Environment Variable topic for setting credentials in an environment variable.
Remove-GroupMember -GroupIdentity "CN=Event Management,OU=Local Recruiting,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -Identity "Brian Regan" -Credential $Cred
See Also
Set-Object
The Set-Object commandlet modifies any object such as a user, contact, group (managed or unmanaged), or mailbox in Directory.
Syntax
Set-Object
-Identity <String>
[-Department <String>]
[-Company <String>]
[-Assistant <String>]
[-HomePage <String>]
[-Alias <String>]
[-EmailAddress <String>]
[-Description <String>]
[-Notes <String>]
[-AdministrativeNotes <String>]
[-DisplayName <String>]
[-SimpleDisplayName <String>]
[-CustomAttribute1 <String>]
[-CustomAttribute2 <String>]
[-CustomAttribute3 <String>]
[-CustomAttribute4 <String>]
[-CustomAttribute5 <String>]
[-CustomAttribute6 <String>]
[-CustomAttribute7 <String>]
[-CustomAttribute8 <String>]
[-CustomAttribute9 <String>]
[-CustomAttribute10 <String>]
[-CustomAttribute11 <String>]
[-CustomAttribute12 <String>]
[-CustomAttribute13 <String>]
[-CustomAttribute14 <String>]
[-CustomAttribute15 <String>]
[-Delimiter <String>]
[-IdentityStoreId <Int32>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <PSCredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- Identity
Example 1:
The following example modifies description of a user specified user against the Identity parameter.
Set-object -identity "Sonia Iqbal" -Description TestUser
See Also
Get-Schedule
The commandlet Get-Schedule retrieves the scheduled jobs created in the identity store connected to the current instance of the Management Shell. By default, this cmdlet returns all the jobs available irrespective of the following:
- whether the identity store with which they belong is enabled.
- whether the jobs are enabled.
This commandlet can also filter the job list if provided with the filtration parameters such as JobType, TriggerType or HavingNotifications. It also accepts a MatchingCriteria parameter that determines whether the criteria are to be joined on the AND basis or OR basis.
Syntax
Get-Schedule [-ScheduleNames <String[]>]
[-IdentityStoreNames <String[]>]
[-JobTypes <JobType[]>]
[-TriggerTypes <TriggerType[]>]
[-HavingNotifications <Boolean>]
[-MatchingCriteria <JoiningOperator>]
[-PreventEnumeration]
[-IdentityStoreId <Int32>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-WarningAction <ActionPreference>]
[-InformationAction <ActionPreference>]
[-WarningVariable <String>]
[-InformationVariable <String>]
[-PipelineVariable <String>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- None
Example 1:
This example retrieves all the scheduled jobs created in the connected identity store.
Get-Schedule
Example 2:
This example retrieves those Group Usage Service – GUS job(s) that have monthly trigger and MatchingCriteria on the And basis.
Get-Schedule -JobType GUS -TriggerType RunMonthly -MatchingCriteria And
Example 3:
This example retrieves the scheduled job with GUS1 name.
Get-Schedule -ScheduleName GUS1
Example 4:
This example retrieves the two scheduled jobs – GUS1 and GLM6 –through the pipeline operator.
'GUS1','GLM6' | Get-Schedule
See Also
Get-TargetSchedules
The commandlet Get-TargetSchedules retrieves the scheduled jobs of the given target (group/OU).
Syntax
Get-TargetSchedules
[-DistinguishedName] <String>
[-Enumerate]
[-IdentityStoreId <Int32>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-WarningAction <ActionPreference>]
[-InformationAction <ActionPreference>]
[-WarningVariable <String>]
[-InformationVariable <String>]
[-PipelineVariable <String>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- DistinguishedName
Example 1:
This example retrieves the schedules operating on an OU with distinguished name OU=WorkingOU,DC=pucit,DC=local.
Get-TargetSchedules -DistinguishedName ‘OU=WorkingOU,DC=pucit,DC=local’
Example 2:
This example retrieves the schedules operating on a group and an OU through the pipeline operator.
'OU=WorkingOU,DC=pucit,DC=local', 'CN=SGroup1,OU=ArslanAhmadOU,OU=WorkingOU,DC=pucit,DC=local' | Get-TargetSchedules
Example 3:
This example selects only the Names and Job Types of the schedules operating on the specified targets through the pipeline operator.
'OU=WorkingOU,DC=pucit,DC=local', 'CN=SGroup1,OU=ArslanAhmadOU,OU=WorkingOU,DC=pucit,DC=local' | Get-TargetSchedules | Select-Object -Property Name,JobType
See Also
Invoke-Schedule
The commandlet Invoke-Schedule executes the specified schedule job.
Syntax
Invoke-Schedule
[-ScheduleName <String>]
[-JobId <Int32>]
[-PassThru]
[-IdentityStoreId <Int32>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-WarningAction <ActionPreference>]
[-InformationAction <ActionPreference>]
[-WarningVariable <String>]
[-InformationVariable <String>]
[-PipelineVariable <String>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- None
Example 1:
This example executes a schedule with name starting smm4_.
Invoke-Schedule -ScheduleName smm4_
Example 2:
This example executes a schedule with GUS as Job Type.
Get-Schedule -JobType GUS | Select-Object -Property Name | Invoke-Schedule
Example 3:
This example executes all the GUS scheduled jobs with daily running trigger.
Get-Schedule -JobType GUS -TriggerType RunDaily -MatchingCriteria And | Select-Object -Property Name | Invoke-Schedule
See Also
New-Schedule
The commandlet New-Schedule creates a new schedule in the identity store connected to the current instance of Management Shell.
Syntax
New-Schedule
-ScheduleName <String>
-Targets <String[]>
-TargetType <SchedulingTargetType>
-IdentityStoreName <String>
-Credentials <PSCredential>
-JobType <JobType>
-TriggerType <TriggerType>
-StartTime <DateTime>
[-WeekDays <DaysOfTheWeek>]
[-YearMonths <MonthsOfTheYear>]
[-MonthDate <Int32>]
[-EnableNotifications]
[-Recepients <String[]>]
[-SendToOwners]
[-NotificationSendingCriteria <NotificationSendingCriteria>]
[-PassThru] [-IdentityStoreId <Int32>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-WarningAction <ActionPreference>]
[-InformationAction <ActionPreference>]
[-WarningVariable <String>]
[-InformationVariable <String>]
[-PipelineVariable <String>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameters
- ScheduleName
- Targets
- TargetType
- IdentityStoreName
- Credentials
- JobType
- TriggerType
- StartTime
Example 1:
This example creates a new schedule using minimum possible parameters. This example contains insecure password.
New-Schedule -ScheduleName SmuTest1 -IdentityStoreName AdStore8 -UserName user -Password password1 -Targets 'OU=ArslanAhmadOU,OU=WorkingOU,DC=pucit,DC=local', 'OU=ArslanAhmadOU,OU=WorkingOU,DC=pucit,DC=local' -JobType SmartGroup -TriggerType Daily -StartTime '16:56'
NOTE: This example uses insecure credentials.
Example 2:
This example creates a smart-group schedule triggering every 7th of every March, August and September.
New-Schedule -ScheduleName SmuTest2 -IdentityStoreName AdStore8 -Credentials $creds -Targets 'OU=ArslanAhmadOU,OU=WorkingOU,DC=pucit,DC=local' -JobType SmartGroup -TriggerType Monthly -StartTime '16:56' -YearMonths 'March','August','September' -MonthDate 7
To use secure credentials, first create them and save them to a variable named ‘creds’.
$creds = Get-Credential
Example 3:
This example creates a GUS job by providing a messaging system.
New-Schedule -ScheduleName GusTest1 -Targets 'OU=ArslanAhmadOU,OU=WorkingOU,DC=pucit,DC=local' -JobType GUS -Credentials $creds -TriggerType Daily -StartTime '16:56' -MessagingSystems 'ARSLANAHMADSVM.PUCIT.LOCAL'
Example 4:
This example creates a GUS job specifying that it should include all containers and messaging systems.
New-Schedule -ScheduleName GusTest2 -IncludeAllContainers -IncludeAllMessagingSystems -JobType GUS -Credentials $creds -TriggerType Daily -StartTime '16:56'
Example 5:
This example creates a job by configuring the notification settings. This commandlet specifies that the notifications for this schedule are enabled and sent to the specified recipients as well as to the owners of the schedule targets. The notifications are only sent when the schedule completes its job successfully.
New-Schedule -ScheduleName GusTest3 -IncludeAllContainers -IncludeAllMessagingSystems -JobType GUS -Credentials $creds -TriggerType Daily -StartTime '16:56' -EnableNotifications -Recepients 'recep1@gid.com','recep2@gid.com' -SendToOwners -NotificationSendingCriteria OnSuccess
See Also
Scheduling Commands
This section covers the cmdlets that perform scheduling-related operations.
- Get-Schedule: retrieves scheduled jobs.
- Get-TargetSchedules: retrieves the scheduled jobs operating on a group or OU.
- Invoke-Schedule: executes a scheduled job.
- New-Schedule: creates a new schedule.
- Remove-Schedule: removes a schedule from an identity store.
- Set-Schedule: modifies a schedule.
- Stop-Schedule: stops a running schedule.
See Also
Remove-Schedule
The commandlet Remove-Schedule removes a schedule (by its name or ID) from the identity store connected to the current instance of the Management Shell.
Syntax
Remove-Schedule
-ScheduleName <String>
[-PassThru]
[-IdentityStoreId <Int32>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-WarningAction <ActionPreference>]
[-InformationAction <ActionPreference>]
[-WarningVariable <String>]
[-InformationVariable <String>]
[-PipelineVariable <String>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- ScheduleName or Scheduled
Example 1:
This example removes a schedule named GUS811_1.
Remove-Schedule -ScheduleName GUS811_1
Example 2:
This example removes two schedules – GUS1 and GUS2 using the pipeline operator.
'GUS_1', 'GUS_2' | Remove-Schedule
Example 3:
This example removes all schedules with job type Glm.
Get-Schedule -JobType Glm | Select-Object -Property Name | Remove-Schedule
See Also
Set-Schedule
The commandlet Set-Schedule modifies the attributes and settings of a schedule in the identity store connected to the current instance of the Management Shell.
Syntax
Set-Schedule
-ScheduleName <string>
[-NewName <string>]
[-TargetOperation {Add | Remove}] [-Targets <string[]>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[-UserName <string>]
[-Password <string>]
[-SetNotifications <bool>]
[-Recepients <string[]>]
[-SendToOwners <bool>]
[-NotificationSendingCriteria {Always | OnSuccess | OnFailure | OnMembershipChanged}]
[-Enabled <bool>]
[-TriggerOperation {add | remove single by id | remove by type | remove all}]
[-TriggerId <int>]
[-TriggerType {Event | Time | Daily | Weekly | Monthly | MonthlyDOW | Idle | Registration | Boot | Logon | SessionStateChange | Custom}]
[-StartTime <datetime>]
[-MonthDate <int>]
[-YearMonths {January | February | March | April | May | June | July | August | September | October | November | December | AllMonths}]
[-MonthWeek {FirstWeek | SecondWeek | ThirdWeek | FourthWeek | LastWeek | AllWeeks}]
[-WeekDays {Sunday | Monday | Tuesday | Wednesday | Thursday | Friday | Saturday | AllDays}]
[-DaysInterval <int>]
[-WeeksInterval <int>]
[-Repeat]
[-RepeatInterval <int>]
[-RepeatDuration <int>]
[-EndDate <datetime>]
[-TriggerDisabled]
[-KillAtDurationEnd]
[-IncludeAllContainers]
[-IncludeSpecifiedContainers]
[-MessagingSystems <string[]>]
[-IncludeAllMessagingServers]
[-IncludeSpecifiedMessagingServers]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- ScheduleName
Example 1:
This example renames a schedule from GUS1 to GUS1-renamed.
Set-Schedule -ScheduleName GUS1 -NewName GUS1_renamed
Example 2:
This example updates the authentication information of GUS1 schedule.
Set-Schedule -SscheduleName GUS1 -Credential $creds
Example 3:
This example removes OU targets from smm4 schedule.
Set-Schedule -ScheduleName smm4_ -TargetOperation Remove -Targets 'OU=ArslanAhmadOU,OU=WorkingOU,DC=pucit,DC=local', 'OU=CustomRole,OU=WorkingOU,DC=pucit,DC=local', 'OU=CustomRole2,OU=WorkingOU,DC=pucit,DC=local'
Example 4:
This example modifies smm4_ schedule by removing its targets.
Set-Schedule -ScheduleName smm4_ -TargetOperation Remove -Targets 'CN=STest1Group,OU=ArslanAhmadOU,OU=WorkingOU,DC=pucit,DC=local', 'OU=CustomRole2,OU=WorkingOU,DC=pucit,DC=local'
Example 5:
This example clears configured notification settings of a schedule smm4.
Set-Schedule -ScheduleName smm4_ -SetNotifications $false
Example 6:
This example changes notification settings of a schedule smm4. It sets notification to be sent to recep1@gid.com every time the job is run.
Set-Schedule -ScheduleName smm4_ -SetNotifications $true -Recepients 'recep1@gid.com' -NotificationSendingCriteria Always
Example 7:
This example adds a monthly trigger for smm4 schedule. It is repeated every 10 minutes for 1 hour on 23rd of March, August and September at 16:56.
Set-Schedule -ScheduleName smm4_ -TriggerOperation Add -TriggerType Monthly -StartTime '16:56' -MonthDate 23 -YearMonths 'March,August,September' -Repeat -RepeatInterval 10 -RepeatDuration 60
Example 8:
This example adds a monthly repeating trigger for smm4_ schedule and has an end date. It stops if it runs at the duration end.
Set-Schedule -ScheduleName smm4_ -TriggerOperation Add -TriggerType Monthly -StartTime '16:56' -MonthDate 23 -YearMonths 'March,August,September' -Repeat -RepeatInterval 10 -RepeatDuration 60 -EndDate '2020/03/29' –KillAtDurationEnd
See Also
Stop-Schedule
The commandlet Stop-Schedule stops a specified schedule if it is already running.
Syntax
Stop-Schedule
[-ScheduleName <String>]
[-JobId <Int32>]
[-PassThru]
[-IdentityStoreId <Int32>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-WarningAction <ActionPreference>]
[-InformationAction <ActionPreference>]
[-WarningVariable <String>]
[-InformationVariable <String>]
[-PipelineVariable <String>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- ScheduleName
Example 1:
This example stops a schedule smm4 by name.
Stop-Schedule -ScheduleName smm4_
Example 2:
This example stops a schedule with job type as GUS.
Stop-Schedule -JobType GUS | Select-Object -Property Name | Invoke-Schedule
Example 3:
This example stops all the daily running GUS jobs.
Get-Schedule -JobType GUS -TriggerType RunDaily -MatchingCriteria And | Select-Object -Property Name | Stop-Schedule
See Also
ConvertTo-StaticGroup
The ConvertTo-StaticGroup commandlet converts an existing Smart Group or a dynasty to a static group by removing the attributes of the Smart Group or the dynasty.
Syntax
ConvertTo-StaticGroup
-IdentityStoreName <string>
[-GroupName <string[]>]
[-SearchContainers <string[]>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- IdentityStoreName
Example 1:
The following commandlets converts a Smart Group in AdStore9 identity store Smart_Training to a static group.
ConvertTo-StaticGroup -IdentityStoreName AdStore9 -GroupName "Smart_Training" -SearchContainers "OU=Recruiting,OU=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US","OU=Outsourcing,OU=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US"
See Also
Get-SmartGroup
Use this commandlet to retrieve Smart Groups and Dynasties that match your given criteria in one or more containers in a domain.
Syntax
Get-SmartGroup
[[-Identity] <string[]>]
[-SmartGroupType <string>]
[-TopLevelOnly <bool>]
[-GroupIDVersion <string>]
[-SearchContainer <string[]>]
[-SearchContainersScopeList <string>]
[-ShouldReturnCollection]
[-MaxItemsToDisplay <int>]
[-ObjectType <string[]>]
[-LdapFilter <string>]
[-SmartFilter <string>]
[-ServerFilter <string>]
[-AttributesToLoad <string[]>]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- None
Example 1:
The following command retrieves only Smart Groups (not Dynasties) in the base container specified by the SearchContainer parameter including sub-containers, using the credentials of current user logged-on to the identity store.
Get-SmartGroup -SmartGroupType "SmartGroup" -SearchContainer "OU=Recuriting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US"
Example 2:
The following command retrieves both Smart Groups and Dynasties that have display names starting with S in the containers specified by the SearchContainer parameter including sub-containers of the first base container and excluding sub-containers of the second one, using the credentials specified in the $Credentials environment variable.
Get-SmartGroup -SearchContainer "OU=Recuriting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US","OU=OutSourcing,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -SearchContainersScopeList "2","1" -LdapFilter "(DisplayName = S*)" -Credential $Cred
See Also
New-SmartGroup
This commandlet helps you to create a new Smart Group (managed group) in Directory. A Smart Group is a conventional distribution or security group that dynamically maintains its membership based on the rules applied by a user-defined LDAP query.
A Smart Group can also be defined as a Password Expiry group. A Password Expiry group is a dynamic group whose membership is based on password policy conditions defined by the administrator. The LDAP query defined for a Smart Group can be updated any time using the Set-SmartGroup commandlet. When the LDAP query is changed, you must update the group once to modify its membership according to the changes made to the query. For information about updating a group, see Update-Group.
You can view events related to this commandlet in GroupID portal, against the History node in the left panel.
Syntax
New-SmartGroup
-SamAccountName <string>
-Name <string>
-OrganizationalUnit <string>
-GroupScope <string>
-Type <string>
-SecurityType <string>
[-SearchContainers <string[]>]
[-SearchContainersScopeList <string[]>]
[-ObjectTypes <string[]>]
[-LdapFilter <string>]
[-IncludeRecipients <string[]>]
[-ExcludeRecipients <string[]>]
[-Storage <string>]
[-DataSourceType <string>]
[-SystemDSN <string>]
[-TableorView <string>]
[-DataSourceUserName <string>]
[-DataSourcePassword <string>]
[-FilePath <string>]
[-Server <string>]
[-Port <int>]
[-LDAPSearchContainer <string>]
[-DataSourceName <string>]
[-DataSourceConnection <string>]
[-DataSourceQuery <string>]
[-KeyMapDB <string>]
[-KeyMapAD <string>]
[-WindowsAthentication]
[-IsPasswordExpiryGroup]
[-DomainExpiration <int>]
[-ExpirationRange <int>]
[-IncludeDisabledUsers <string>]
[-IncludePasswordNeverExpireUsers <string>]
[-Script <string>]
[-ScriptFilePath <string>]
[-Sun_Container <string>]
[-GroupAlias <string>]
[-ManagedBy <string[]>]
[-DisplayName <string>]
[-MailEnabled <string>]
[-Description <string>]
[-AdditionalOwners <string[]>]
[-NotifyOptOutAdditionalOwners <string[]>]
[-Members <string[]>]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameters
- SamAccountName
- Name
- OrganizationalUnit
- GroupScope
- Type
- SecurityType
Example 1:
The following command creates a new mail-enabled, universal, distribution Smart Group in the container specified by the OrganizationalUnit parameter, using the credentials of current user logged-on to the identity store.
New-SmartGroup -OrganizationalUnit "OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -Name "Smart_Training" -GroupAlias "Smart_Training" -MailEnable True -SamAccountName "Smart_Training" -GroupScope "Universal Group" -Type "Distribution"
NOTE: In Microsoft Exchange 2007 and later, mail-enabled groups are created with Universal Group Scope.
Example 2:
The following command creates a new universal, distribution Smart Group in the container specified by the OrganizationalUnit parameter and builds its membership by retrieving those objects from the containers specified in the SearchContainers parameter excluding sub-containers that have Display Names matching the Names in a text file.
New-SmartGroup -OrganizationalUnit "OU=Recruiting,OU=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -Name "Smart_Enrollment" -SamAccountName "Smart_Enrollment" -GroupScope "Universal Group" -Type "Distribution" -SearchContainers "OU=Recruiting,OU=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US","OU=Outsourcing,OU=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -SearchContainersScopeList "1","1" -LdapFilter "(displayName=Database.[Name])" -DataSourceType "Microsoft Text Driver (*.txt,*.csv)" -FilePath "D:\Inputs\Names.txt" -DataSourceQuery "SELECT [Name] FROM [Names.txt]"
Example 3:
The following command creates a new local, distribution, Password Expiry group, using the credentials set in the $Credentials environment variable. Those users will be members of the group who have passwords aged 20 days or older. Disabled users will also be included in the membership.
New-SmartGroup -OrganizationalUnit "OU=Recruiting,OU=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -Name "Password_Expiry" -GroupAlias "Password_Expiry" -SamAccountName "Password_Expiry" -GroupScope "Domain Local" -Type "Distribution" -IsPasswordExpiryGroup -DomainExpiration 30 -ExpirationRange 10 -IncludeDisabledUsers True -Credential $Cred
See Also
Smart Group Commands
This section covers cmdlets for managing Smart Groups.
- ConvertTo-StaticGroup: converts a Smart Group or a Dynasty to a static group.
- Get-SmartGroup: retrieves Smart Groups and Dynasties that match the given criteria.
- New-SmartGroup: creates a new Smart Group (managed group) in the directory.
- Set-SmartGroup: modifies a Smart Group in the directory.
- Update-Group: modifies the membership of a Smart Group or Dynasty according to the results returned by the LDAP query.
- Upgrade-Group: upgrades managed (Smart Groups and Dynasties) and non-managed groups from GroupID 9 and 10 to GroupID 11.
See Also
Set-SmartGroup
The Set-SmartGroup commandlet modifies a Smart Group in Directory. Attributes that are common to both Smart Groups and unmanaged groups can also be modified using the Set-Group commandlet.
You can view events related to this commandlet in GroupID portal, against the History node in the left panel.
Syntax
Set-SmartGroup
-Identity <string>
[-SearchContainers <string[]>]
[-SearchContainersScopeList <string[]>]
[-ObjectTypes <string[]>]
[-LdapFilter <string>]
[-IncludeRecipients <string[]>]
[-ExcludeRecipients <string[]>]
[-Storage <string>]
[-DataSourceType <string>]
[-SystemDSN <string>]
[-TableOrView <string>]
[-DataSourceUserName <string>]
[-DataSourcePassword <string>]
[-FilePath <string>]
[-Server <string>]
[-Port <int>]
[-LDAPSearchContainer <string>]
[-DataSourceName <string>]
[-DataSourceQuery <string>]
[-WindowsAuthentication]
[-EnableUpdate <string>]
[-IsPasswordExpirySmartDL]
[-ExpirationRange <int>]
[-DomainExpiration <int>]
[-MaximumPasswordAge <int>]
[-MinimumPasswordAge <int>]
[-IncludeDisabledUsers <string>]
[-IncludePasswordNeverExpireUsers <string>]
[-SendEmail <string>]
[-EmailTemplatePath <string>]
[-Script <string>]
[-ScriptFilePath <string>]
[-Provider_Container <string>]
[-PowerTools <ArrayList>]
[-KeyMapAD <string>]
[-KeyMapDB <string>]
[-ExtendGroupLife]
[-ExpirationPolicy <int>]
[-MsExchCoManagedByLink <string[]>]
[-IsExpired <string>]
[-GroupScope <string>]
[-Type <string>]
[-Prefix <string>]
[-SecurityType <string>]
[-ManagedBy <string[]>]
[-MaxSendSize <int>]
[-AcceptMessagesOnlyFrom <string[]>]
[-RejectMessagesFrom <string[]>]
[-AcceptMessagesOnlyFromGroups <string[]>]
[-RejectMessagesFromGroup <string[]>]
[-AdditionalOwners <string[]>]
[-NotifyOptOutAdditionalOwners <string[]>]
[-ExpansionServer <string>]
[-BypassOwnersPolicy <string>]
[-MsExchRequireAuthToSendTo <string>]
[-HiddenFromAddressListEnabled <string>]
[-SendOofMessageToOriginatorEnabled <string>]
[-HideMembershipFromAddressListEnabled <string>]
[-ReportToManagerEnabled <string>]
[-ReportToOriginatorEnabled <string>]
[-UpdateMembershipByManagerEnabled <string>]
[-Add <hashtable[]>]
[-Remove <hashtable[]>]
[-Replace <hashtable[]>]
[-Clear <string[]>]
[-Department <string>]
[-Company <string>]
[-Assistant <string>]
[-HomePage <string>]
[-Alias <string>]
[-EmailAddress <string>]
[-Description <string>]
[-Notes <string>]
[-AdministrativeNotes <string>]
[-DisplayName <string>]
[-SimpleDisplayName <string>]
[-CustomAttribute1 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute2 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute3 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute4 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute5 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute6 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute7 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute8 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute9 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute10 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute11 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute12 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute13 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute14 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute15 <string>]
[-Delimiter <string>]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- Identity
Example 1:
The following command modifies a Smart Group by adding Administrator statically in the group membership, regardless of whether it is returned by the query, using the credentials of current user logged-on to the identity store.
Set-SmartGroup -Identity "CN=Smart_Training,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -IncludeRecipients "CN=Administrator,CN=Users,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US"
Example 2:
The following command modifies the LDAP query of a Smart Group to retrieve all mail-enabled objects that are members of the group Training, using the credentials set in the $Credentials environment variable.
Set-SmartGroup -Identity "CN=Smart_Training,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -ObjectTypes "ExchangeUsers","ExternalUsers","ExternalContacts","EmailGroups" -LdapFilter "(MemberOf=Training)" -Credential $Cred
Example 3:
The following command modifies the Password Expiry group using the credentials of current user logged-on to the identity store. To be added are those users who reside in the containers specified in the Add parameter (including sub-containers) and whose password is 20 days or more older and set to never expire.
Set-SmartGroup -Identity "CN=Password_Expiry,OU=Recruiting,OU=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -Add @{SearchContainers="OU=Recruiting,OU=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US#2","OU=Outsourcing,OU=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US#2" -IsPasswordExpirySmartDL -DomainExpiration 30 -ExpirationRange 10 -IncludePasswordNeverExpireUsers True]
Example 4:
The following command modifies the membership of a Smart Group based on the script given in the script file.
Set-SmartGroup -Identity "CN=Smart_Training,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" –ScriptFilePath "c:\MembershipUpdateScript.vb"
Example 5:
The following command overwrites the Includes and Excludes lists of a Smart Group by adding two groups in the Includes list and one group in the Excludes list.
Set-SmartGroup -Identity "CN=imrantest, OU=Testit, DC=minion,DC=local" –Replace @{Includes = "CN=Shizasss,CN=Users,DC=minion,DC=Local","CN=ShezaOfc,CN=Users,DC=minion,DC=Local" ; Excludes="CN=Administrator,CN=Users,DC=minion,DC=local" , "CN=TestMailbox,CN=Users,DC=minion,DC=local"]
Exampe 6:
The following command modifies lists of members a Smart Group can accept and reject messages from.
Set-SmartGroup -Identity "CN=Smart_Training,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" –Add @{ RejectMessagesFrom = "CN=Roger_Manson,OU=ResignedStaff,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US"} -Add @(AcceptMessageOnlyFrom = "CN=PKWing,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US","CN=USWing,OU=Recruiting,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US")
See Also
Update-Group
The Update-Group commandlet modifies the membership of a Smart Group or Dynasty according to the results returned by the LDAP query. This query is associated with the group or Dynasty creation and can be updated anytime using the Set-SmartGroup commandlet. When the Update-Group commandlet is executed, it searches the directory to find recipients matching the criteria defined in the query and modifies the group membership list with the returned recipients, if any.
You can view events related to this commandlet in GroupID portal, against the History node in the left panel.
Syntax
Update-Group
-Identity <string>
[-SearchContainer <string>]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- Identity
Example 1:
The following command updates all the GroupID group(s), by using the credentials of a locally logged on user, in a container specified by the "SearchContainer" parameter.
Update-Group -SearchContainer “OU=Sales,DC=Contoso,DC=com”
Example 2:
The following command updates all Smart Groups and Dynasties present in the container Training, using the credentials set in the $Credentials environment variable. See the Set the $Credentials Environment Variable topic for setting credentials in an environment variable.
Update-Group -SearchContainer "OU=Training,DC=HR,DC=Imanami,DC=US" -Credential $Cred
See Also
Upgrade-Group
The Upgrade-Group commandlet upgrades managed (Smart Groups and Dynasties) and non-managed Groups of GroupID 9 and 10 to GroupID 11.0 version.
NOTE: GroupID upgrades groups from the connected database to the current instance of GroupID. This database can be an upgraded version or copied database from the previous GroupID versions i.e. GroupID 9 and 10.
Syntax
Upgrade-Group
-SQLServer <string>
-Database <string>
-SQLUserName <string>
-Password <string>
-GroupIDVersion <int>
[-SearchContainer <List[string]>]
[-SearchContainerScopeList <List[int]>]
[-Identity <List[string]>]
[-GroupType <List[int]>]
[-KeepUserHistory]
[-ExtensionDataAttributes <List[string]>]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameters
- SQLServer
- Database
- SQLUserName
- Password
- GroupIDVersion
Example 1:
The following command upgrades a GroupID 10.0 Smart Group GIDSmart1 using the database GroupID10 which resides on SQL server sqlexpress. To upgrade the Smart Group to GroupID 11.0 version, the command uses sa user account of the specified SQL server.
Upgrade-Group -Identity "GIDsmart1" -SQLServer "msvr02\sqlexpress" -SQLUserName "sa" -Database "GroupID10" -Password "support123R" -GroupIDVersion "10.0" -GroupType "2"
Example 2:
The following command upgrades all GroupID 10.0 Smart Groups in the Jobs container using the GroupID10 database which resides on SQL server sqlexpress. To upgrade the Smart Groups to GroupID 11.0 version, the command use the sa user account of the specified SQL server.
Upgrade-Group -SearchContainer "OU=Jobs,DC=Demo1,DC=com" -SQLServer "msvr02\sqlexpress" -SQLUserName "sa" -Database "GroupID10" -Password "support123R" -GroupIDVersion "10.0" -GroupType "2"
Example 3:
The following command upgrades all GroupID 10.0 dynasties in Jobs container using the GroupID10 database which resides on SQL server sqlexpress. To upgrade the dynasties to GroupID 11.0 version, the command uses the sa user account of the specified SQL server.
Upgrade-Group -SearchContainer "OU=Jobs,DC=Demo1,DC=com" -SQLServer "msvr02\sqlexpress" -SQLUserName "sa" -Database "GroupID10" -Password "support123R" -GroupIDVersion "10.0" -GroupType "3"
Example 4:
The following command upgrades non managed groups in GID10 container using the GroupID10 database which resides on SQL server sqlexpress. To upgrade the non-managed groups to GroupID 11.0 version, the command uses the sa user account of the specified SQL server.
Upgrade-Group -Identity "departsales" -SearchContainer "OU=GID10,DC=Demo1,DC=com" -SQLServer "msvr02\sqlexpress" -SQLUserName "sa" -Database "GroupID10" -Password "support123R" -GroupIDVersion "10.0" -GroupType "1"
See Also
Get-User
Use the Get-User commandlet to retrieve basic information about a user that match your given criteria.
Syntax
Get-User
[[-Identity] <string[]>]
[-SearchContainer <string[]>]
[-SearchContainersScopeList <string>]
[-ShouldReturnCollection]
[-MaxItemsToDisplay <int>]
[-ObjectType <string[]>]
[-LdapFilter <string>]
[-SmartFilter <string>]
[-ServerFilter <string>]
[-AttributesToLoad <string[]>]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- None
Example:
The following command retrieves the specified user from the connected identity store.
Get-User -Identity "Osama"
See Also
Get-UserEnrollment
The commandlet Get-UserEnrollment retrieves enrollment information of a user.
Syntax
Get-UserEnrollment
-Identity <string>
[-EnrollmentTypes {None | Mobile | SecurityQuestions | Email | Authenticator | LinkAccount | Yubikey | WindowsHello | All | Any}]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- Identity
Example 1:
If a user is enrolled, this cmdlet will enlist the authentication type(s) the user is enrolled with.
Get-UserEnrollment -Identity euser1
Example 2:
Check whether the specified user is enrolled in the specified enrollment type(s).
Get-UserEnrollment -Identity euser1 -EnrollmentTypes SecurityQuestions, Email
Example 3:
This example gets user enrollment information through the pipeline operator.
'euser1', 'euser2' | Get-UserEnrollment
See Also
New-User
Use the New-User commandlet to create a new user in Directory. Most user properties can be directly added by using the parameters of this commandlet.
Syntax
New-User
-Name <string>
-OrganizationalUnit <string>
-SAMAccountName <string>
-Password <string>
-FirstName <string>
-LastName <string>
-DisplayName <string>
[-UPNSuffix <string>]
[-Title <string>]
[-City <string>]
[-State <string>]
[-Zip <string>]
[-Country <string>]
[-Initials <string>]
[-Address <string>]
[-Office <string>]
[-Business <string>]
[-Business2 <string>]
[-Alias <string>]
[-EmailAddress <string>]
[-Department <string>]
[-Company <string>]
[-Mobile <string>]
[-Home <string>]
[-AccountDisabled <string>]
[-PasswordNeverExpires <string>]
[-PasswordForceChange <string>]
[-Manager <string[]>]
[-HomePage <string>]
[-Assistant <string>]
[-Notes <string>]
[-MailEnabled <string>]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameters
- Name
- OrganizationalUnit
- SAMAccountName
- Password
- FirstName
- LastName
- DisplayName
Example:
The following command creates a new user in the container specified by the OrganizationalUnit parameter. The command also specifies the logon name, password, first name, last name and display name of the new user.
New-User -Name "OsamaUser" -OrganizationalUnit "OU=osamamu,DC=naveed,DC=local" -SAMAccountName "OsamaUser11" -Password "webdir123R" -FirstName "Osama" -LastName "Shahbaz" -DisplayName "Osama"
See Also
User Commands
This section covers cmdlets for performing user-related tasks such as:
- Get-User: retrieves a user.
- Get-UserEnrollment: displays information about the status of user enrollment.
- New-User: creates a new user.
- Remove-User: removes a user from the directory.
- Set-User : modifies a user in the directory
See Also
Remove-User
Use the Remove-User commandlet to delete a user from directory.
Syntax
Remove-User
-Identity <string[]>
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- Identity
Example:
The following command deletes a user with the specified name.
Remove-User -Identity "osama"
See Also
Set-User
The Set-User commandlet modifies a user in Directory. Most user properties can be directly modified by using the parameters of this commandlet.
Syntax
Set-User
-Identity <string>
[-FirstName <string>]
[-LastName <string>]
[-Title <string>]
[-City <string>]
[-State <string>]
[-Zip <string>]
[-Country <string>]
[-Initials <string>]
[-Address <string>]
[-Office <string>]
[-Business <string>]
[-Add <hashtable[]>]
[-Remove <hashtable[]>]
[-Replace <hashtable[]>]
[-Clear <string[]>]
[-Department <string>]
[-Company <string>]
[-Assistant <string>]
[-HomePage <string>]
[-Alias <string>]
[-EmailAddress <string>]
[-Description <string>]
[-Notes <string>]
[-AdministrativeNotes <string>]
[-DisplayName <string>]
[-SimpleDisplayName <string>]
[-CustomAttribute1 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute2 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute3 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute4 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute5 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute6 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute7 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute8 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute9 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute10 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute11 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute12 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute13 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute14 <string>]
[-CustomAttribute15 <string>]
[-Delimiter <string>]
[-IdentityStoreId <int>]
[-SecurityToken <CustomClaimsPrincipal>]
[-Credential <pscredential>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Required Parameter
- Identity
Example:
The following command modifies the display name of the specified user.
Set-User -Identity "Osama" -DisplayName "Osama123"
See Also