Global Settings
From this section, you can apply settings globally to all Endpoint Protector entities.
- If there are no settings defined granularly for a computer, and it does not belong to a group, these are the settings it will inherit.
- If the computer belongs to a group, then it will inherit that group’s settings.
NOTE: Several settings from this section also relate to other modules apart from the Device Control module (Content Aware Protection, eDiscovery, etc.).
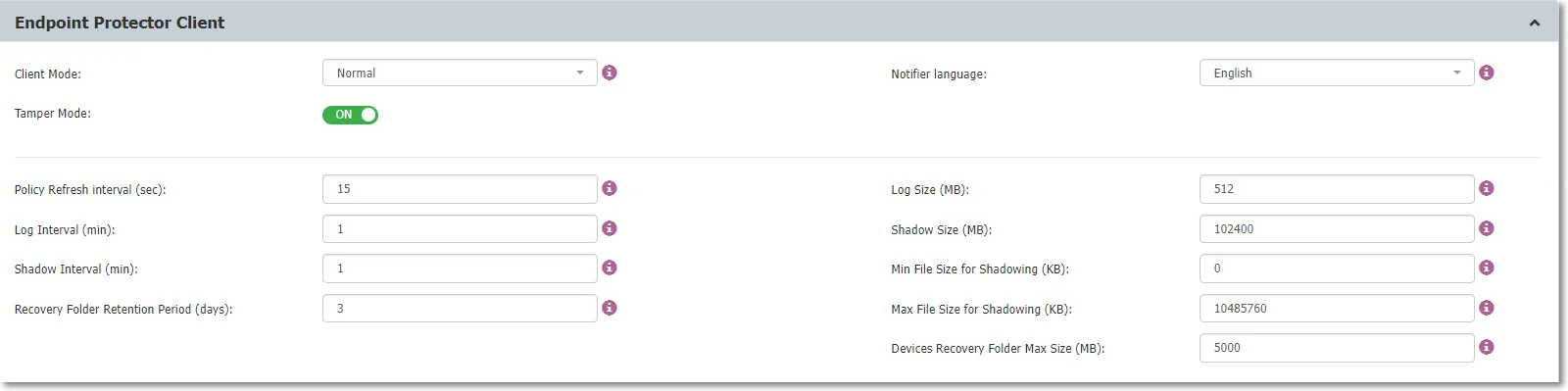
Client Settings
From this section, you can manage settings that relate directly to the Endpoint Protector Client and the Client’s behavior for each specific entity (Global, Groups, and Computers).
-
Client Mode – select a mode to change Endpoint Protector Client behavior.
NOTE: Learn more from the Client Mode section.
-
Notifier Language – Configure the Endpoint Protector Client to automatically match the OS language of the user for notifications. When set to "Automatic," the client adjusts its language to the user's OS language preference without any server interactions, enhancing the user experience and reducing confusion.
To configure the Endpoint Protector Notifier language selection:
Step 1 – Navigate to Device Control > Global Settings in the Endpoint Protector Console.
Step 2 – In the "Notifier language" section, select either "Automatic" or "Default" based on your preferences.
- “Automatic" means the language will be detected automatically from the OS, without server interaction.
- "Default" means the language selected on the server will be applied. If the "Automatic" language was selected on the server, the "Automatic" language will be used.
Step 3 – Save your settings to apply the chosen language selection.
With this enhanced language selection feature, Endpoint Protector provides a more accommodating experience for users, making notifications and alerts more accessible and user-centric.
- Tamper Mode – enable this setting to protect the Endpoint Protector Client from unauthorized termination and modification
CAUTION: A machine or service reboot is mandatory after enabling this setting to work correctly.
-
Policy Refresh Interval (sec) – enter the time interval at which the Client checks with the Server and updates with the latest settings, rights, and policies.
NOTE: The policy refresh cycles may be influenced by Azure Active Directory sync intervals (or Active Directory syncs) if Endpoint Protector is configured to sync entities. Please consider the sync intervals of your Azure Active Directory or Active Directory sync processes when determining an appropriate policy refresh interval.
-
Log Interval (min) – enter the time interval at which the Client attempts to re-send the Logs to the Server.
-
Shadow Interval (min) – enter a time interval between 0-720 minutes at which the Endpoint Protector Client sends the file Shadows to the Endpoint Protector Server.
NOTE: Set the interval to 0 to send the file shadows instantly.
-
Recovery Folder Retention Period (days) – this setting is specific for Mac and Linux computers. It acts as a quarantine folder before a transferred file has been fully inspected for content, avoiding any potential file loss due to blocked transfers. After the specified time interval, the files are permanently deleted.
-
Log Size (MB) – enter the largest size of all logs stored on the Client. If the value is reached, new logs will overwrite the oldest ones. These circumstances occur only when the Client and Server do not communicate for a large period of time.
-
Shadow Size (MB) – enter the largest size of all file shadows on the Client. If the value is reached, new shadows will overwrite the oldest ones. These circumstances occur only when the Client and Server do not communicate for a large period of time.
-
Min File Size for Shadowing (KB) – enter the smallest size of a file at which a File Shadow is created.
-
Max File Size for Shadowing (KB) – enter the largest size of a file at which a File Shadow is created.
-
Devices Recovery Folder Max Size (MB) – this setting is specific for Mac and Linux computers. Maximum size for the quarantine folder. If the value is reached, new files will overwrite the oldest ones.
-
Custom Client Notifications - if enabled, the Client Notifications can be customized.
-
Mandatory OTP Justification - if enabled, the Justification a User has to provide when requesting or using an Offline Temporary Password is mandatory.
-
Extend Source Code Detection - if enabled, this will extend the detection also inside of file type, such as PDF, Docx, etc. With Monitor Webmail setting enabled, you can also detect source code in emails in subject and body using web browsers.
NOTE: Source Code Detection may encounter challenges when dealing with small code snippets. This can occur due to the potential overlap among various programming languages. It's important to consider these limitations when configuring and utilizing Source Code Detection for optimal results.
-
User edited information - if enabled, the User can edit the user and computer information from within the Endpoint Protector Client.
-
Optical Character Recognition - if enabled, JPEG, PNG, GIF, BMP, and TIFF file types can be inspected for content. This option will also change the global MIME Type Allowlists.
-
Disable OCR notifications – if enabled, this will disable all notifications generated by the Optical Character Recognition setting.
-
Limit Reporting Content Aware Protection - if enabled, this will allow information discovered after reaching the Threat Threshold or after matching the Content Detection Rule that contains AND operator for a Report Only Content Aware Protection policy, to no longer be logged. This considerably reduces the number of logs, therefore, optimizing the allocated storage space.
-
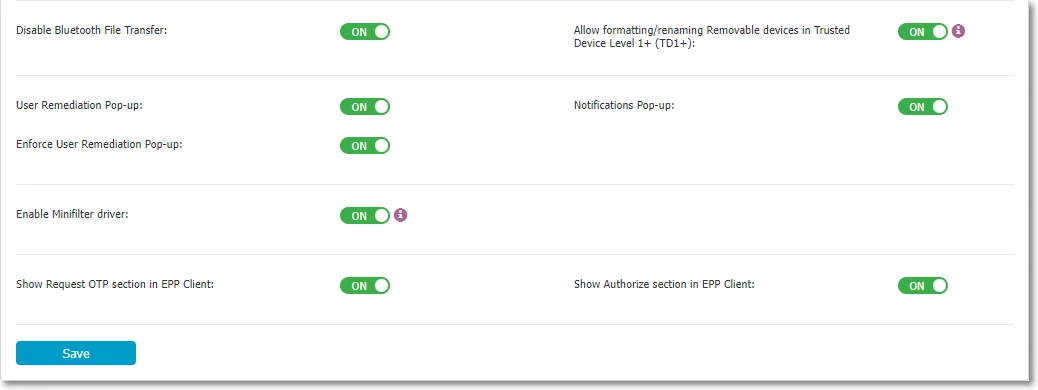
Disable Bluetooth File Transfer – if enabled, this setting will block transfers to Bluetooth Devices, without considering if they are paired or not to the endpoint. This only applies to Windows endpoints.
-
Allow formatting/renaming Removable devices in Trusted Device™ Level 1+ (TD1+) – only available for Windows, enable this setting to allow the user to format or rename a USB device that has TD1-x access permission.
NOTE: For this setting to work successfully, enable the Minifilter Driver setting.
-
User Remediation Pop-up – this setting is available when the User Remediation feature is active and enables User Remediation pop-up notifications for end-users.
-
Enforce User Remediation Pop-up - this setting is available only if the User Remediation Pop-up setting is enabled. When this setting is enabled, end-users cannot disable User Remediation Pop-up notifications.
-
Notifications Pop-up – you can select between the traditional notification, system tray, or pop-up notifications.
-
Enable Minifilter driver – only available for Windows, this setting allows the use of an enhanced driver that provides more reliability and ease of maintenance. You can also enable this setting on the Computers/Users/Groups/Global Rights sections with Manage Settings from the Actions column.
-
User Remediation Notification Template - you can select from the drop-down list a custom notification.
-
Show Request OTP section in Endpoint Protector Client – disable this setting to hide the Request OTP action from Endpoint Protector Client
-
Show Authorize section in Endpoint Protector Client – disable this setting to hide the Authorize action from Endpoint Protector Client
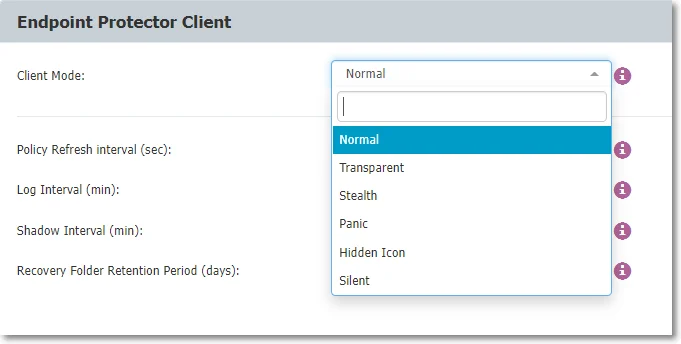
Client Mode
Select from the drop-down list a client mode to define the Endpoint Protector Client behavior.
-
Normal – this is the default and recommended setting to use before being fully aware of what the other modes imply. Normal mode does not apply to Content Aware Protection; all other client modes, except Silent mode, are specific to Device Control.
NOTE: If the Normal Mode does not suit your needs, consider the Hidden or Silent modes as the best alternatives.
-
Transparent – use this mode to block all devices whilst maintaining users unaware of any restrictions or presence of the Endpoint Protector Client. Transparent mode does not apply to Content Aware Protection; all other client modes, except Silent mode, are specific to Device Control.
Selecting this mode will:
-
Not display the system tray icon
-
Not display system tray notifications
-
Block all devices, regardless of authorization, with the following exceptions:
- Keyboards are blocked either when a third one is connected to the same computer or after 48 hours have passed
- Wi-Fi connections are not blocked
- Bluetooth devices remain operational
- USB modems are not blocked
-
Administrator receives alerts for all activities
-
-
Stealth - Use this mode to discreetly monitor users and computers with a focus on Device Control and file-tracing. Stealth mode does not apply to Content Aware Protection; all other client modes, except Silent mode, are specific to Device Control.
NOTE: As everything is allowed, there will be no disruptions in the daily activities of the users.
Selecting this mode will:
- Not display the system tray icon
- Not display system tray notifications
- Allow everything, regardless of authorized or not
- Enable file shadowing and file tracing to view and monitor all user activity
- Administrator receives alerts for all activities
-
Panic – This mode should be selected under extreme situations when a user’s malicious intent or activity is detected by the Endpoint Protector Admin. Panic mode does not apply to Content Aware Protection; all other client modes, except Silent mode, are specific to Device Control.
RECOMMENDED: It is recommended to use this mode for selected users/groups/computers only, as it will block all devices and generate a high volume of logs.
Selecting this mode will:
-
Display the system tray icon
-
Display system tray notifications
-
Block all devices, regardless of authorization,, with the following exceptions:
- Keyboards are blocked either when a third one is connected to the same computer or after 48 hours have passed
- Wi-Fi connections are not blocked
- Bluetooth devices remain operational
- USB modems are not blocked
-
Enable file shadowing and file tracing to view and monitor all user activity
-
Administrator receives alerts when computers go in and out of Panic Mode
-
-
Hidden Icon - this mode is similar to Normal mode, except that the Endpoint Protector Client is not visible to the user. Hidden Icon mode does not apply to Content Aware Protection; all other client modes, except Silent mode, are specific to Device Control.
Selecting this mode will:
- Not display the system tray icon
- Not display system tray notifications
- Apply all set rights and settings as per their configuration
-
Silent - this mode is similar to Normal mode, except that pop-up notifications are not visible to the user.
Selecting this mode will:
- Display the system tray icon
- Not display system tray notifications
- Apply all set rights and settings as per their configuration
NOTE: Certain Linux distributions (like SLED) lack system tray support, resulting in the absence of an Endpoint Protector Notifier icon. To receive Endpoint Protector notifications in these systems, keep the Endpoint Protector Notifier window open.
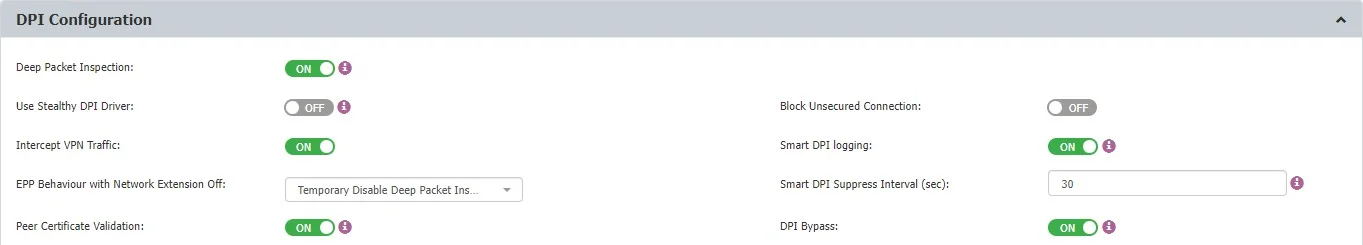
DPI Configuration
In this section, you can manage the following settings:
-
Deep Packet Inspection - if enabled, network and browser traffic can be inspected for content. This option is required for both the Deep Packet Inspection Allowlists and URL and Domain Denylist
-
Use Stealthy DPI Driver – enable this driver to improve interoperability with independent software vendors
-
Intercept VPN Traffic – if you enable this setting, you allow the Endpoint Protector Client to intercept VPN traffic on macOS using the network extension framework
NOTE: Learn more from the Intercept VPN Traffic topic.
-
Endpoint Protector Behavior with Network Extension Off – select a behavior type from the available entries
-
Peer Certificate Validation – enable this setting to turn on the Endpoint Protector certificate validation of the websites that are accessed by the user when DPI is active
- Ignore Expiration Date - when checked, expired certificates will be ignored and traffic will be permitted.
- Ignore Trust - when checked, certificates will not be validated against the Root Certificate.
- Ignore Hostname - when checked, the certificate hostname property will not be validated against the server hostname.
CAUTION: Disabling setting ‘Peer Certificate Validation’ will not impact Endpoint Protector functionality. It should only be disabled when an alternative network traffic inspection product, such as a Secure Web Gateway Solution, is validating website certificates.
-
Display Dialog Boxes for DPI Dropped Connections - enable this setting to display Dialog windows on endpoint machines, containing more details.
-
Disable DPI Dropped Connections Notifications - check this setting to suppress notifications shown by the Notification Center nearby the System tray.
-
Block Unsecured Connection - if enabled, unsecured access through HTTP will be blocked and user access restricted.
NOTE: The Block Unsecured Connection feature is only available when the Deep Packet Inspection feature is enabled.
-
DPI Bypass Traffic – this setting automatically bypasses non-inspectable traffic and sends an event for allowed traffic.
Possible Bypass reasons:
-
Bypass DPI Certificate Rejection by Third-Party Applications
-
Enable this setting, if SSL errors are encountered from the source applications, such as web browsers, like:
SSL_R_TLSV1_ALERT_UNKNOWN_CA
SSL_R_SSLV3_ALERT_CERTIFICATE_UNKNOWN
- This signifies that the source application failed to validate the server certificate, which was issued by Endpoint Protector.
- The absence of the DPI certificate in the system keychain may also contribute to this scenario.
- ‘Certificate Pinning’ also falls under this category.
NOTE: Learn more about Using Wireshark for Network Traffic Analysis.
-
-
Bypass Unknown TLS Handshakes
-
Enable this setting, when a secure port connection employs custom encryption instead of TLS, the DPI bypass is activated.
- This is exemplified by configuring Telegram.app for DPI monitoring, logging into the app, and encountering an unknown TLS handshake.
-
-
Bypass Websites Temporarily Whitelisted (Possible mTLS Connection/SSL Setup Failure/Unsupported TLS Protocol)
-
Enable this setting where an SSL setup failure or an unsupported TLS protocol error occurs on the server side of an SSL connection. Endpoint Protector temporarily allow-lists the website.
- While specific examples are infrequent, such instances involve potential mTLS connections.
-
-
Bypass Websockets
-
Enable this setting, when Websites utilize websockets with arbitrary data protocols.
- Endpoint Protector passthroughs connections upon the HTTP connection's upgrade to a websocket.
- Examples are applications, such as WhatsApp Web, Firefox Send etc.
-
-
Bypass on HTTP Errors Indicating mTLS Requirement
-
Enable this setting, when a server indicates the requirement of a client certificate (mTLS).
- Endpoint Protector triggers bypass for HTTP error codes like ‘400 Bad Response’ and ‘496 SSL Certificate Required’.
- Accessing https://client.badssl.com/ from a web browser without providing the necessary client certificate illustrates such situations.
-
-
Bypass Invalid Peer Certificates
-
Enable this setting, to permit connections with invalid peer certificates when ‘Peer Certificate Validation’ is enabled.
- If both ‘Bypass Invalid Peer Certificates’ and ‘Peer Certificate Validation’ are enabled, ‘Bypass Invalid Peer Certificates’ will override setting ‘Peer Certificate Validation’.
- Accessing https://expired.badssl.com/from a web browser with both settings ‘Bypass Invalid Peer Certificates’ and ‘Peer Certificate Validation’ enabled, illustrates such situations (the website will be accessible).
-
CAUTION: Please be aware that the current Default DPI list and the new Default DPI bypass list are exclusively utilized when manually checked within CAP (Content Aware Protection) policies.
NOTE: Learn more about Timeout Period for Bypassed Websites, and Handling of Bypassed Domains and Applications.
-
-
DPI Bypass Event Logging – this setting will automatically send DPI Bypass events/reasons to Endpoint Protector Server when connections are being bypassed on endpoints.
NOTE: Learn more about Bypass Log Reporting Frequency.
![]()
Intercept VPN Traffic
If you enable this setting, the Endpoint Protector Client will intercept VPN traffic on macOS using the network extension framework.
NOTE: The Intercept VPN Traffic feature is only available when the Deep Packet Inspection feature is enabled. It will only work for macOS from version 11.0 onwards and only if Deep Packet Inspection Certificate is also added.
To use this feature, follow these steps:
Step 1 – Enable Deep Packet Inspection.
Step 2 – Enable Intercept VPN Traffic.
Step 3 – Select an option for Endpoint Protector behavior when network extension is disabled
- Temporary Disable Deep Packet Inspection – this will disable Deep Packet Inspection temporary
- Block Internet Access - this will block the Internet connection until the user approves the Endpoint Protector Proxy configuration. The user also can allow the configuration after rebooting the PC.
- Repeat VPN notification – this will display the VPN pop-up window multiple times even after the user has previously denied permission.
Step 4 – Click Save.
Step 5 – On the pop-up window informing the user that a System Extension is blocked, click OK to allow.
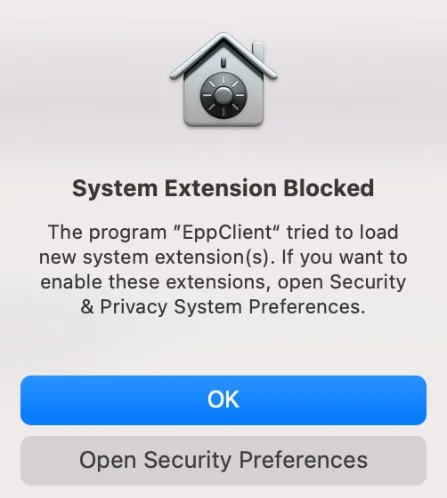
Step 6 – Go to System Preferences >Security and Privacy > General, and then allow the Endpoint Protector Client Extension.
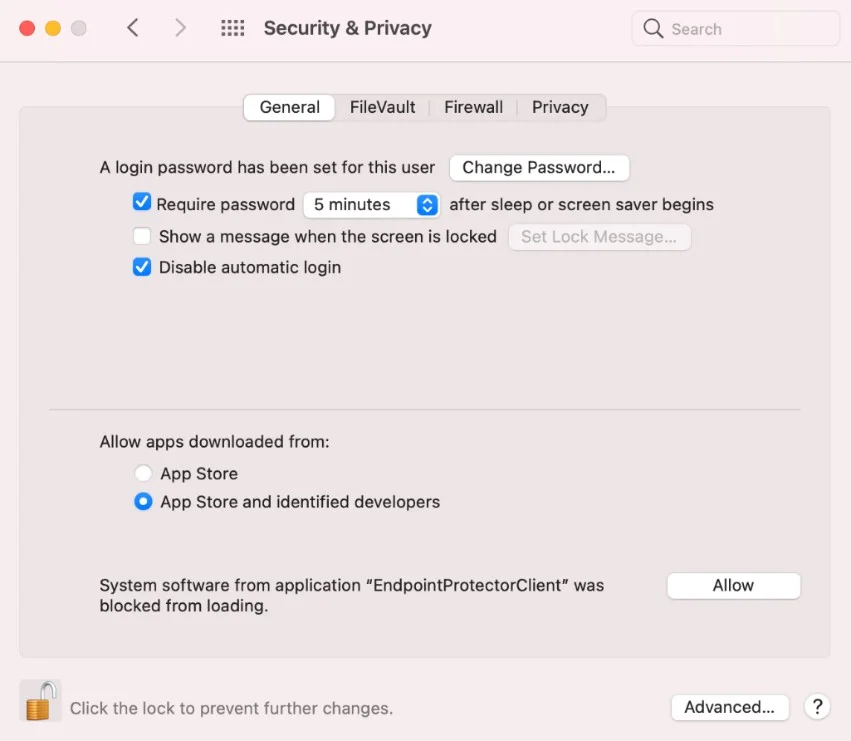
Step 7 – On the Endpoint Protector Proxy Configuration pop-up window, click Allow.
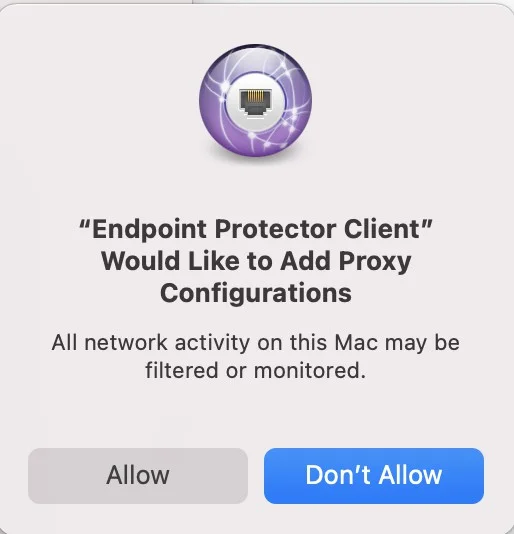
NOTE: When network extension is successfully enabled, a Client Integrity OK log is generated.
Step 8 – Go to System Configuration > System Settings > Deep Packet Inspection Certificate, and then download the CA Certificate.
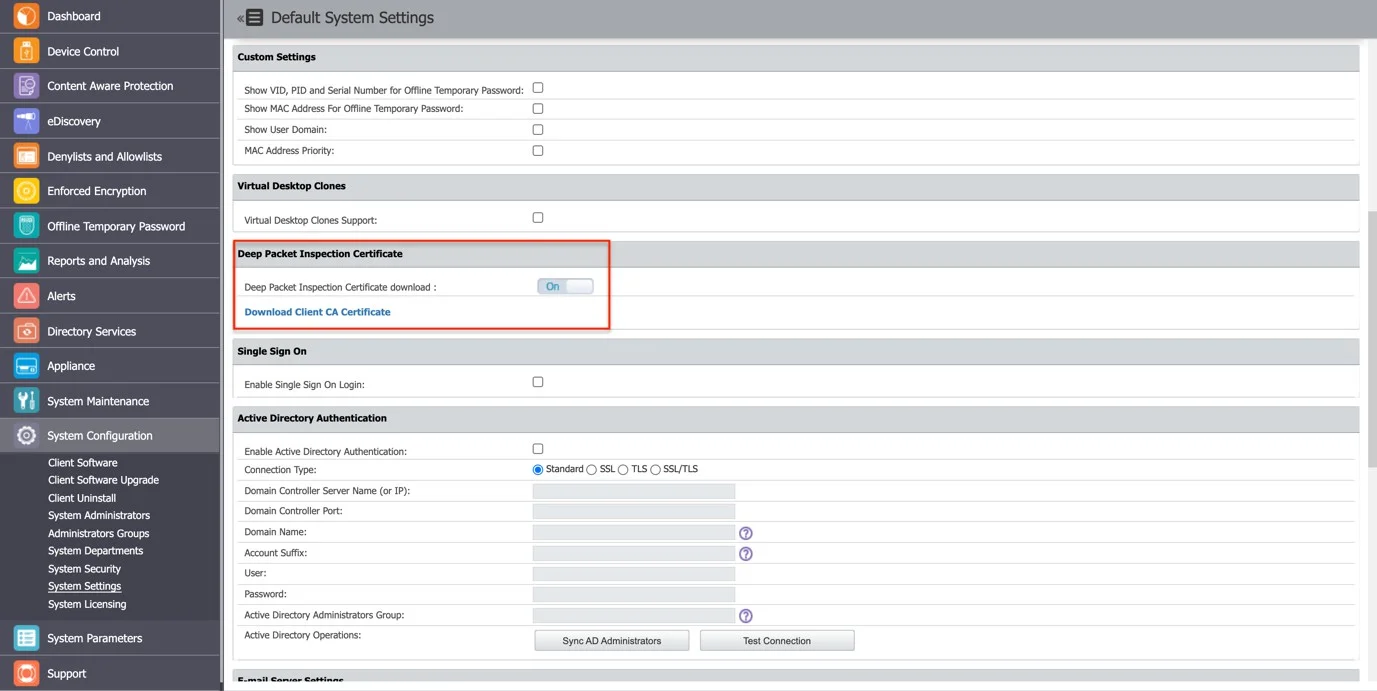
Step 9 – On your macOS, open the Keychain Access application and go to System.
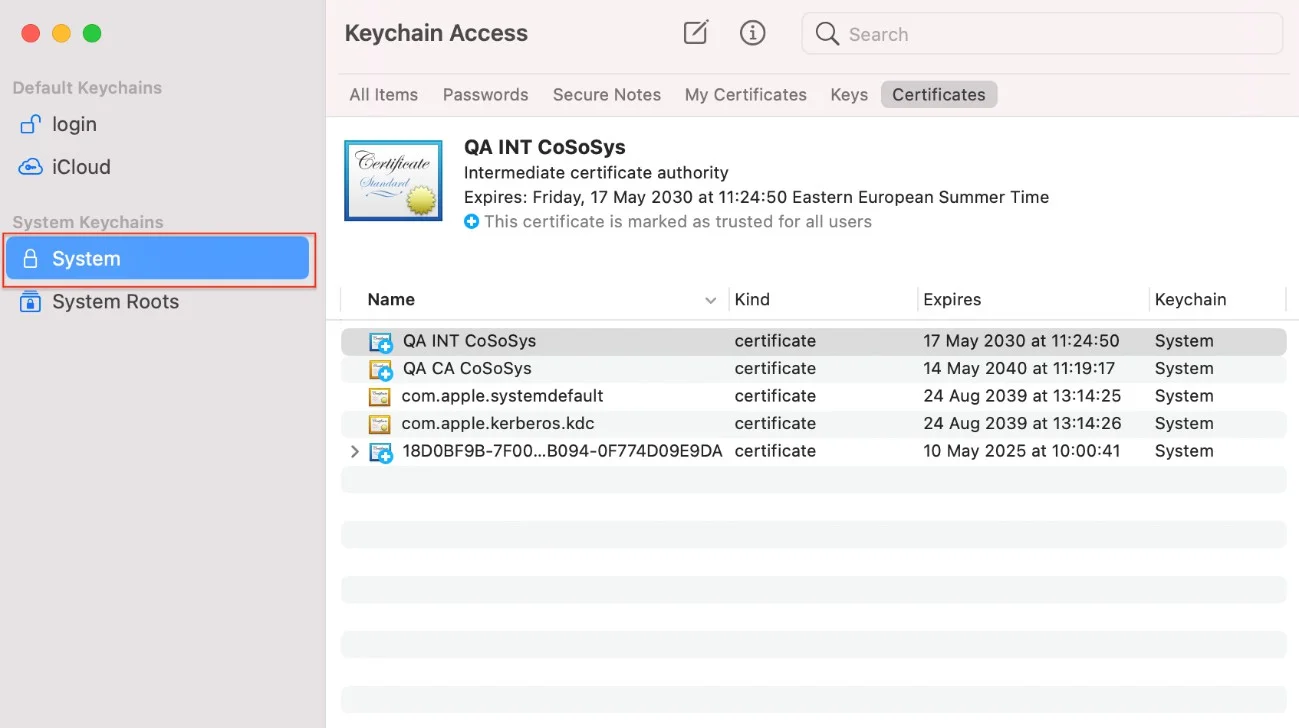
Step 10 – Decompress the ClientCerts file.
Step 11 – Select the cacert.pem file and drag and drop it under System > Keychain Access.
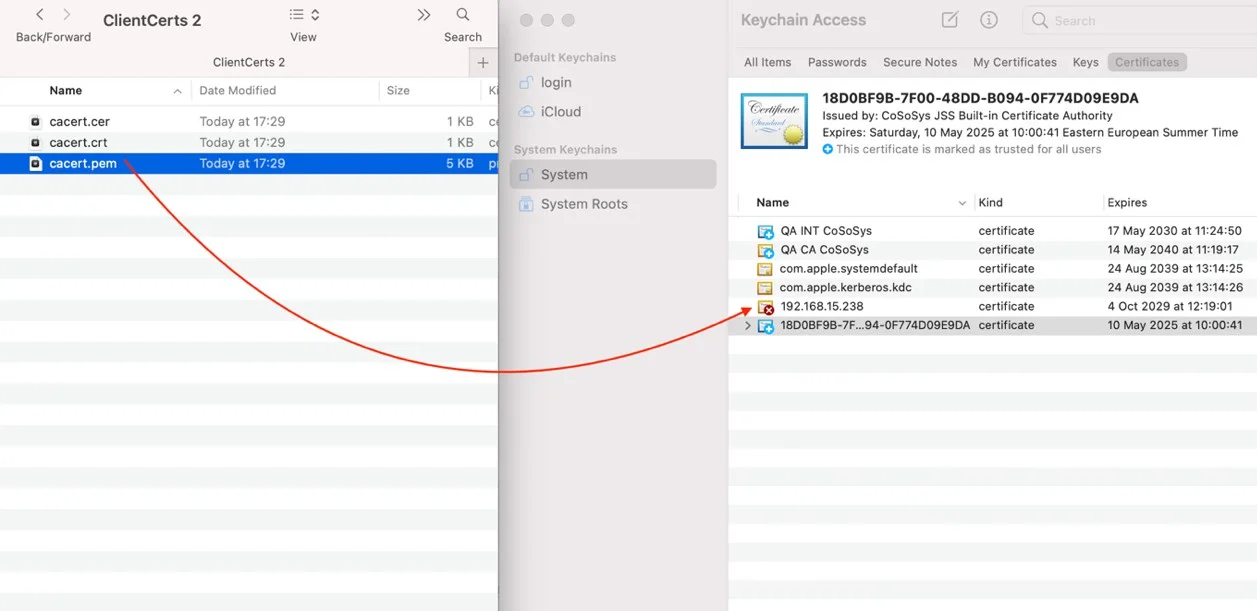
Step 12 – Double click the X from the newly added certificate and select Always Trust from the Trust section.
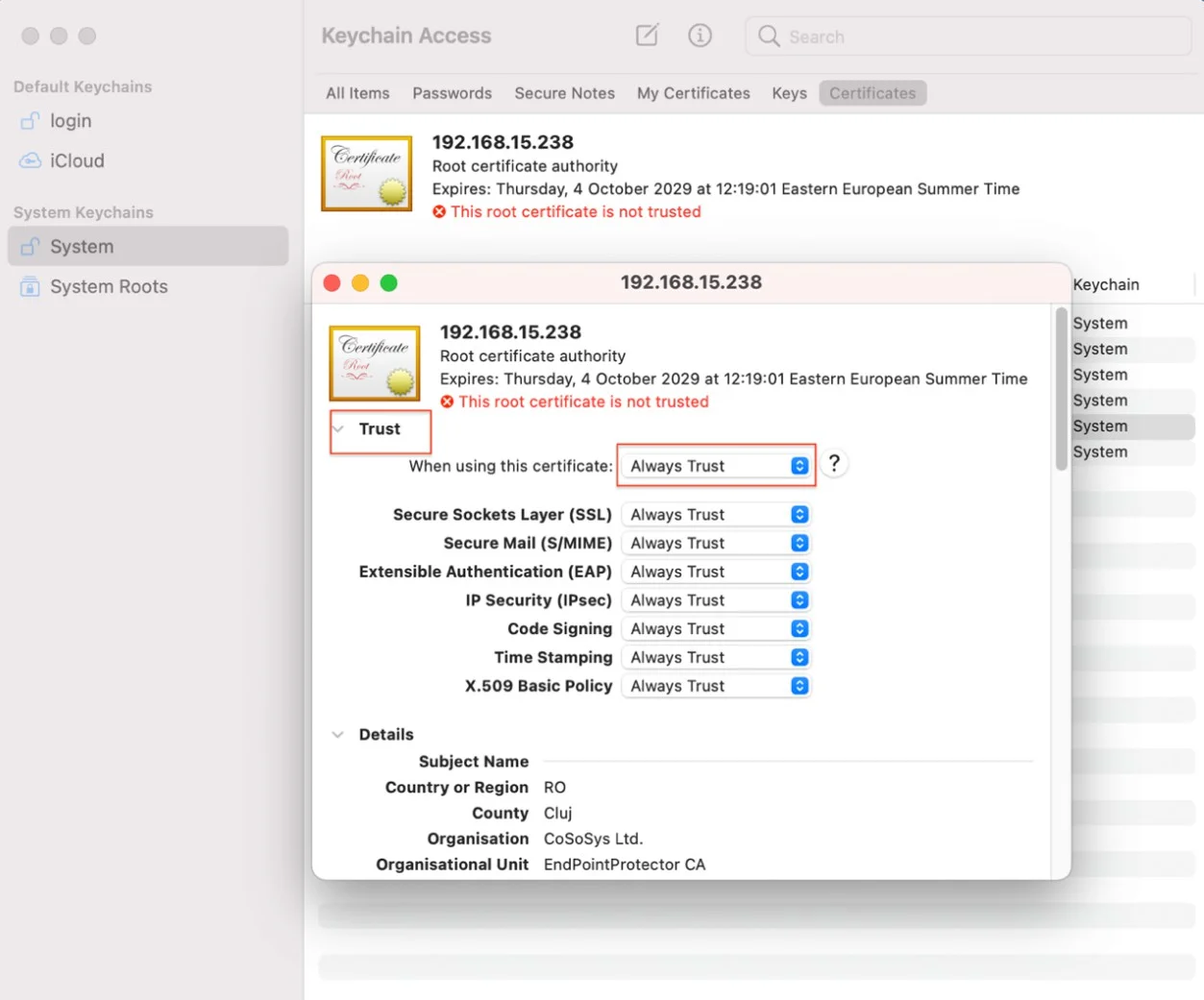
Step 13 – Save the changes.
Smart DPI (Log Throttling)
Enable this setting to address the number of excessive false positives for URL Denylists. This improvement provides you with a configuration option to filter out non-relevant information, resulting in a more accurate log that focuses on true false positives and reduces unnecessary noise saving database storage.
Bypass Log Reporting Frequency
Endpoint Protector's agent ensures efficient resource utilization by reporting each domain name and application pair at most once every two weeks. This approach prevents an overwhelming influx of logs, which could reach excessive numbers if reported more frequently.
Timeout Period for Bypassed Websites
To maintain a streamlined process, Endpoint Protector enforces a timeout period of two weeks. During this time frame, the state for bypassed websites is retained. Beyond this period, the bypass state is automatically removed, contributing to effective resource management.
Handling of Bypassed Domains and Applications
Endpoint Protector employs a nuanced approach to handle bypassed domains and applications:
Memory and Disk Persistence
Bypassed website information is stored in both memory and on disk. This dual storage ensures that the list of skipped websites is readily accessible for efficient future reference. By persisting this information, the frequency of log generation can be controlled to avoid unnecessary strain on resources.
Clearing Bypass State
To reset the bypass state and clear associated records, administrators can initiate a simple process. Temporarily disabling and subsequently re-enabling the bypass DPI setting on the Endpoint Protector server achieves this reset.
Using Wireshark for Network Traffic Analysis
Prior to a "DPI certificate rejected" event, Wireshark can be instrumental in diagnosing network traffic. The presence of a "TLS alert" error in Wireshark signals the impending event.
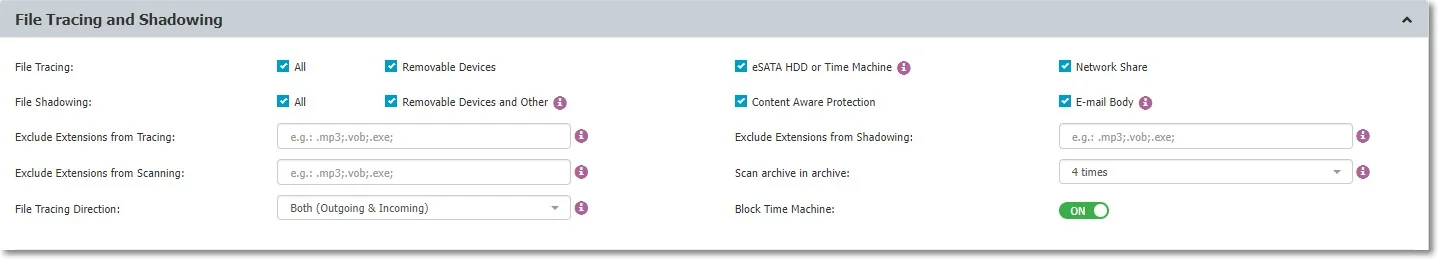
File Tracing and Shadowing
In this section, you can manage the following settings:
-
File Tracing – this feature allows you to monitor data traffic between protected endpoints and removable devices, internal eSATA HDDs, and Network Shares. It also shows other actions that took place, such as files named, deleted, accessed, modified, etc.
To enable this feature, you can do so from Device Control, Global Settings, or granularly for Groups or Computers.
-
File Shadowing – this feature extends the information provided by File Tracing, creating exact copies of files accessed by users.
The creation of shadow copies can be triggered by the following events: file copy, file write, and file read. Events such as file deleted, file renamed, etc. do not trigger the function. You can enable File Shadowing on all supported Removable Devices:
- eSATA HDDs or Time Machines
- Network Shares
- Content Aware Protection - file transfers through various exit points such as online applications, printers, clipboards, etc.
- E-mail Body
CAUTION: File Shadowing cannot be used without File Tracing.
File Shadowing can be delayed due to network traffic and Endpoint Protector Settings for different computers or file sizes. Shadowed files are usually available after a few minutes. Shadow creation may not occur for newly created files; however, the system diligently tracks file activities and generates File Shadowing for subsequent file events as expected.
NOTE: For your deployment, we strongly advise activating File Shadowing for not more than 15% of your total endpoint capacity (e.g., for a 1000 endpoint deployment, File Shadowing should be set to a maximum of 150 endpoints for optimal performance). For more users, please contact customer support for recommended settings.
-
Exclude Extensions from Tracing – you can disable File Tracing for specific file types.
-
Exclude Extensions from Scanning – you can disable scanning for specific file types.
-
File Tracing Direction – this setting enables you to monitor file transfers based on transfer direction:
- Outgoing File Tracing Direction is defined by transfers made from the local machine to removable devices.
- Incoming File Tracing Direction indicates transfers from the removable devices to the local machine.
- Both (Outgoing & Incoming) allows you to monitor all types of transfers that are made between removable devices and the local machine.
NOTE: The File Tracing Direction setting only applies for transfers between removable devices, computers, and network shares and works only on Windows and macOS starting with version 11.0.
NOTE: MTP (Media Transfers Protocols) file transfer is currently supported only on Windows client machines. It allows you to transfer files in one direction, from your PC to your Android device.
-
Exclude Extensions from Shadowing – use this setting to disable File Shadowing for specific file types.
-
Scan archive in archive – use this setting to define the archive depth in which content is inspected.
-
Block Time Machine – if you enable this setting, you will block Time Machine backups on macOS.
-
Metadata Scanning - if you disable this setting, metadata will not be scanned for PDFs, ZIPs, and Office Files DOCX, XLSX, PPTX, DOC, XLX, PPT).
-
Advanced Printer and MTP Scanning – Advanced Printer and MTP Scanning – if you enable this setting, a DLL is loaded into certain Windows applications when they are launched. This DLL enables Endpoint Protector to monitor printing and files copied to MTP devices by hooking into Windows API functions responsible for these actions. For example, when a user opens Microsoft Word, an Endpoint Protector DLL is loaded into Word’s address space. If the user attempts to print a document, the DLL scans the printed document content, and if sensitive data is detected, Endpoint Protector can block the print operation.
NOTE: This feature increases accuracy and reduces false positives for File Tracing and File Shadowing. It is available only for Windows and will require a computer restart.
-
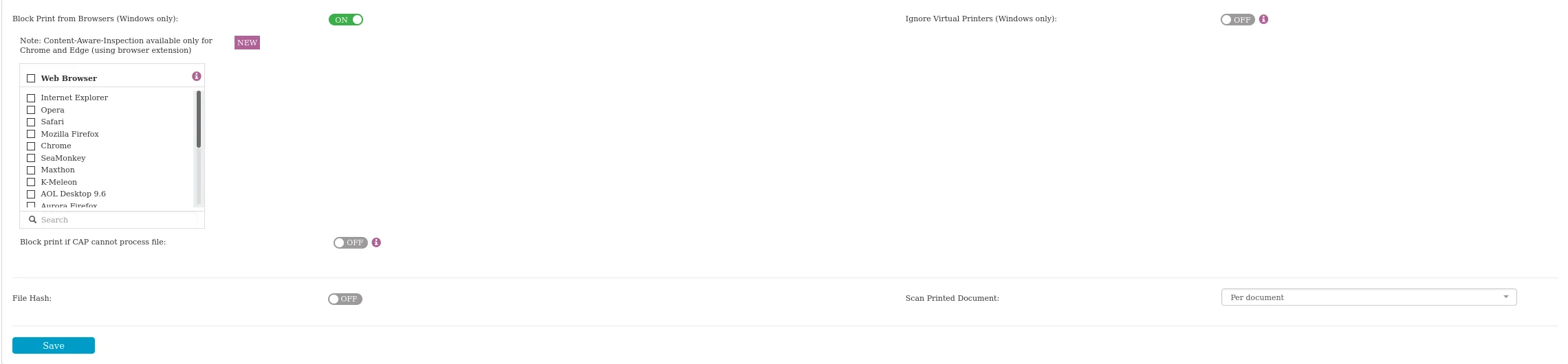
Block Print from Browsers – Enable this setting to prevent users from printing web pages from any supported browser on Windows.
NOTE: The Content-Aware Protection (CAP) feature is available only for Chrome and Edge via a dedicated extension. For other browsers, this setting will block print functionality.
-
Block Print if CAP Cannot Process File – This setting determines the action if CAP cannot access the file content. By default, printing is allowed. This option applies only to Chrome and Edge with the browser extension on Windows.
-
File Hash - if you enable this setting, a file hash will be generated and included in the file transfer logs.
-
Scan Printed Document – select if you want to be notified a threat was restricted on the whole document or on the specific page.
CAUTION: Newer Linux Ubuntu versions have 'snap'-based applications installed by default, affecting Endpoint Protector Client functionality. This may result in missing file-related events in File Tracing and File Shadow artifacts. The reliance on 'snap'-based applications also affects file-related web browser activities, exacerbating this limitation. Consider non-’snap’-based applications (where possible) as alternative configurations for optimal functionality.
Block Print from Browsers
Enable this setting to restrict the user from printing web pages from various browser types available, define the specific browsers, and create and enforce a Content Aware Policy that includes Printers from the Policy Exit Points section.
NOTE: This setting is available only for Windows.
CAUTION: After enabling the Block Print from Browsers setting and applying the configuration on the Client to enforce it, please be aware that open browser tabs will need to be reloaded, or a browser restart will be required for the changes to take effect.
CAUTION: Since version 5.9.4.1, Endpoint Protector Clients require binding to the new Endpoint Protector web printing extensions. Customers using GPO configuration, should ensure that the browser extension ID configured in the GPO is updated. The old extensions will soon be deprecated. Customers using this feature and older Endpoint Protector Clients than version 5.9.4.1 should immediately enforce an Endpoint Protector Client upgrade process. After updating the GPO configurations and completing the Endpoint Protector Client upgrade process, a full computer reboot is required for the changes to take effect.
CAUTION: Upgrading the Endpoint Protector Client with the browser plug-in enabled will require a full computer restart.
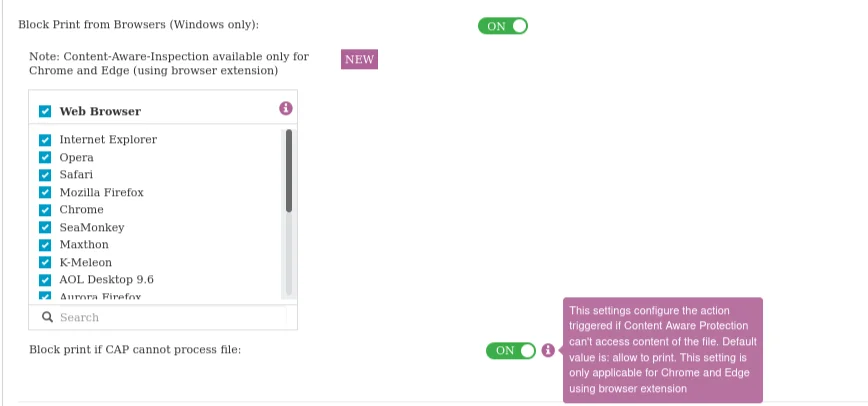
Users printing from Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge can utilize content-aware detection by enforcing a Content Aware Policy that includes Printers from the Policy Exit Points section. For seamless protection, the Endpoint Protector Browser Connection extension installs automatically the first time upon enabling the Block Print from Browsers setting. This extension enhances content scanning capabilities during web document printing, integrating seamlessly on both server and client sides.
NOTE: The extension does not function in 'in Private/Incognito' mode. If it fails to load, it reverts to full Block-mode with Printing, providing comprehensive protection.
NOTE: To ensure the extensions' stability and prevent user interference, use Group Policy Objects (GPO), the exclusive and recommended method for installing on both Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge.
CAUTION: Use the Group Policies to set PDF files to be downloaded instead of opened in the web browser for the block print from the browser to function accurately.
CAUTION: Group Policy Objects (GPO) are the only supported method to prevent users from disabling or uninstalling the Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge extension.
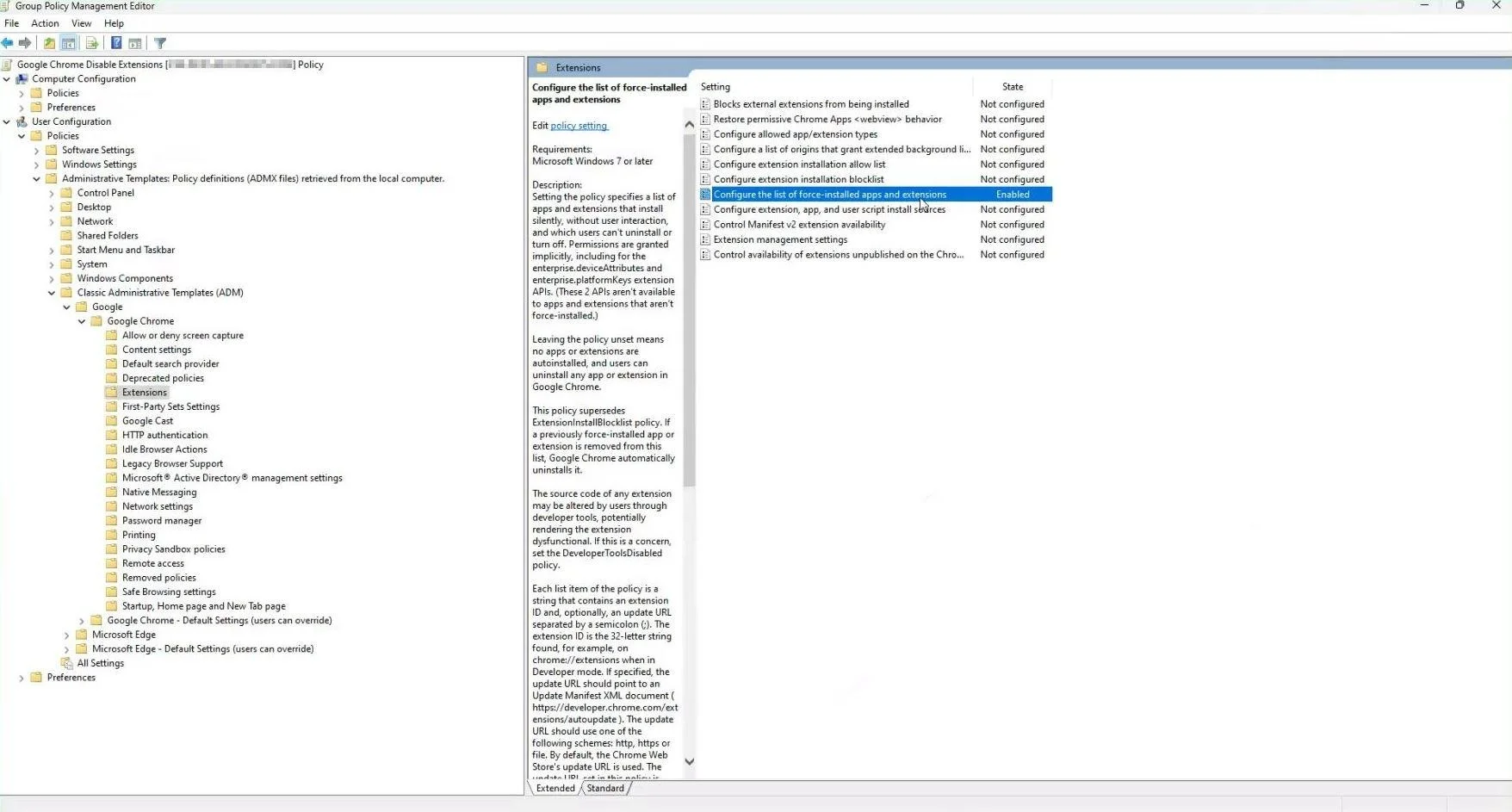
Configuring GPO for Browser Extensions
To configure Group Policy Objects (GPO) to deploy a browser extension to Windows machines and prevent users from removing it, follow these steps:
-
Google Chrome
Step 1 – Refer to the official Google support guide for detailed instructions.
Step 2 – Download the Chrome Group Policy.
Step 3 – Configure your Group Policy as shown below.
- Endpoint Protector Browser Connector ID: nnnaeanocbmnnjjlcfhcbpefmlgbcgoi
-
Microsoft Edge
Step 1 – Utilize the Configure Microsoft Edge guide provided by Microsoft.
Step 2 – Download the Edge Group Policy Template.
Step 3 – Configure your Group Policy as shown below.
- Endpoint Protector Browser Connector ID: nnnaeanocbmnnjjlcfhcbpefmlgbcgoi
CAUTION: Make sure to thoroughly test the configuration in a controlled environment to ensure the intended behavior. Always keep endpoint security policies updated and aligned with organizational security standards.
Ignore Virtual Printers
The option to Ignore Virtual Printing events, empowers users to have control over Content Aware Protection and File Tracing visibility over virtual printers like Microsoft to PDF, PDFCreator, and more. This not only helps conserve valuable log space but also reduces the workload on your analytics and administration teams. With this option, users can focus on tracking PDFs only when they exit your organization's environment and not when they have been created, streamlining monitoring efforts and improving efficiency.
NOTE: This feature only applies for Windows.
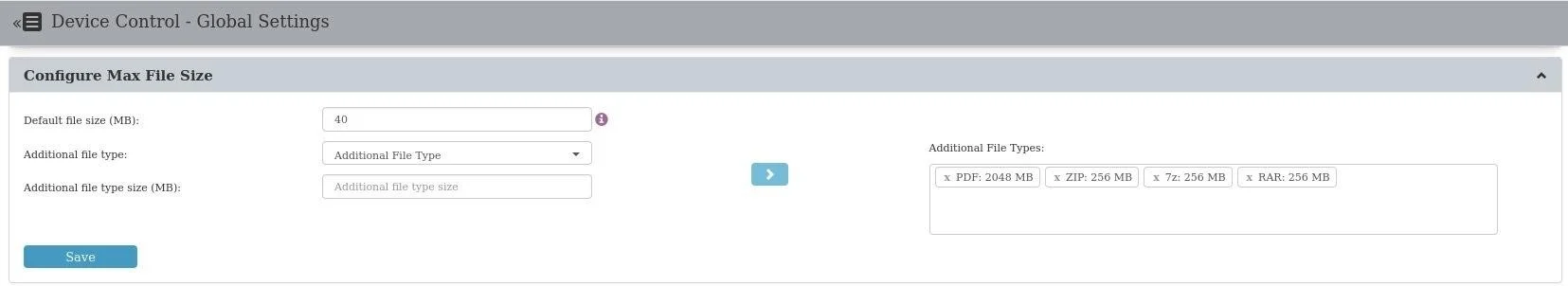
Configure Max File Size
This section allows customers to tailor Content Aware Protection scanner’s file size settings according to their specific needs. By customizing these settings, users can ensure Endpoint Protector meets their organization's requirements. The default maximum file size is set at 40 MB, with a maximum limit of 4096 MB.
Furthermore, users have the flexibility to configure additional file type sizes, which are set as follows by default: PDF (2048 MB) and Archives (256 MB). These file type sizes can be adjusted within the range of 1 KB to 4 GB to accommodate your specific needs.
Additionally, in the Windows environment, a default time-out of 10 seconds is applied. For MacOS, a strict 10-second time-out is enforced due to Apple OS architecture, which terminates processes that do not respond promptly. Linux currently operates without a specific time-out limitation.
NOTE: This setting only applies to Content Aware Protection policies and does not affect eDiscovery Policies and Max File Size for File Shadows.
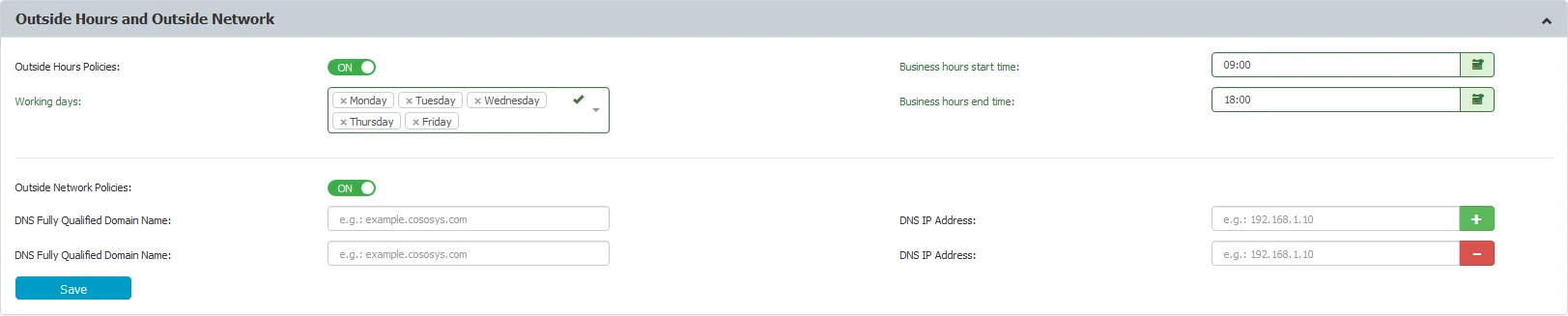
Outside Hours and Outside Network
From this section, users can manage Outside Network and Outside Hours Policies, for both Device Control and Content Aware modules.
- Outside Hours policies – enable the setting and then set the Working days, Business hours start time, and end time.
- Outside Network policies – enable the setting and then add the DNS Fully Qualified Domain Name and DNS IP Addresses.
Once these settings are made, the fallback device type rights can be set Globally, per Groups, Users, or Computers.
CAUTION: When triggered, fallback policies supersede the standard device rights. Regarding fallback policies, the Outside Network Policies supersede the Outside Hours Policies.
NOTE: For Content Aware Protection, the Outside Network and Outside Hours Policy Type also needs to be selected.
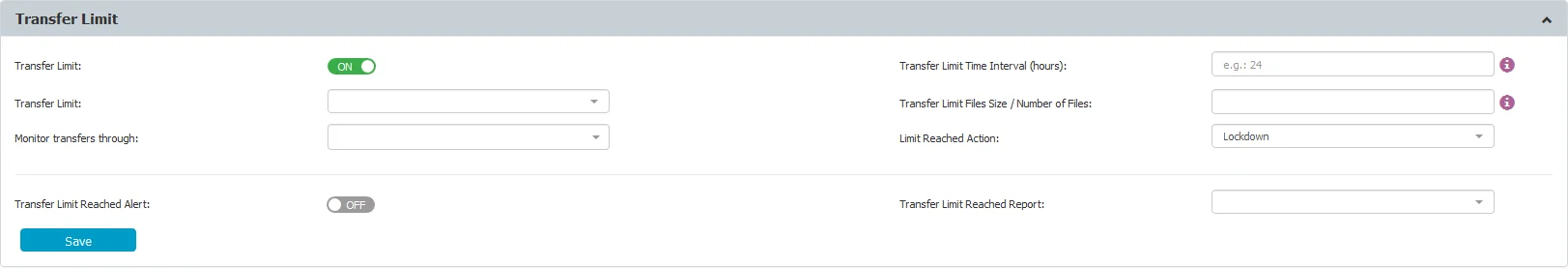
Transfer Limit
From this section, users can set the transfer limit, within a specific time interval (hours). Once the limit is reached, file transfers to storage devices (Device Control) to control applications (Content Aware Protection) will no longer be possible, until the time interval expires and the count is reset. Similarly, file transfers through Network Shares can also be included in the Transfer Limit.
The mechanism that checks when the Transfer Limit is reached has been designed in such a way that it does not impact the performance of the computer.
Therefore, there might be a slight delay between the exact time the limit is reached and the enforcement of the transfer restrictions. In general, it’s just a few seconds but also depending on the network, it could be up to a few minutes.
There are three actions to choose from when the Transfer Limit is reached:
- Monitor Only – this setting reports when the limit is reached
- Restrict – this setting blocks the devices and applications that have been defined in the Device Control policies
- Lockdown – this setting blocks all devices, regardless if they have been defined within the Device Control policies, including the network interfaces and therefore, any type of transfer
NOTE: To re-establish the Server-Client communication before the Transfer Limit Time Interval expires, a Transfer Limit Reached Offline Temporary Password is available. For detailed information, refer to the Offline Temporary Password chapter.
You can enable a Transfer Limit Reached Alert and schedule a Transfer Limit Reached Report on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis.
Debug Logging
You can use this feature to collect logs for a specific issue and send the resulting archive to the Endpoint Protector Server on the Reports and analysis section, the Logs Report page.
By enabling this feature, the Endpoint Protector Client will create the log file (general log file), and if Deep Packet Inspection is enabled, it will collect supplementary Deep Packet Inspection logs along with sslsplit logs.
NOTE: We recommend using the Debug level mode as it contains more than error and warning type information.
Debug Logging Usage
To use the debug feature and collect logs, follow these steps:
Manual Logging
On the Global > Computer > User Settings page, configure the following settings:
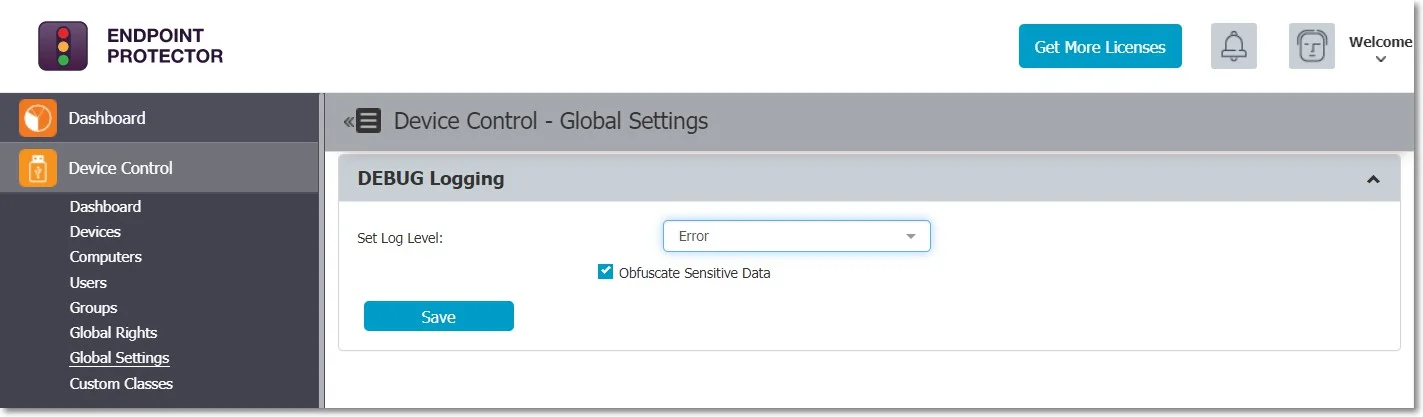
Step 1 – Enable Debug Mode from the DEBUG logging section.
Step 2 – Click and select an option on the set logs level (None, Error, Warning, Informational, Debug) drop down.
Step 3 – For Error, Warning, Informational, and Debug log levels select obfuscate sensitive data.
Step 4 – Save.
NOTE: Read the Data Obfuscation Rules section for more information.
Step 5 – Right-click the Endpoint Protector Client icon and select Update Policies Now.
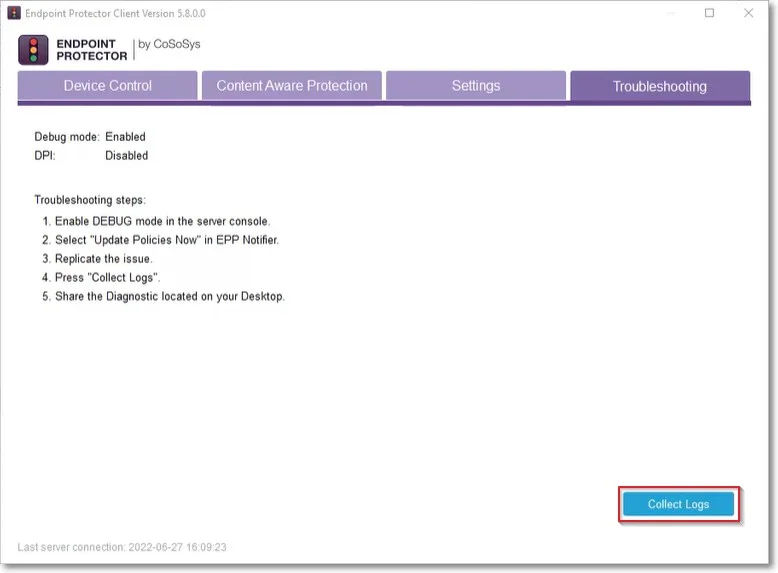
Step 6 – Replicate the issue to generate the corresponding logs.
Step 7 – Open the Endpoint Protector Client and go to the Troubleshooting tab.
Step 8 – Click Upload Logs - this will upload the logs on the Endpoint Protector Server.
Step 9 – Go to the Global Settings page and disable Debug Mode.
Automatic Logging
You can also substitute the user action from the Manual Logging procedure by using the automatic logging option.
- This option is available under Device Control on the Computer page.
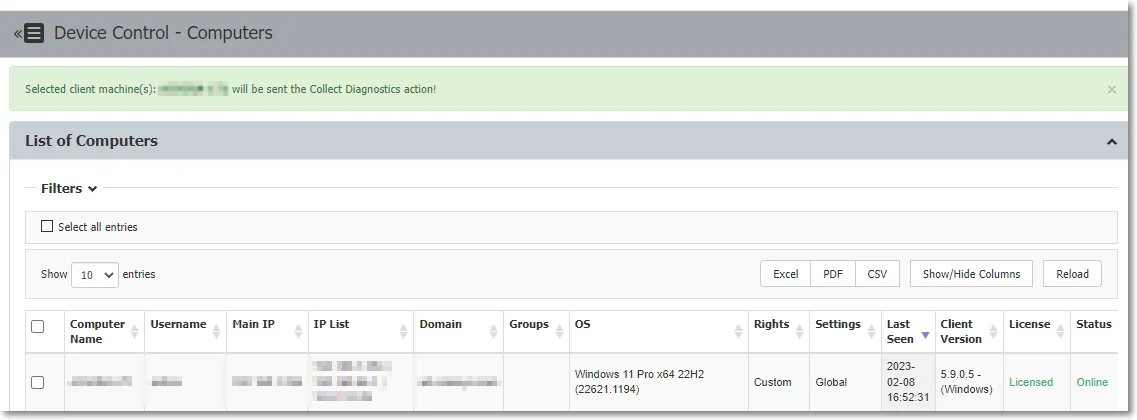
- Hover over a computer, right-click, and select Collect diagnostic - this will collect logs from a specific computer without input or knowledge from the computer user.
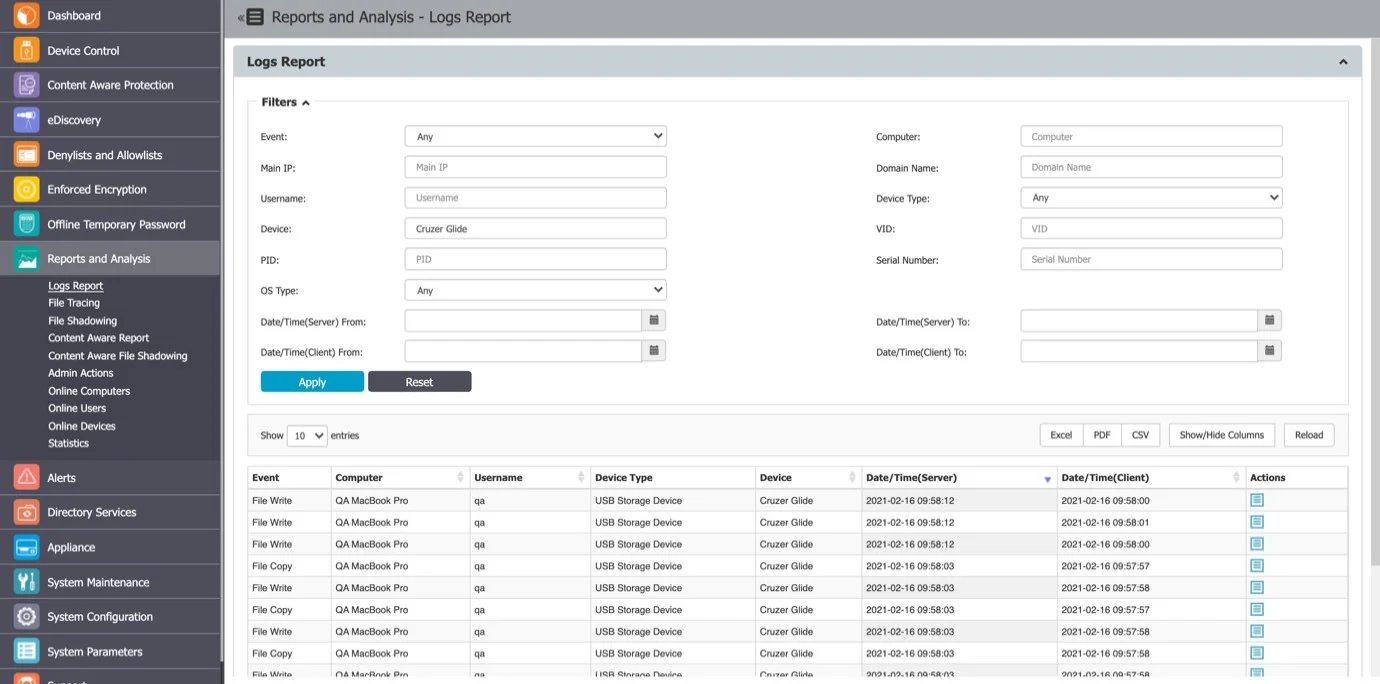
Logs will be sent to the Endpoint Protector Server on the Logs Report page, Artifact Received events are registered when diagnostic data are received.
Debug Logging Actions
To view the log actions, go to the Device Control module, on the Computers page and click the Actions column.
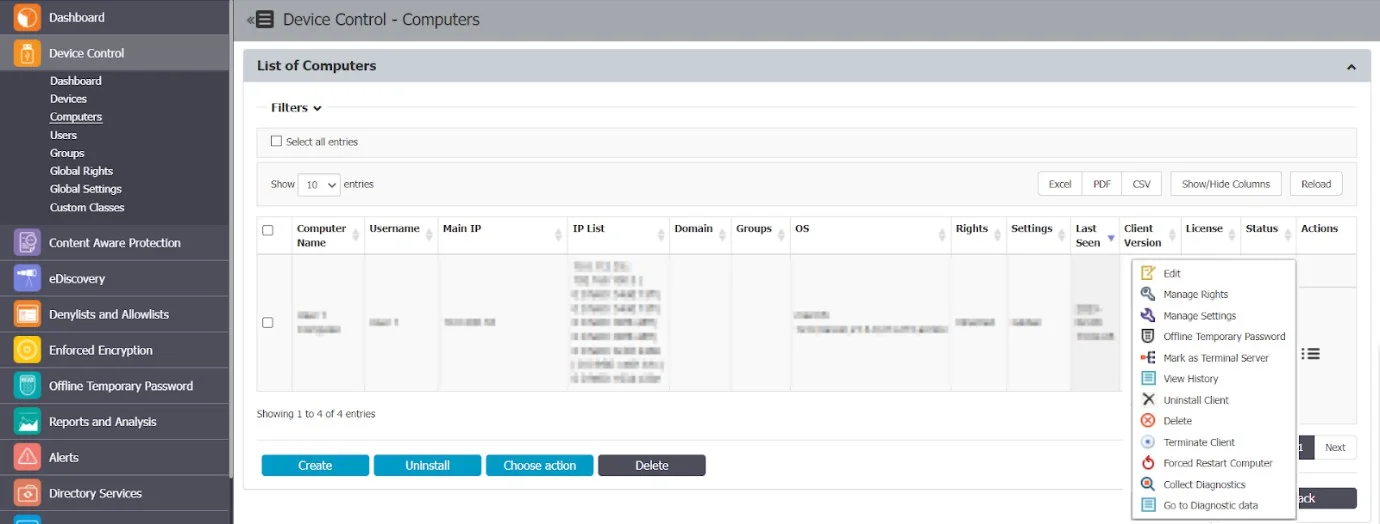
- Collect Diagnostics - registers an event when diagnostic data are requested (Artifact requested event)
- Go to Diagnostic data - this option redirects the user to the Reports and Analysis module on the Logs Report page to Artifact received type events with debug mode logs
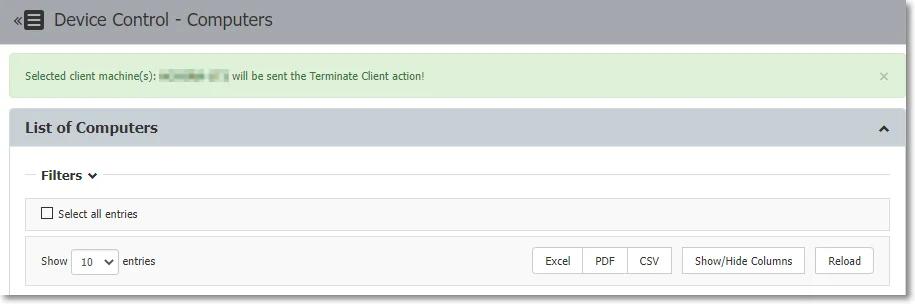
- Terminate Client - this option terminates the Endpoint Protector Client
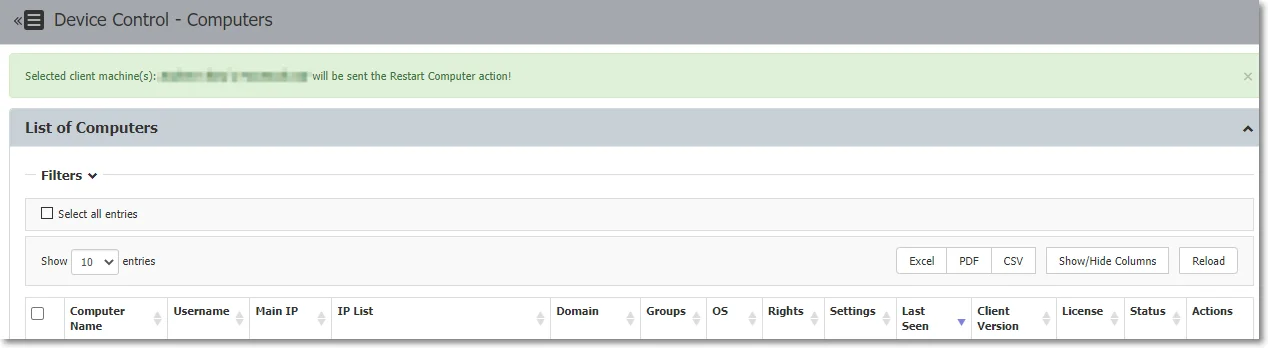
- Forced Restart Computer - this option sends a force reboot command to the computer, restarting it in 10 minutes after using the command. The user receives a message warning to avoid losing unsaved documents.
Data Obfuscation Rules
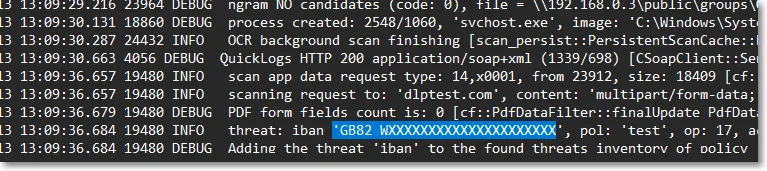
All data is obfuscated according to the following rules:
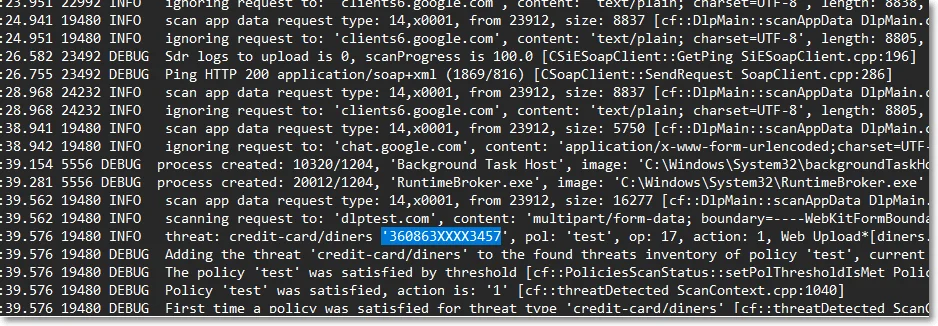
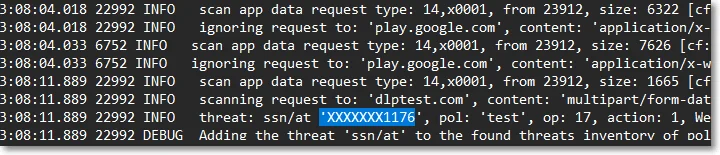
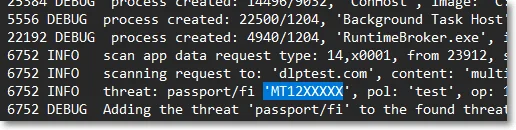
- the first 4 characters are displayed if the length of the threat is lower than 12 characters, or
- the first 6 characters are displayed if the length of the threat is longer than 12 characters
Specific use cases:
- For credit cards, the PCI Security Standards were implemented
- For SSNs, the last 4 characters are displayed
- For Brazil ID (CPF), the first 3 and the last 2 characters are obfuscated
NOTE: Data is not obfuscated for the file-type threat, file-size threat, and date threat.
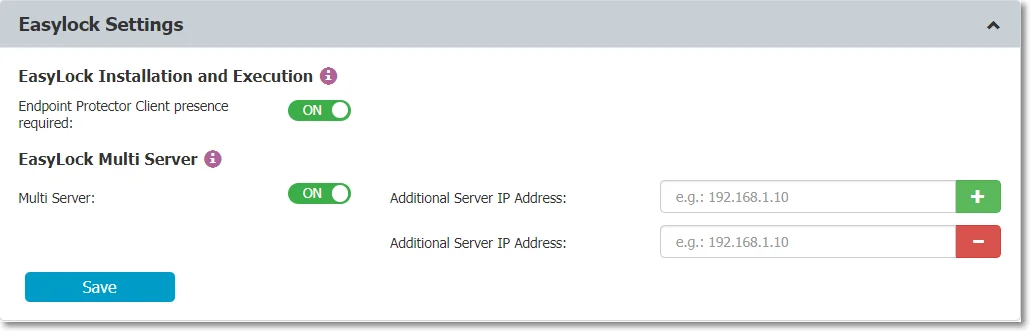
EasyLock Settings
From this section you can allow EasyLock to be installed and run only on computers that have Endpoint Protector installed or in relation to a list of trusted Endpoint Protector Servers.
Additional Information
From this section you can restore global settings to default and view the name and date when the action was performed.
Display Settings
From this section you can set the maximum number of logs displayed on the Endpoint Protector Server and the number of reports per page.
You can set a maximum number of 10 000 logs to be displayed per report. To export all entries when the log number exceeds the maximum 10 000 limit, use the Create export option or narrow the search using filters.
NOTE: The information you set on this setting will also be applied for eDiscovery.
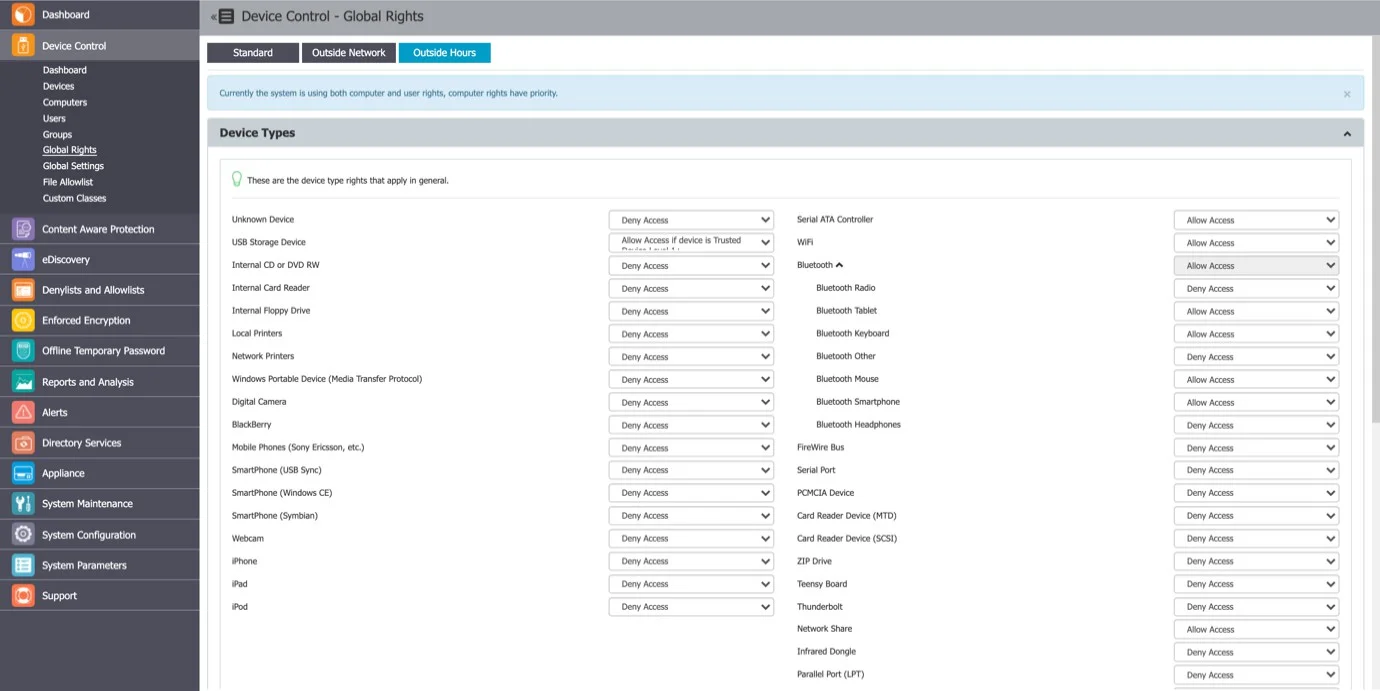
Global Rights
From this section, you can manage the entire system and specify what rights and settings apply globally, to all Endpoint Protector entities.
NOTE: If device rights or other settings will be configured granularly for entities, the priority order, starting with the highest, will be as follows:
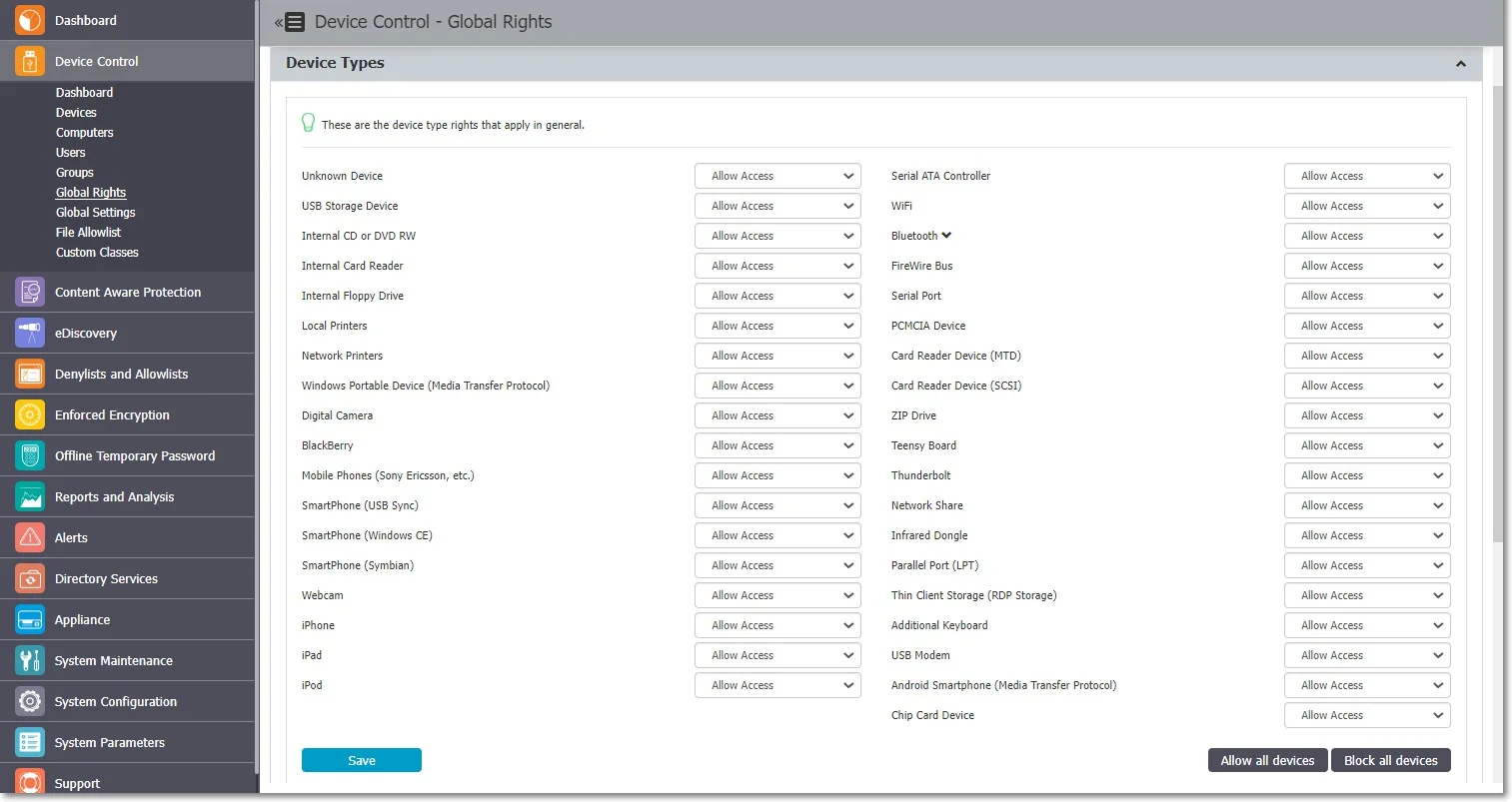
This section relates to the entire system, allowing you to specify what Device Types and Specific Devices can be accessible. While Standard Rights Policies are the default ones, Outside Hours or Outside Network Policies are also available. These are dependent on first activating settings from Global Settings.
Device Types (Standard)
Endpoint Protector supports a wide range of device types, which represent key sources of security breaches. These devices can be authorized, which makes it possible for the users to view, create, or modify their content and for administrators to view the data transferred to and from the authorized devices.
- Removable Storage Devices
- Normal USB Flash Drives, U3 and Autorun Drives, Disk on Key, etc.
- USB 1.1, USB 2.0, USB 3.0
- Memory Cards - SD Cards, MMC Cards, Compact Flash Cards, etc.
- Card Readers - internal and external
- CD/DVD-Player/Burner - internal and external
- Digital Cameras
- Smartphones / Handhelds / PDAs (includes Nokia N-Series, Blackberry, and Windows CE compatible devices, Windows Mobile devices, etc.)
- iPods / iPhones / iPads
- MP3 Player / Media Player Devices
- External HDDs / portable hard disks
- FireWire Devices
- PCMCIA Devices
- Biometric Devices
- Bluetooth
- Printers (applies to serial, USB, and LTP connection methods)
- Express Card (SSD)
- Wireless USB
- LPT/Parallel ports *applies only to storage devices
- Floppy disk drives
- Serial ATA Controllers
- Network Printers
Depending on the device type, besides the Allow and Deny Access rights, additional rights are also available. These include Read-Only Access or multiple combinations of Allow Access but with various limitations, such as Allow access but exclude from CAP scanning or Allow Access if Trusted Device Level 1 to 4.
The Trusted Device™ technology integrated within Endpoint Protector is available in four security levels, depending on the degree of protection offered by a device (trusted devices using Enforced Encryption are TD level 1).
For detailed information on Trusted Device™ and Enforced Encryption, refer to the Trusted Device™ topic.
NOTE: With the WiFi – Block if wired network is present option you can disable the WiFi connection, while a wired network connection is present. The WiFi connection will be available when the wired network is not present.
NOTE: On macOS version 14 (Sonoma) and higher, Bluetooth devices are managed only when the device is connected and visible under ‘My Devices’ in the Bluetooth section of ‘System settings’.
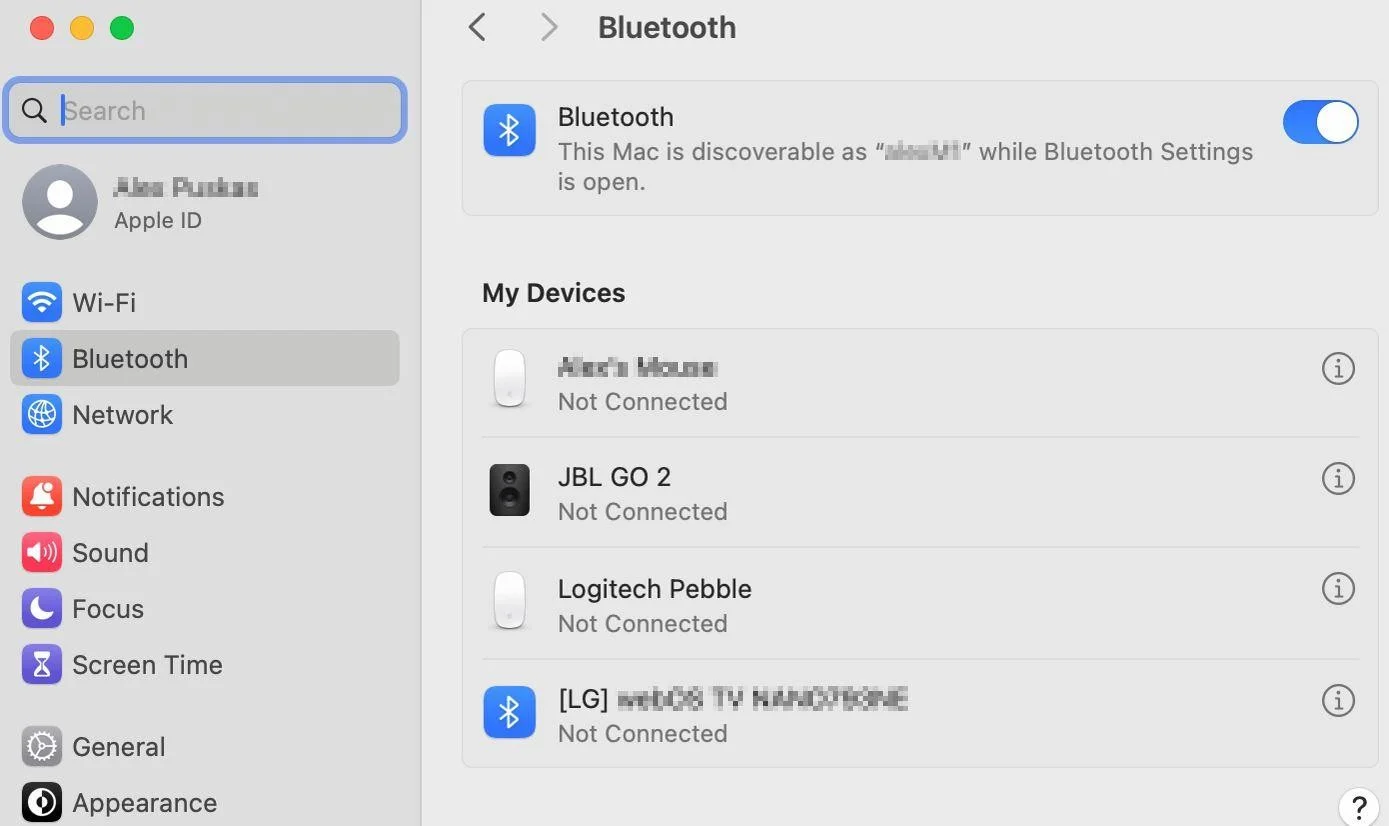
By default, the majority of device types are blocked. However, as a working internet connection or wireless keyboards are needed during the configuration process, several devices are set to Allow Access. These include Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Network Share, Additional Keyboard, and USB Modem.
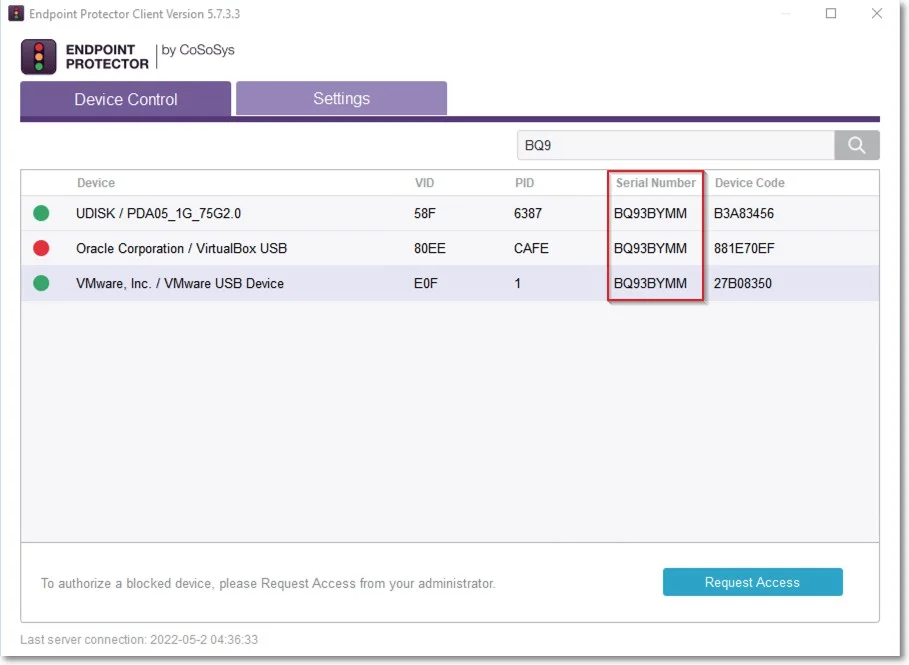
VM USB Device Usage
The VM USB device type extends Endpoint Protector applicability for VMWare and VirtualBox virtual environments.
You can also use this option to manage USB access through the virtual environment.
When using a virtual environment, the USB devices will not be displayed in the Endpoint Protector Notifier with their original names, VID and PID information. Only the original information will remain the serial number.
For example; in the below image, you can view the 3 devices detected by Endpoint Protector have different VID, PID and device code, but they all have the same serial number.
NOTE: The Endpoint Protector Client does not distinguish between USB devices (e.g. USB hard drive vs USB Webcam) by Device name/VID/PID.
Specific Devices (Standard)
From this section, you can manage access rights for a specific device.
Device rights can be set either Globally or, per Group, User, or Computer, by using the Manage Rights action from each section/entity.
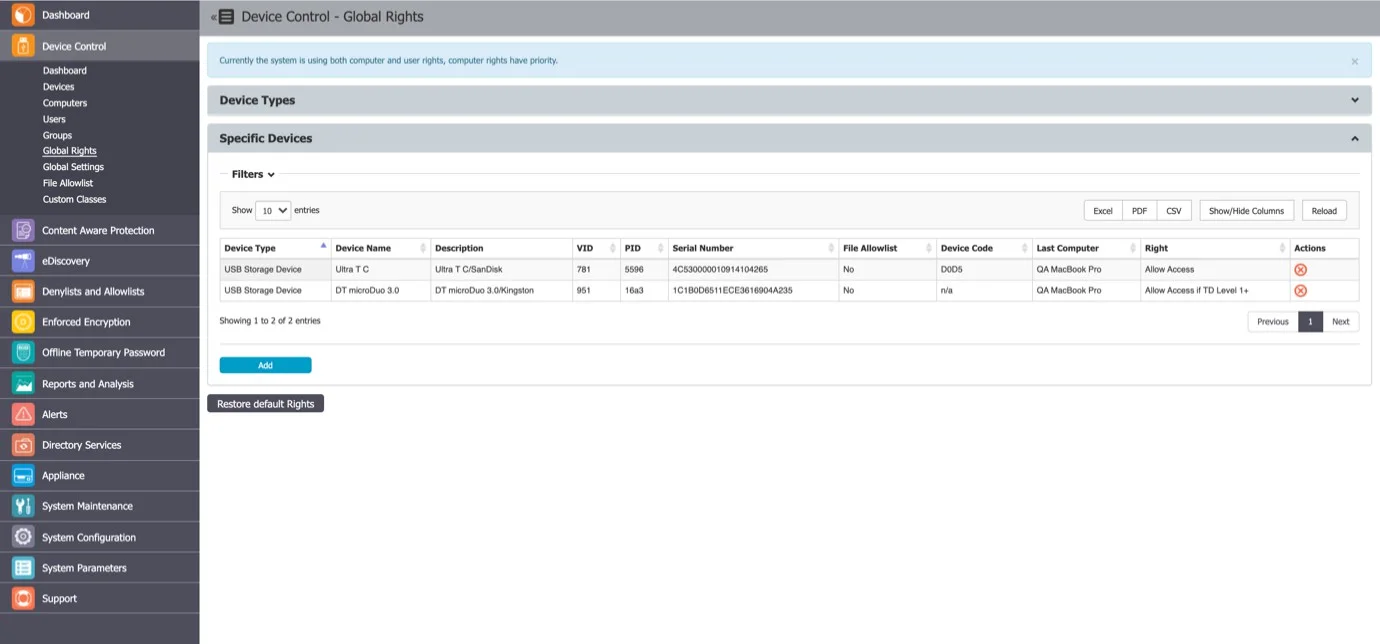
To add a new device click Add and provide the mandatory information. There are multiple ways of adding devices:
- New Device (VID, PID, Serial Number) – will allow at Step 2 to add new devices based on Vendor ID, Product ID, and Serial Number.
- Existing Device (Wizard) – will allow at Step 2 to add devices previously connected to protected computers and already in the Endpoint Protector database.
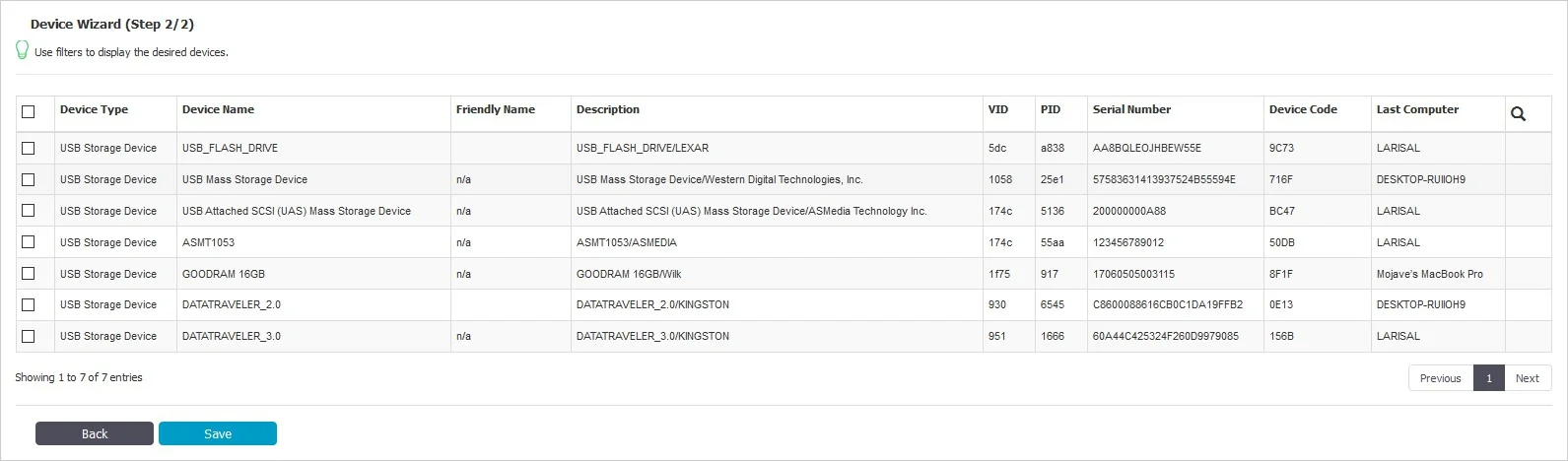
- Device Serial Number Range – will allow at Step 2 to add multiple devices at the same time, by specifying the first and last Serial Number in the range. The recommended use for this feature is for devices that have a consecutive range, with a clear, noticeable pattern.
NOTE: Although this feature can work in situations where the Serial Number range does not follow a noticeable pattern, this is not recommended. In this type of situation, some devices will be ignored by Endpoint Protector and will not have the expected effect.
- Bulk List of Devices – will allow at Step 2 to add up to 1000 devices at the same time. There are two methods to choose from, either importing a list or simply pasting the information.
The File Allowlist feature is also available for USB storage devices that have allowed access. For detailed information on using the File Allowlist, refer to the File Denylists and Allowlists topic.
Outside Network
NOTE: To use this setting, the feature needs to be enabled in the Global Settings section.
From this section, you can define fallback policies that will apply when outside the network. All of the functionalities are identical to the Standard section.
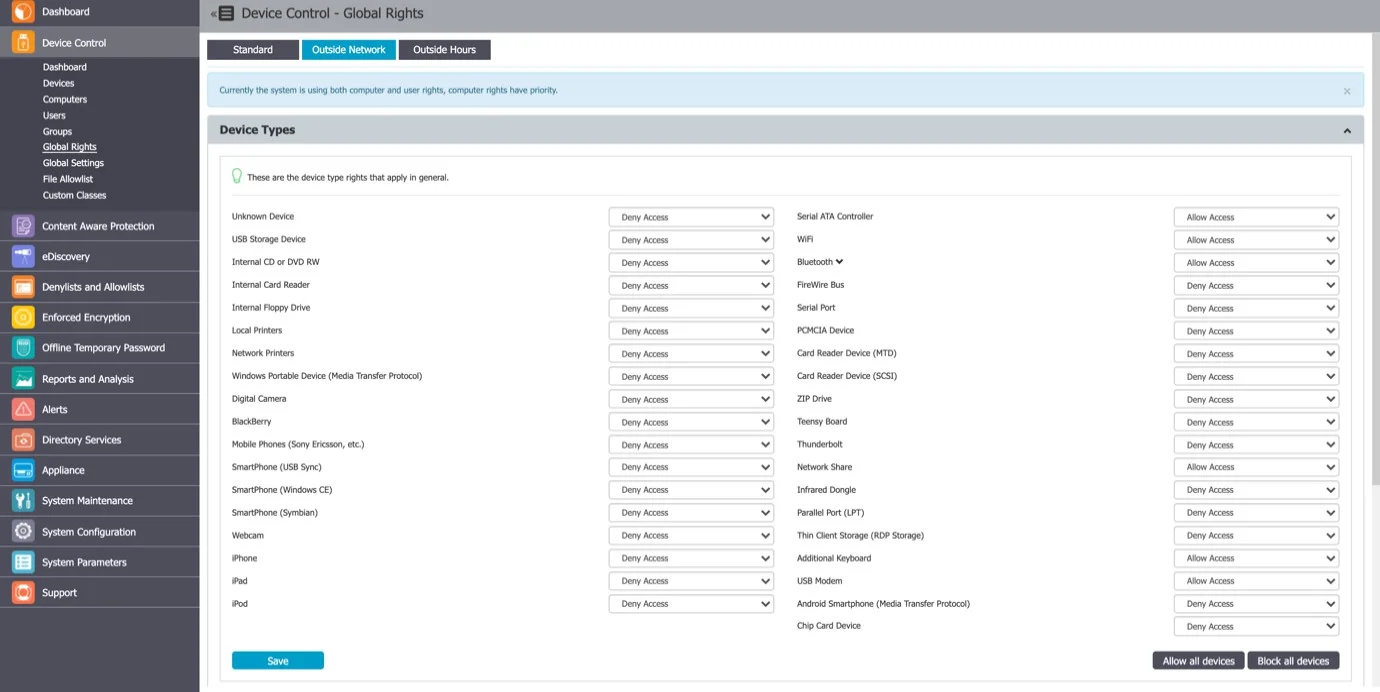
Outside Hours
NOTE: To use this setting, the feature needs to be enabled in the Global Settings section.
From this section, you can define fallback policies that will apply when outside working hours. All of the functionalities are identical to the Standard section.