Risk Management
The Risk Management module provides tools for identifying assignments of entitlement that pose a security risk. The module helps analyze and mitigate different kinds of risks such as Segregation of Duties or High Privilege. This is the basis for auditing and performing access certifications with a risk-based method.
Overview
A Risk describes a sensitive situation of entitlement assignments that needs to be monitored.
Risk management is essential to auditing. End-users can define models of risks, assigned to identities based on their entitlement assignments. This action identifies identities whose entitlement landscape might pose a threat or a surface of attack. The identified risks for a given identity inform the auditor about the exact nature of the threat to help making decisions and finding methods of remediation.
To identify the identities that represent the highest risk, Identity Manager computes a risk score for all identities, based on both the roles already assigned and the roles that are subject of the current request. The higher the score, the higher the threat. The identities with the highest risk scores are the priority of the next Access Certification campaign.
See the Manage Risks topic for additional information on how to use the risk management module to identify entitlement assignments that pose a security risk.
Risk Definition
A Risk is an object that describes a sensitive situation of assignments of entitlements.
The assignment of a risk to an identity highlights, for a potential auditor, the need to closely reconsider said the assignments of said identity.
A risk is always:
- part of a Policy;
- assigned to identities belonging to a specific entity type that was decided during the risk creation;
- organized inside a type;
- linked to an exemption policy.
Risk Type
The type of a risk informs the auditor about the exact nature of the situation that the risk describes. It helps understand the possible causes, the importance of the security threat and methods of remediation.
Identity Manager supports two types of risks:
- a segregation-of-duties risk identifies a threat due to the conjunction of two or more fine-grained entitlements for the same identity, for example if an identity requests an entitlement and is also the validator for said entitlement;
- a high-privilege risk identifies a threat due to the assignment of one or more highly sensitive
entitlements, for example the
Domain Usergroup in an Active Directory.
Risk Exemption Policy
All risks are assigned an exemption policy that defines the behavior of Identity Manager regarding risks when entitlements are manually requested.
Blocking
Risk-triggering permission requests can be forbidden with the blocking exemption policy. If at least one of the detected risks in the requested entitlement set has the blocking exemption policy, then Identity Manager does not allow the set to be requested at all. A message is displayed and the request must be cancelled:
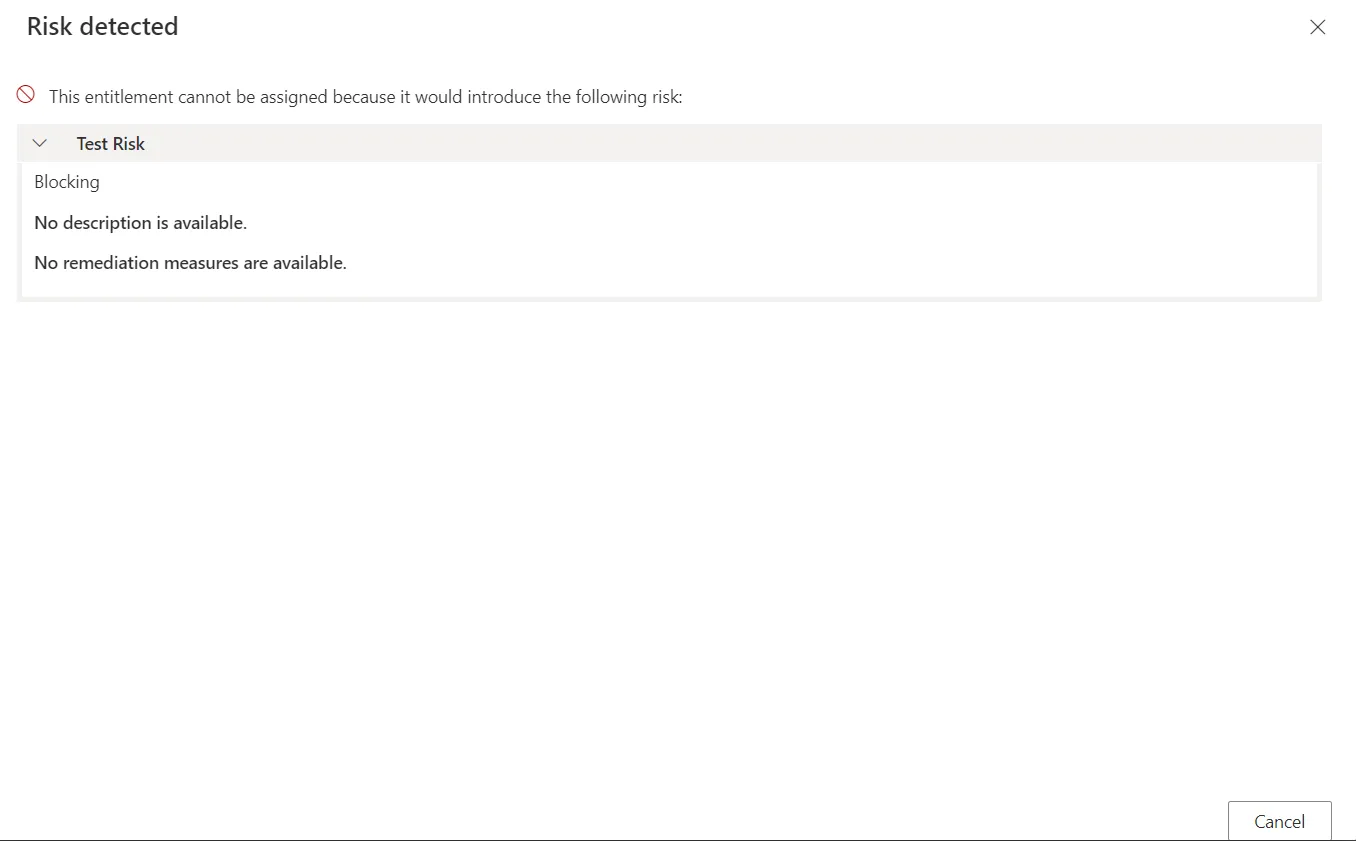
Approval Required
Yet, instead of being unilaterally forbidden, risk-triggering permission requests can be authorized with an additional role review approval with the approval required exemption policy. If at least one of the detected risks in the requested entitlement set has the approval required exemption policy, then Identity Manager adds a step where this new set must be reviewed by a knowledgeable user like a security officer. A message is displayed and the request can be continued or cancelled:
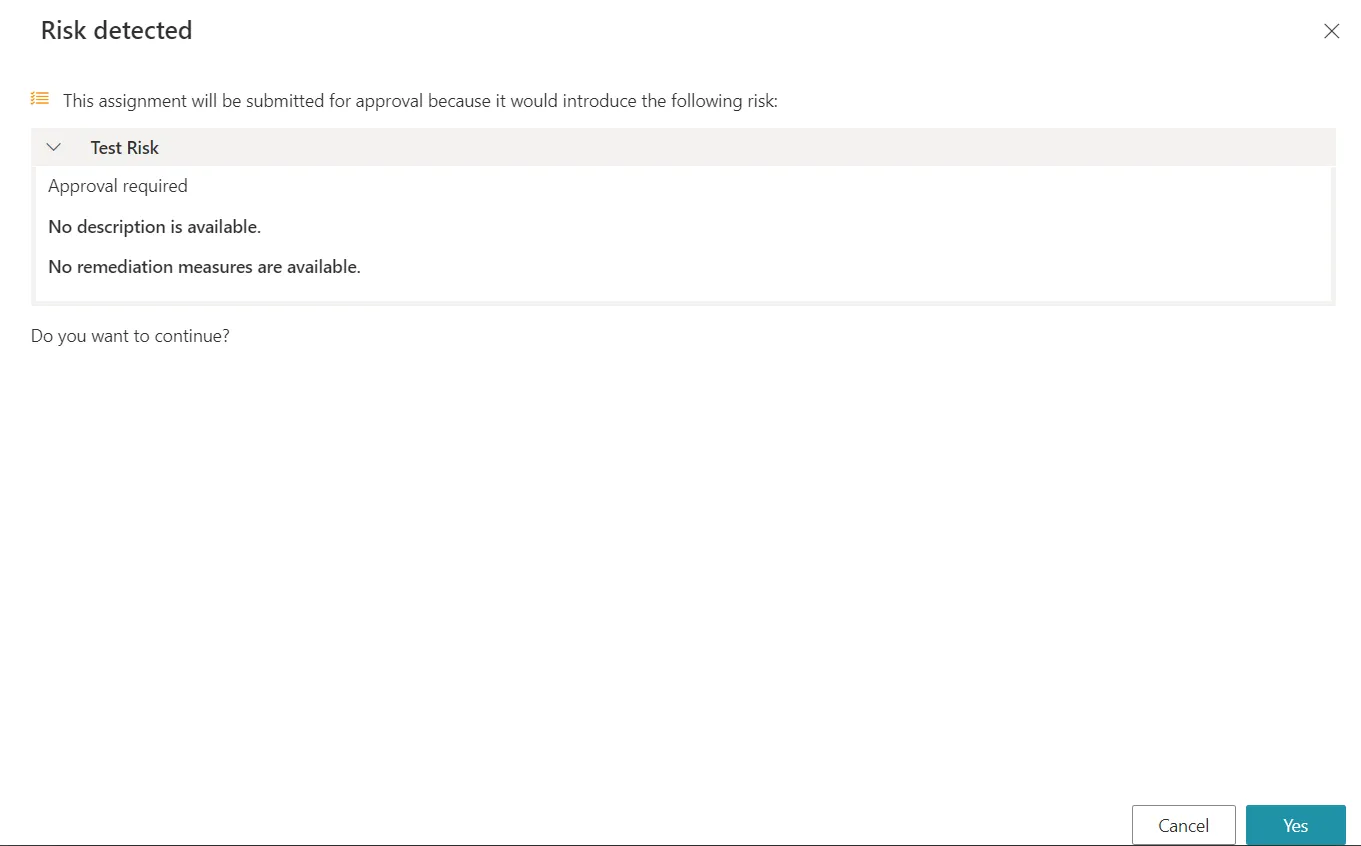
If the request is performed, then a line appears on the Role Review screen.
The workflow state of said request is Manual, Pending approval (risks) and shows the following
risk icon.
Warning
Risk-triggering permissions can also be allowed with only a warning with the warning exemption policy. If all detected risks in the requested entitlement set has the warning exemption policy, then Identity Manager displays a message and the request can be continued or cancelled:
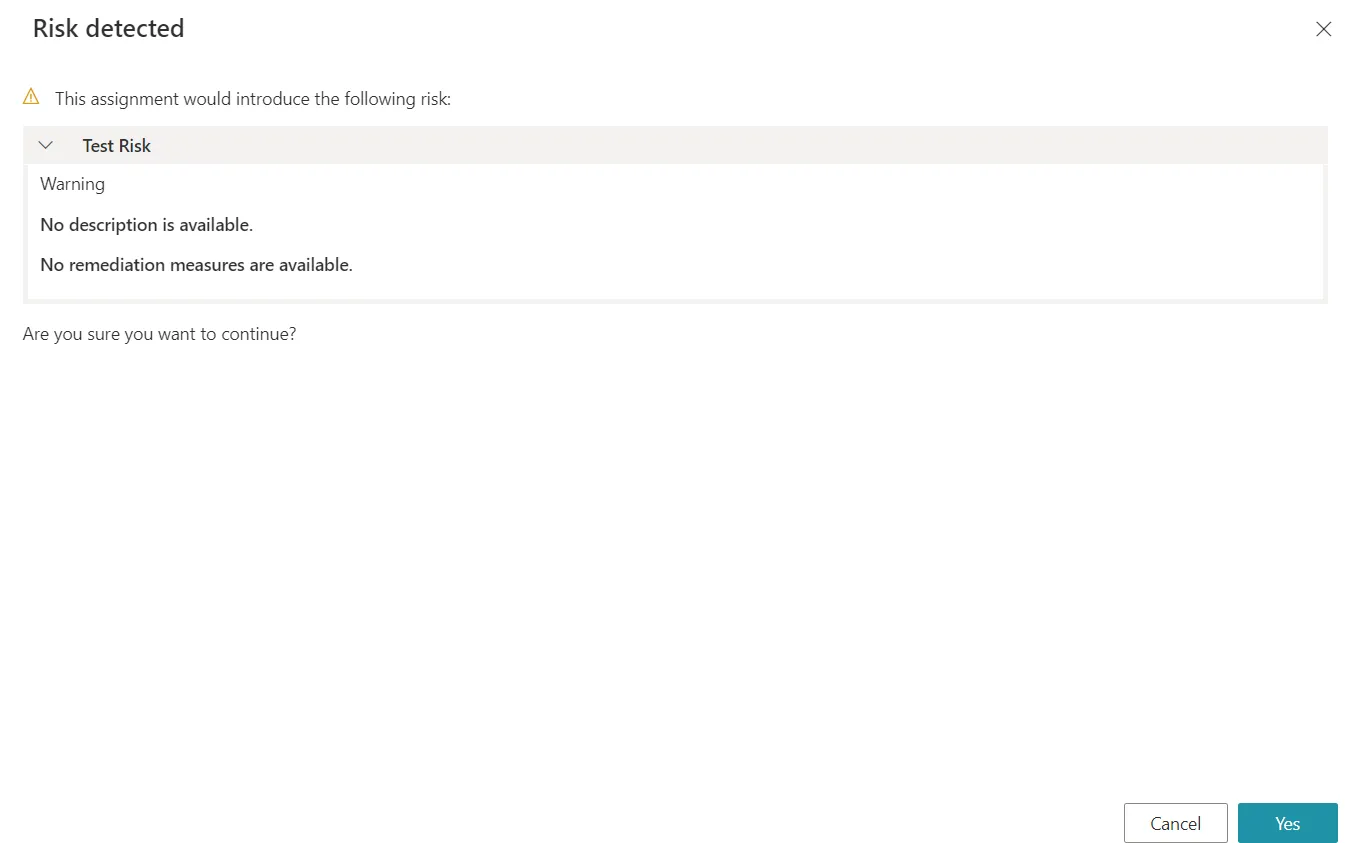
Upon Profile
The blocking and approval required exemption policies can be ignored according to the profile of the user and their scope of responsibility, with respectively the blocking upon profile and approval required upon profile exemption policies. Then they can be assimilated to the warning policy if the user has the right permission, respectively /ProvisioningPolicy/Risk/OverrideBlocking and /ProvisioningPolicy/Risk/OverrideApproval, otherwise they behave like the blocking and approval required policies.
Like in the example below, the two permissions can be chained together. For the connected user, a risk that would have been blocking otherwise, is just a warning.
<AccessControlRule Profile="Administrator" EntityType="Risk" Identifier="Administrator_Risk_Override" DisplayName_L1="Administrator_Risk_Override"> <Entry Permission="/ProvisioningPolicy/Risk/OverrideBlocking" CanExecute="true" /> <Entry Permission="/ProvisioningPolicy/Risk/OverrideApproval" CanExecute="true" /> </AccessControlRule>
Risk Assignment
Risk Rules
Risk are assigned to resources manually by a knowledgeable user or automatically, by the Evaluate Policy algorithm.
When a risk is assigned to a resource, a new identified risk is created under the
UP_IdentifiedRisks table.
Automatic assignment of risks is based on Risk rules. For each new fine-grained assignment on a resource, risk rules are applied. If one of the rules matches the resource state, the related risks are assigned to the resource. Those rules are themselves based on fine-grained entitlements, such as an Active Directory account or group membership, modeled by the navigation rules within Identity Manager. See the Resource Type topic for additional information.
A risk rule states that a risk is assigned to a resource if the resource has one or several specific fine-grained entitlements. The number of triggering entitlements depends on the risk type. For example, the segregation-of-duties risks depends on at least two entitlements. The other types of risk depend on one or more entitlements.
Fine-grained entitlement
A fine-grained entitlement assigned to a resource-identity in Identity Manager is modeled by navigation property values of the resources owned by the identity.
To write a risk rule, the end-user has to describe a fine-grained entitlement for a resource-identity.
This is the way:
- Choose an Entity Type of which the resource-identity could be owner.
- Choose a navigation property of that entity type.
- Choose a value for that navigation property. The value would be a resource from the unified resource repository.
This final value is a fine-grained entitlement, linked to the owner resource-identity through the navigation property and the ownership relationship.
Risk Score
Once Risk are assigned to identities, Identity Manager computes a risk score for each relevant identity.
This score allows an auditor to prioritize the Access Certification campaign. The identity with the highest risk score poses a more serious security threat and has to be handled first.
During access certification, assignments that are responsible for triggering the risk will be examined and then, kept or discarded.
The risk score computation is performed by the risk score task.
Manage Risks
How to use the Risk Management module to identify entitlement assignments that pose a security risk, especially about segregation of duties and high privileges.
Overview
A Risk describes a sensitive situation in which entitlement assignments need to be monitored for security purposes. Examples include:
- Segregation of duties: a situation where at least two entitlements pose a risk when assigned to the same identity.
- High privilege: a particularly sensitive entitlement.
Risk Management is essential to auditing. Among other things, it allows auditors to:
- Identify the identities representing the highest security risk.
- Compute the corresponding risk score.
- Schedule and Perform Access Certification accordingly.
Using risks involves three steps:
- Create a risk: declare the nature of the risk.
- Create risk rules: create the rules that assign risks to identities, depending on identities' entitlement assignments.
- Monitor risks: via the Identified Risks screen or certification campaigns.
Participants and Artifacts
Integrators may need the help of the application owner, security manager and role model officers to assess risks inherent to entitlements.
| Input | Output |
|---|---|
| Identity repository (required) Role catalog (required) | Risks catalog |
See the Create the Workforce Repository and Create Roles in the Role Catalog topics for additional information.
Create a Risk
Create a risk by proceeding as follows:
-
On the home page in the Configuration section, click on Risks.
-
On the risks page, click on the addition button at the top right corner.
-
Fill in the fields.
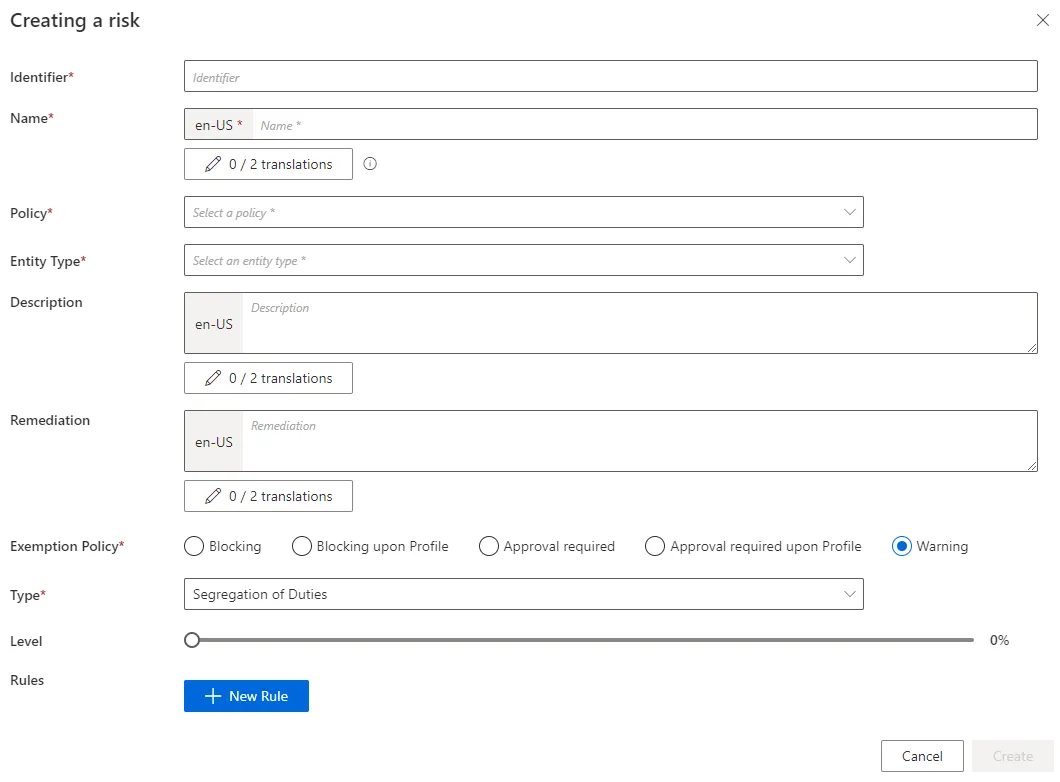
Identifier: must be unique among risks and without any whitespace.Name: will be displayed in the UI to identify the risk.Policy: Create a Policy in which the risk exists.Entity Type: Create an Entity Type targeted by the risk.Description: explanation of the risk that will be displayed with the exemption policy message.Remediation: potential alternative solutions that will be displayed with the exemption policy message.Exemption PolicySee the Risk Management topic for additional information.TypeLevel: risk level that is used to compute risk scores.Rules: a risk is based on the union of rules, themselves based on the intersection of rule items. A rule item specifies the risk-triggering resource(s). A high-privilege risk must contain at least one rule with one rule item. A segregation-of-duties risk must contain at least two rule items in the same rule.
When risks are based on the exemption policy called Approval required, the corresponding role requests appear on the Role Review screen with a specific workflow state. See below this note. See the Reconcile a Role topic for additional information.
Write risk rules
A risk rule is simply the condition that triggers the assignment of a risk to an identity, depending on the identity's entitlements.
Within Identity Manager, an entitlement assigned to an identity is represented by the value of a given navigation property, in a resource owned by said identity. See the Create an Entity Type topic for additional information.
For example, imagine that we want to grant unlimited Internet access to the administrator profile of an identity. This entitlement won't be assigned directly to the identity but to their AD administration account. In our Active Directory, there is a resource called
DL-INTERNET-Restrictedidentified from among AD entries as a group. Therefore, we need to add this group membership to the properties of the identity's AD account, usingDL-INTERNET-Restrictedas a value of thememberOfproperty. -
Choose the resource type to be targetted by the risk. See the Categorize Resources topic for additional information.
We choose
AD User (administration)to prevent this situation from happening in our example. -
Choose the navigation property that corresponds to the situation.
memberOfin our example. -
Choose a value for this navigation property. The value would be a resource from the unified resource repository. See the Identity Management topic for additional information.
The group
DL-INTERNET-Restrictedin our example.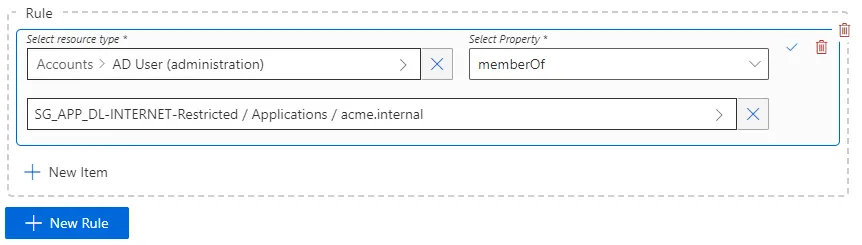
This final value is an entitlement, linked to the owner identity through the navigation property and the ownership relationship.
This final value is an entitlement, linked to the owner identity through the navigation property and the ownership relationship.
In our example, a risk is identified for a person as soon as their administration AD account is part of the
DL-INTERNET-Restrictedgroup. -
Click on Create.
Risks are taken into account from the moment the
Compute Resource Risk Scorestask runs (or the complete job which contains said task).The
Compute Resource Risk Scorestask doesn't need to be launched right away, but new risks can't be identified before it runs at least once.
Monitor Identified Risks
After creating at least one risk and computing risk scores, identified risks are listed on the Identified Risks screen, accessible from the home page in the Administration section.
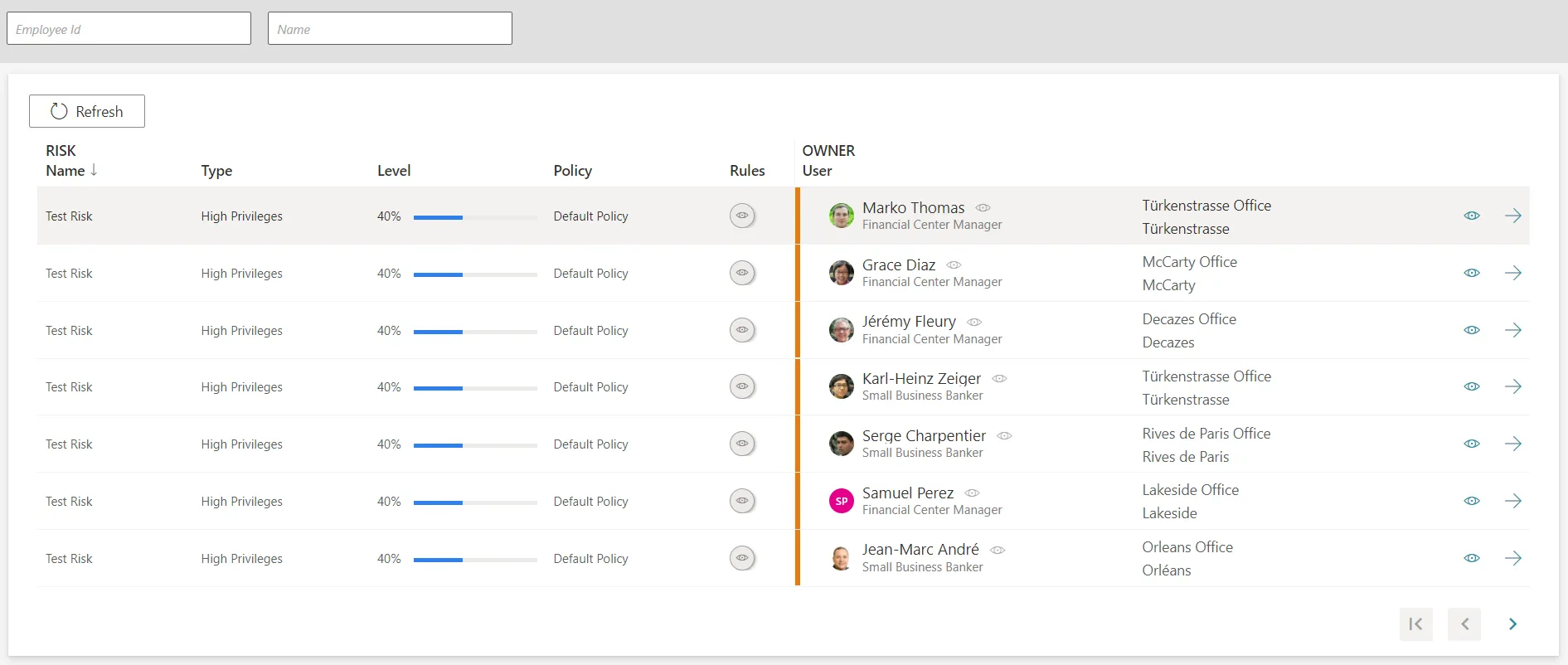
For a given identity in the list, user information can be viewed and accessed by clicking respectively on the eye and arrow buttons on the right-hand side.
Impact of Modifications
Modifications in a risk are taken into account only after running the Compute Risk Scores task.
Therefore, risk scores are computed according to the new parameters.
After a modification: while risk scores are computed for all identities and assignments (pre-existing and newly created), a modified exemption policy is applied only to future entitlement assignments. For example, changing the exemption policy of a risk from warning to blocking won't remove entitlements from the identities who already have them. But future assignments are going to be blocked.
The deletion of a risk simply triggers the computation of risk scores during the next
Compute Risk Scores task, and removes any exemption policy steps in an assignment request. See the
Risk Management topic for additional
information.
Verify Risk Management
In order to verify the process, assign to a fake identity a permission that is supposed to trigger the created risk, and check the consequences:
- The message displayed at the end of the entitlement request must correspond to the configuration of the exemption policy. See the Risk Management topic for additional information.
- Once the entitlement is assigned, a line must appear on the Identified Risks page.