Entity Model
At the heart of any successful IGA project, dwells an efficient data model.
The data involved in the project, be it reference data, identities, or from the managed systems', needs to be modeled in a way that is both relevant to the organization and to Identity Manager.
Identity Manager allows integrators to adapt the data model to the target organization, instead of forcing the organization to fit in a pre-conceived hardwired model. This philosophy has proven successful by Identity Manager's field experience and project feedback.
Entity-Relationship model
The model for all resources (that means data from the managed system, reference data and identities) is written in the Toolkit for XML Configuration in the form of an Entity-Relationship model, called the entity model.
The model is organized into cohesive connectors, one for each managed system, and one for the reference data/identity repository.
An entity model describes the shape of resources (the metadata) and how they are built from real world sources of truth (the mapping).
Metadata
The metadata of a resource is the description of the resources' shape. Using the Entity-Relationship vocabulary, it's a list of property names and types for a resource.
The metadata is written using Entity Type , Entity Type and Entity Association .
Entity types
Every resource is assigned an Entity Type that describes its shape.
It's a description of the resource: it can be a managed system's resource or a real world entity such as an identity or a department.
An Entity Type includes:
- One or more Entity Type
- Zero or more Entity Association
Entity properties
Properties are key-value pairs, with a name and type that describes the nature of the value held by the property. They are described by Entity Type .
There are two kind of properties: Scalar Properties and Navigation Properties.
Scalar Properties simply hold a value: a string, a number, a date for example.
Available types include:
StringBytesInt32(32 bits integer)Int64(64 bits integer)DateTimeBool(boolean)GuidDoubleBinary(binary file like an image)
For these types, the UI and binding system transforms the value retrieved from the database into the corresponding type for display.
Navigation Properties properties hold links between the parent resource and another resource.
Navigation Properties type is ForeignKey.
Navigation Properties are completed by an Entity Association that explicitly describe the nature of the link.
Entity association
An Entity Association describes a link between entity types. It connects a pair of navigation properties, from two Entity Types.
There are two types of navigational properties:
- mono-valued, that link to a single entity;
- multi-valued, that link to a collection of entities.
Given a navigation property A of EntityType 1, linking EntityType 1 to navigation properties B of EntityType 2, then navigation property B is called the reverse property of navigation property A and navigation property A is called the reverse property of navigation property B.
For example,
- The User entity type has the navigational property Positions (a link to zero or more_Position_ entities);
- The Position entity type has the navigational property Person (a link to zero or one_User_ entity);
- The navigational property Person is the reverse link of the navigational property Positions;
- The User entity type has the navigational property Manager (a link to zero or one_User_ entity);
- The User entity type has the navigational property Subordinates (a link to zero or more_User_ entities);
- The navigational property Subordinates is the reverse link of the navigational property Manager.
Locatable property
Some property values must be available in several languages. In this case, we define a neutral property and as many corresponding properties as languages.
The built-in InternalDisplayName property is a neutral property. Its associated properties are
named _InternalDisplayName___L{Index}_ where _Index_ reference the
Languages.
Computed property
A property can be calculated from other properties. The Entity Type element allows the expression of a computed property. It references the property (specifying the entity type's identifier and the property's identifier) and expresses the calculation based on a given entity using the Expressions.
An element <EntityPropertyExpression> can be used to calculate a scalar property or a mono-valued
navigation property. In the latter case, the expression must return an integer that corresponds to
the primary key of the target entity.
Display name
Every declared EntityType automatically has the InternalDisplayName property even if it is not
explicitly declared in the applicative configuration.
It represents a user-friendly name for EntityType that is used in the UI if needed.
Its value can be explicitly computed by an
Entity Type. Otherwise, a default value
is automatically computed by Identity Manager using the first property of the EntityType where
identifier contains the string "name". If no such property is found, the first declared property
of the EntityType is used instead.
The InternalDisplayName property will be used as a default label of the entity in the UI.
Database mapping
Resources from the resource repository are stored in the generic UR_Resources table.
This table has:
-
128 columns to store scalar properties (index 0 to 127). The first four are reserved for big scalar properties values (as many as 4000 unicode char). he other columns are limited to 442 unicode char. These columns are named C0 to C3V following a base-32 convention for naming.
-
25 columns to store mono-valued navigational properties values (index 128 to 152). These columns are named
I0toI4Nfollowing a base-32 convention for naming.
Multi-valued navigation property values are stored in the UR_ResourceLinks junction table.
Binary property values (such as pictures or files) are stored in the UR_ResourceFiles table.
Mapping
Identity Manager's Entity Model also contains a mapping between the external data and Entity Type or Entity Association. That's why entity types are organized into connectors. The mapping_connects_ entity types to external sources of truth.
This information is provided by the Entity Type Mapping, their Entity Type Mapping and Entity Association Mapping.
To build Identity Manager resources from external data found in the managed system, the entity model provides a mapping between the external data (often in the form of CSV files, see Upward Data Synchronization) and entity properties. This information is provided by the Entity Type Mapping, their Entity Type Mappingand Entity Association Mapping.
Every Entity Type Mappingmaps a CSV column to a scalar Entity Type.
Every Entity Association Mapping maps a CSV column to a navigation Entity Type.
Format
When exporting entries from an external system, the results are usually retrieved as simple strings, written in a CSV file, and imported into the Identity Manager Database as-is. But an external system will rarely uses the same format as Identity Manager to store objects such as dates.
Let's take, for example, a case where we want to store an employee's start date:
- In the external system, the date is stored as a string with the format
2020-09-29 22:00:00. - In Identity Manager, dates are stored as strings in the format
20200929220000
We need to transform the input data, from the export, into something readable by Identity Manager and, when writing to the external system, transform Identity Manager's data back into something readable by the external system.
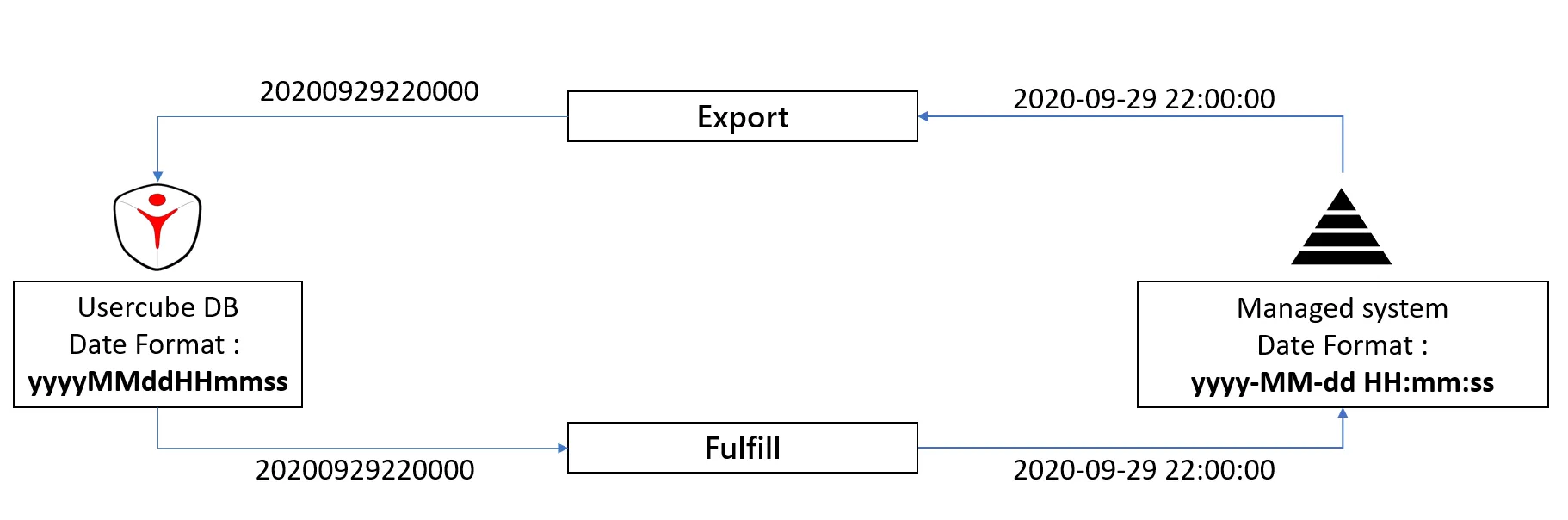
The format used in the external system can be provided through the Entity Type Mapping using the References: Format for the EntityPropertyMapping attribute to help Identity Manager to convert data appropriately.
If the field in the external system is not forced to a specific value type, but is free-form
(example: a string field in which date values are stored but which can sometimes hold other values),
we strongly recommend not using the Format attribute to prevent inconsistent user input in the
external system.
Primary key
When writing an Entity Type Mapping, one of the scalar properties should be chosen as Entity Type Mapping. This property will be used by Identity Manager to uniquely identify a resource. It is hence crucial to choose carefully as many of Identity Manager's processes and optimizations depend on this choice.
SQL views
The UR_Resource table contains resources from all the connectors, for all the Entity Types.
Columns names are not semantically meaningful because they have generic I*/C* names. For this
reason, Identity Manager provides SQL views to help the user explore the resource repository from
the database. The views are useful to understand how Identity Manager works or to debug a faulty
configuration.
SQL Views are built by the Create Database Views Task.
SQL Views created by this tool are identified in the database by a zz_ prefix.
Created views are not used by the Identity Manager engine directly. Identity Manager's engine always
creates, reads, updates and deletes from the UR_* tables.
Records
The entity model is enhanced with records to handle positions and movements of staff. See the Identity Management topic for additional information.