Predefining rights
What are predefined rights?
Permissions for organisational structures can be carried out separately for every record. Although this method enables you to very closely control every intended permission structure, it is not really efficient. On the one hand, there is too much configuration work involved, while on the other hand, there is a danger that people who should also receive permissions to access data are forgotten. In addition, many users should not even have the right to set permissions. “Predefining rights” is a suitable method to simplify the permissions and reduce error rates by using automated processes. This page covers the configuration of predefined rights, please also refer to the sections Working with predefined rights and their Scope of validity for predefined rights.
Organisational structures as a basis
Organisational structure can be very useful in many areas in Netwrix Password Secure. In this example, they provide the basic framework for the automated granting of rights. In the broadest sense, these organisational structures should always be entered in accordance with existing departments in a company. The following example specifically focuses on an IT department. The following 3 hierarchies (Roles) have been defined within this IT department:
- IT employee
- IT manager
- Administrator
Predefine rights
In general, a senior employee is granted more extensive rights than those granted to a trainee. This hierarchy and the associated permission structure can be predefined. In the OOrganisational structure module, we now select those OUs (departments) for which rights should be predefined and select *predefine rights” in the ribbon.
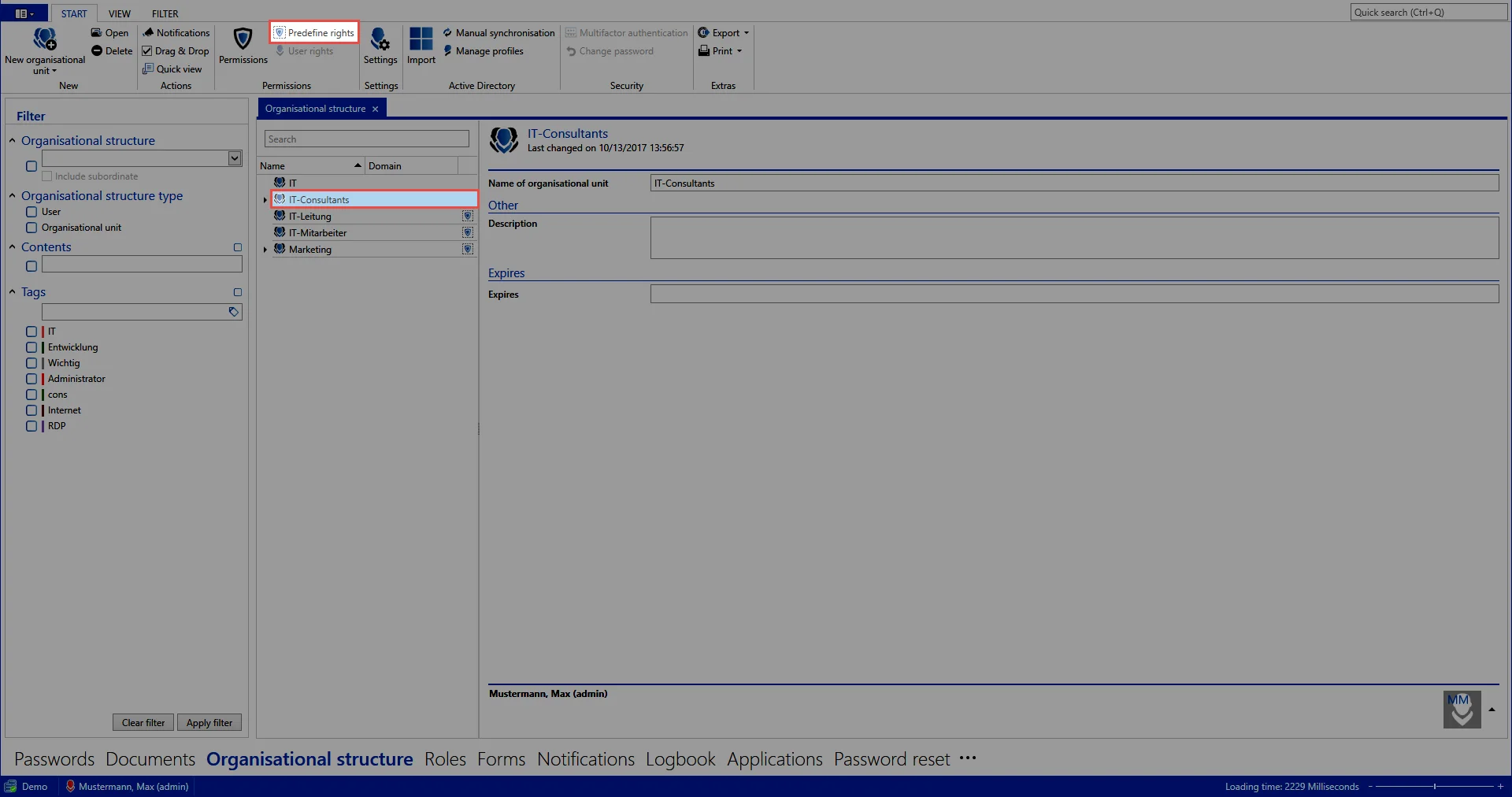
- Creating the first template group: A new window will appear after clicking on the icon for adding a new template group (green arrow) in which a meaningful name for the template group should be entered.
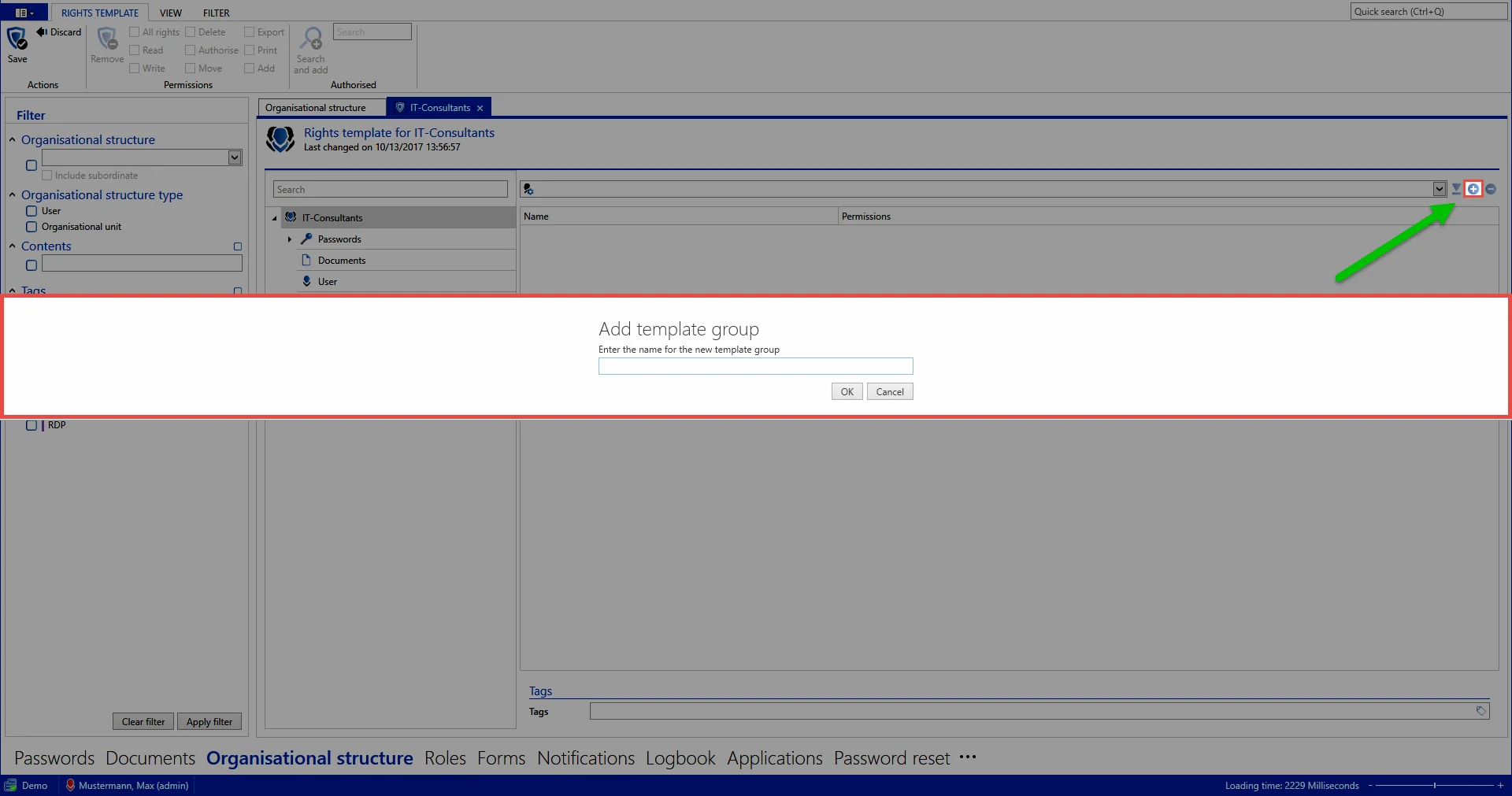
Roles and users can now be added to this template via the ribbon or through the context menu (right mouse click). This was already completed in the example. The role IT employee only has the "read permission", the IT manager also has the "write permission" and the capability of managing permissions. Administrators possess all available permissions. Configuration of the permission structures is explained in Manual setting of permissions.
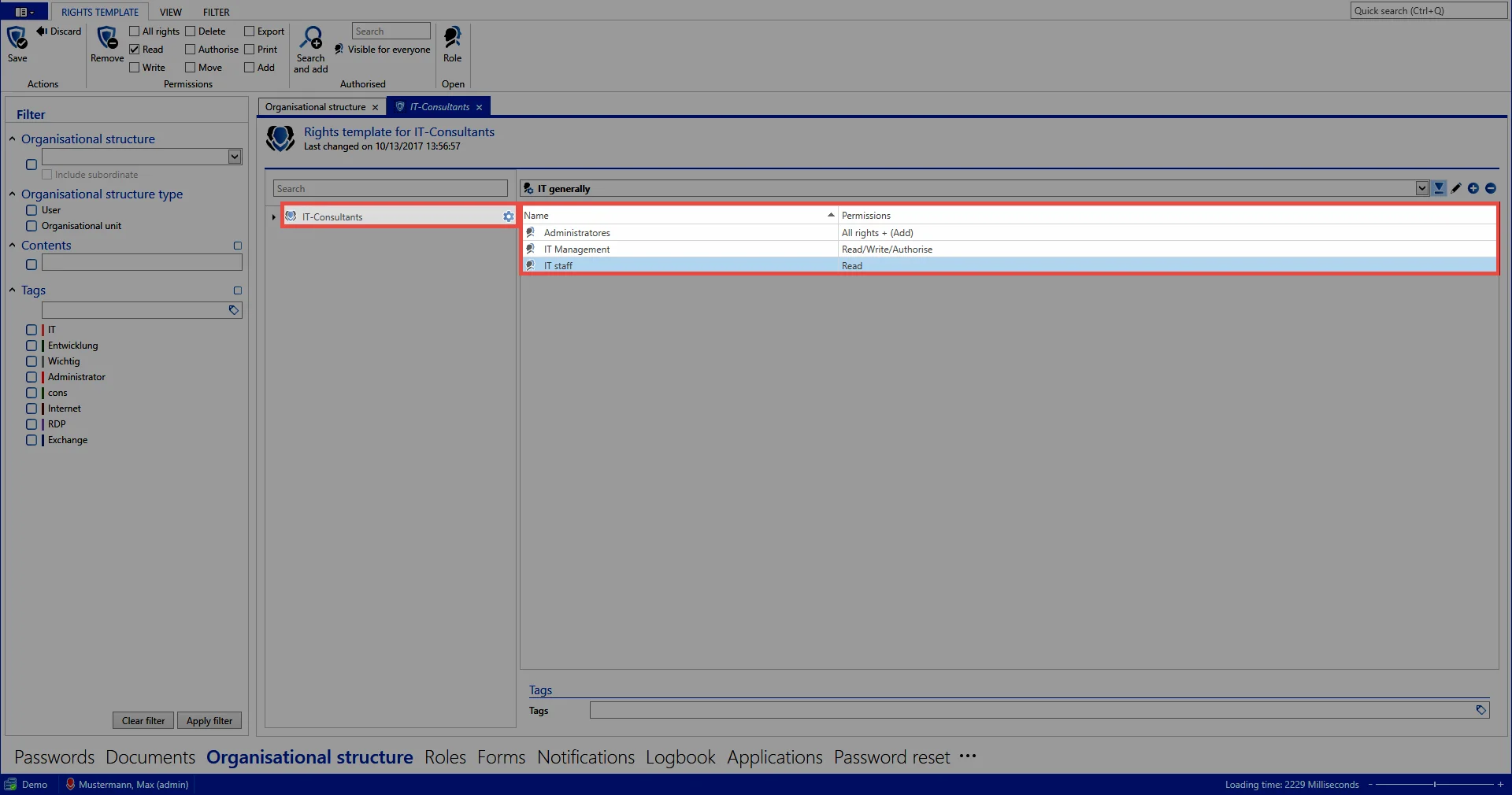
Adding other template groups
It is also possible to configure several different right templates within one department. This may be necessary e.g. if there are several areas of competency within one department which should each receive different permissions. Alongside the IT general area, the template groups Exchange and Firewall have also been defined below.
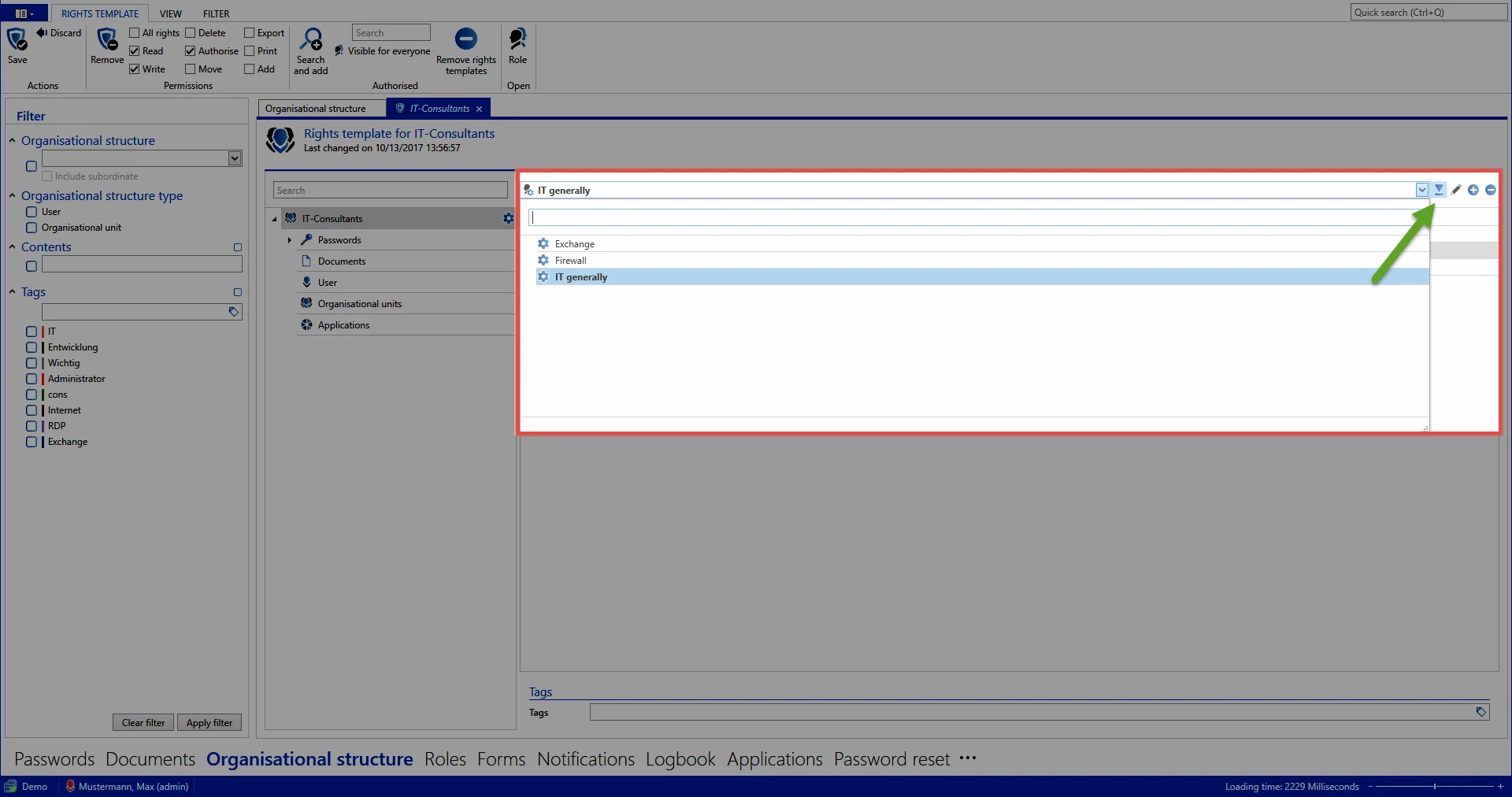
A default template group can be defined directly next to the drop-down menu for selecting the template group (green arrow). This is always pre-configured when you select “IT” as the OU to save records.
Issuing tags for predefining rights
In the same way that permissions are defined within right templates, it is also possible to automatically set tags. Their configuration is carried out in the same way as issuing Tags for records.
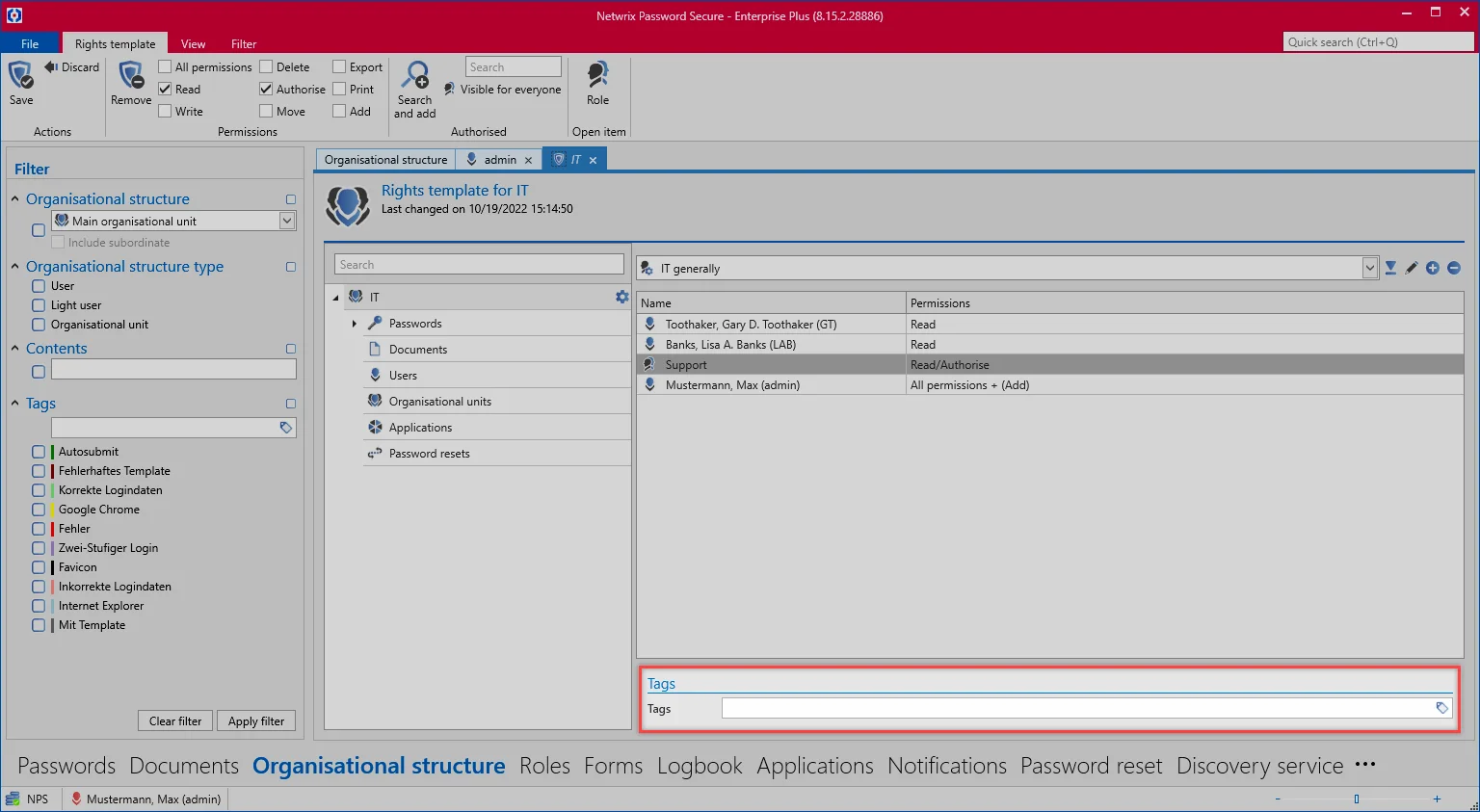
This process ensures that a special tag is automatically issued when using a certain template group. Example cases can be found in the Working with predefined rights.
Relevant user rights
User rights for predefined rights
The user rights section provides all of the basic information required for handling user rights . Nevertheless, the four user rights related to “predefining rights” are explained below.
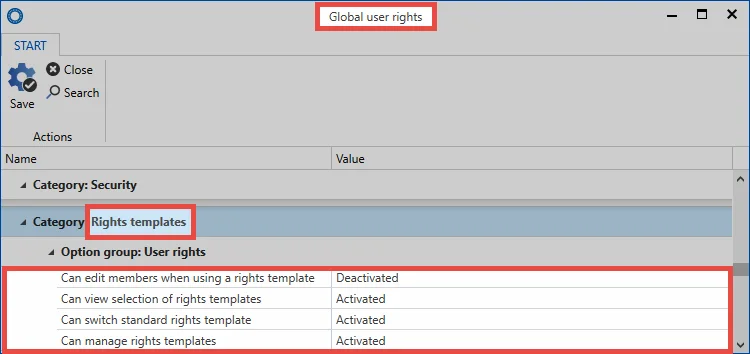
- Can switch default rights templates: When selecting the rights template, a diverse range of rights template groups can be selected. To be able to select a different template to the default template, the right “Can switch default rights templates” is required. If this right has not been granted, you are forced to use the default template.
- Can manage rights templates: If the user has the right to manage rights templates, they can open the management function for the rights template via the button “predefine rights”. To receive full rights to manage the rights templates for an organisational unit, the rights “read” and “authorize” are required for the corresponding organisational unit.
- Can view selection of rights templates: This right controls whether the rights template selection function is displayed or not when creating new records. If this right has not been granted, the user is thus not able to see for which roles and users the user rights are being defined.
- Can remove members from rights templates: Roles defined within the rights templates cannot be removed without this right. If this right has not been granted, the roles defined in the templates are always authorized for records in this organisational structure. If the user right is activated: The user can remove the roles via the “x” icon:
Scope of validity for predefined rights
In general, all of the predefined rights for an organisational structure are applied to all underlying objects. These objects could be passwords, forms, form fields documents, users, applications or also other nested organisational structures in the hierarchy. In the following example, the rights template IT general has been defined for the organisational unit IT.
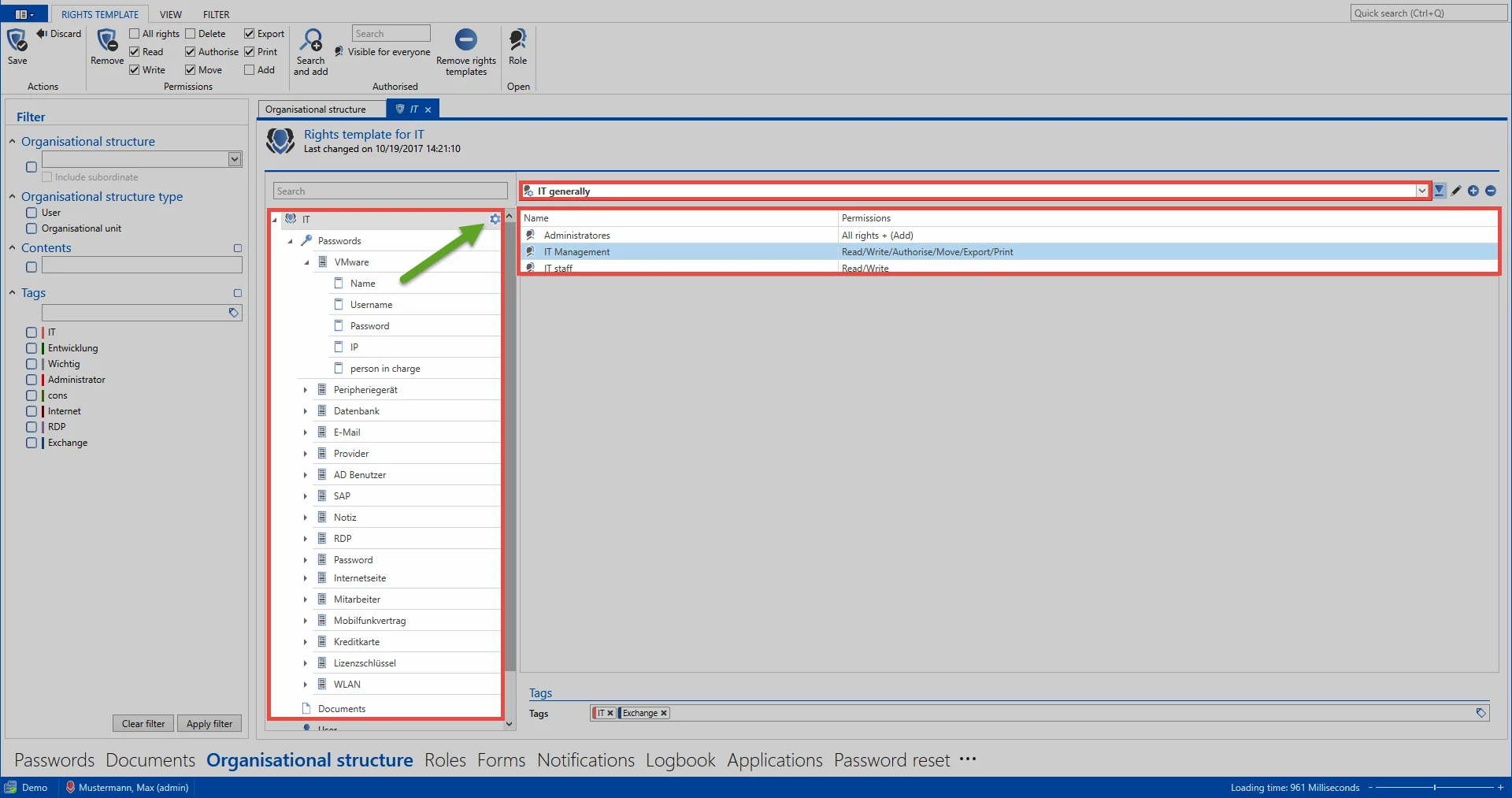
If this type of “preset” has been defined, the corresponding icon is displayed at the corresponding level (= green arrow). As no other icons exist below this level, this means that the preset is valid for all underlying objects.
The following example shows how a preset can be defined for when the “password” form is used that not only grants the existing permissions to the roles but also provides the sales manager with read rights.
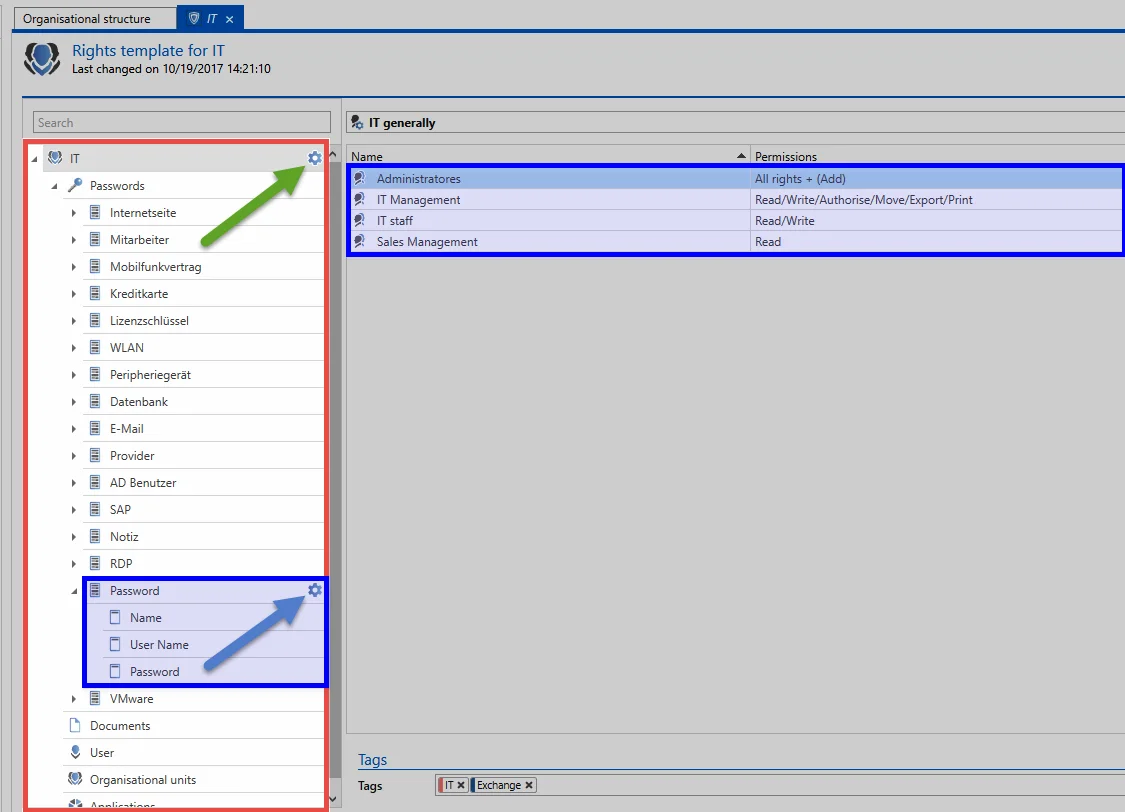
As can be seen, the preset “IT general” is valid for all objects. An exception here is the “password” form because a unique preset has been defined for this form (blue arrow). As a result, all records created using the “password” form receive permissions as defined in this preset (incl. the sales manager).
Working with predefined rights
Using predefined rights when creating passwords
After you have configured Predefining rights, you can then use them to create new records. Proceed here as follows:
- Select the password module
- “New password” via the ribbon
- Select a form
In the next window to appear, the organisational unit “IT” and the template group “Exchange” are selected.
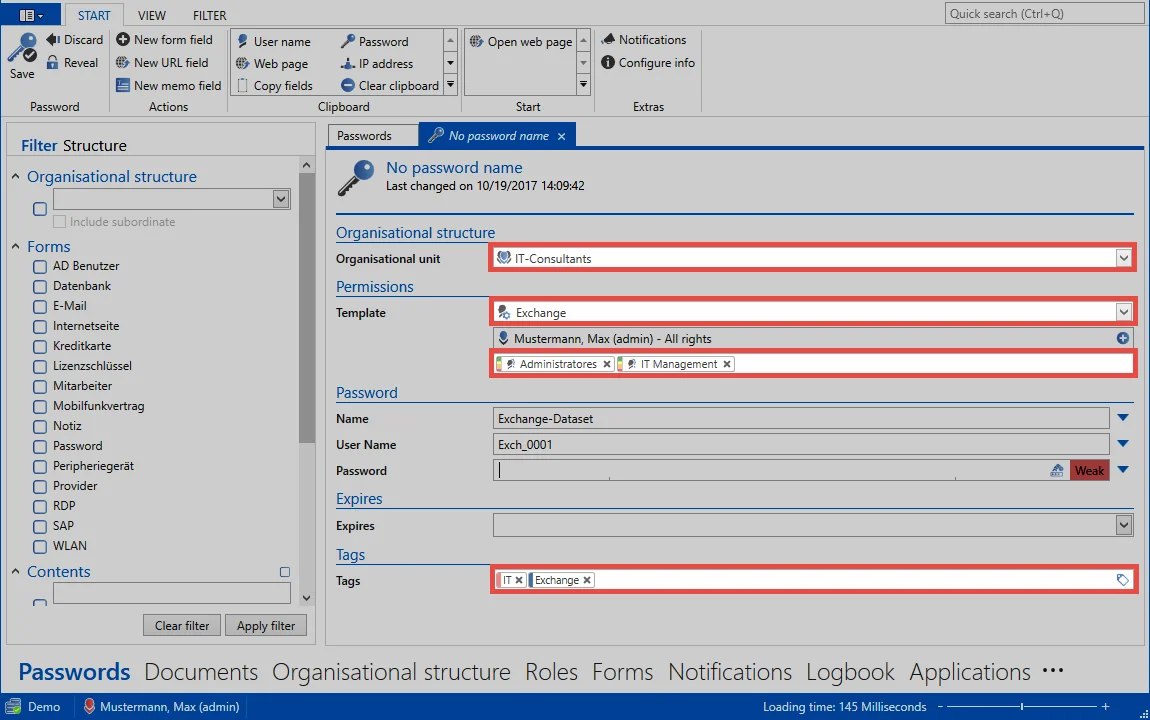
Here is the underlying rights template as a comparison:
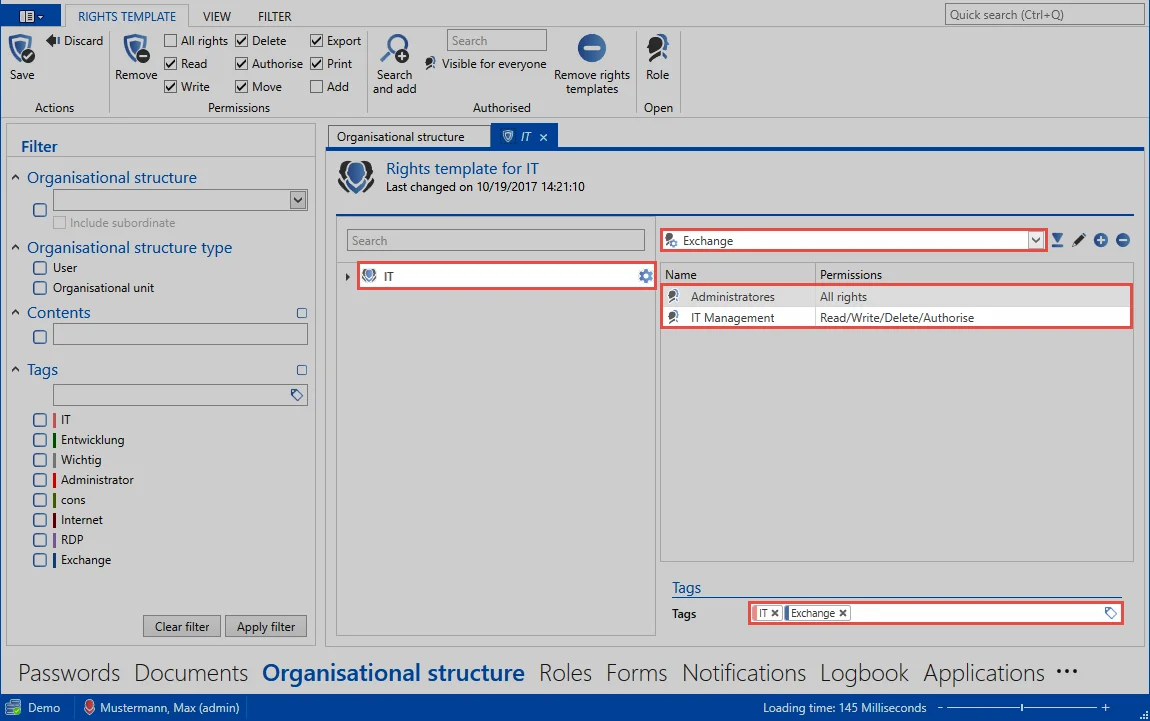
The relationship between them is obvious. It can be immediately seen that by selecting the organisational unit “IT” based on the rights configured in the rights template, permissions are granted for the roles “IT management” and also “Administrators”. The underlying tags “IT” and “Exchange” are also set.
Preview of the permissions to be set
When using rights templates, the permissions to be granted can be very quickly classified via a color table. The actual permissions can also be viewed as usual via the Ribbon. The following color key is used with the associated permissions:
| Color | Permission |
|---|---|
| Green | Read |
| Yellow | Write |
| Orange | Delete |
| Red | Authorize |
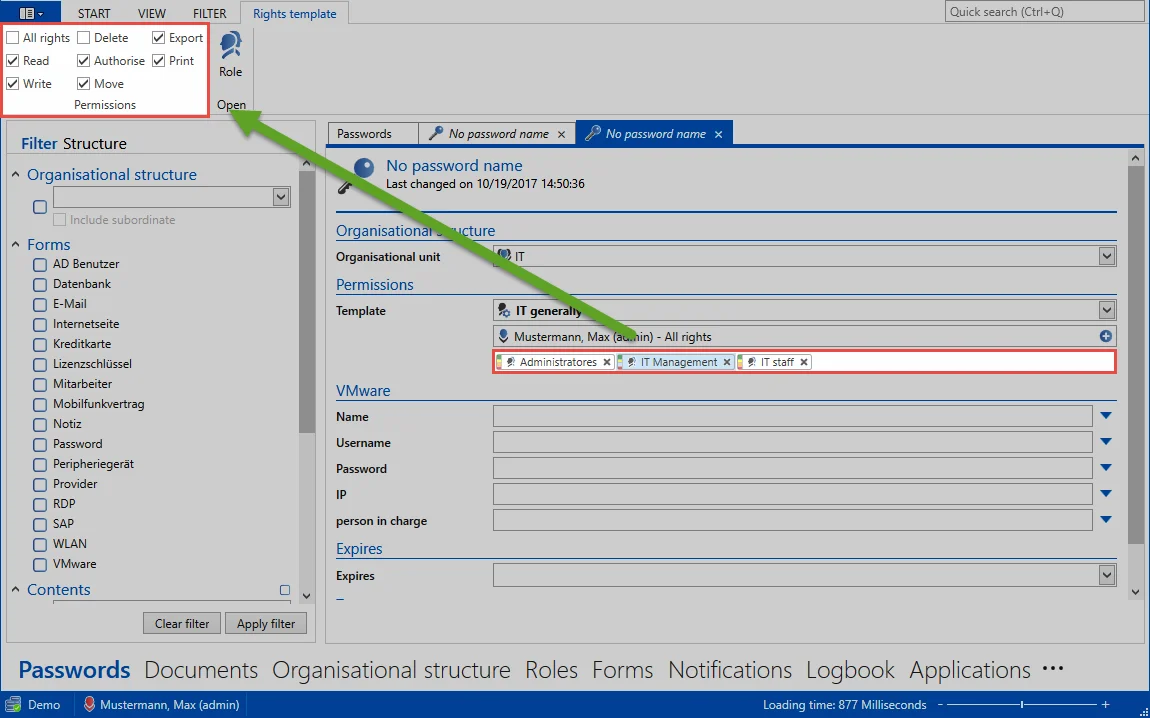
Other rights also exist that are, however, not separately indicated by a color. The overview in the ribbon can be used to see whether the “move”, “export” and “print” rights are set or not. The permissions for the selected role/user are always displayed – in this case for the role “IT management”.
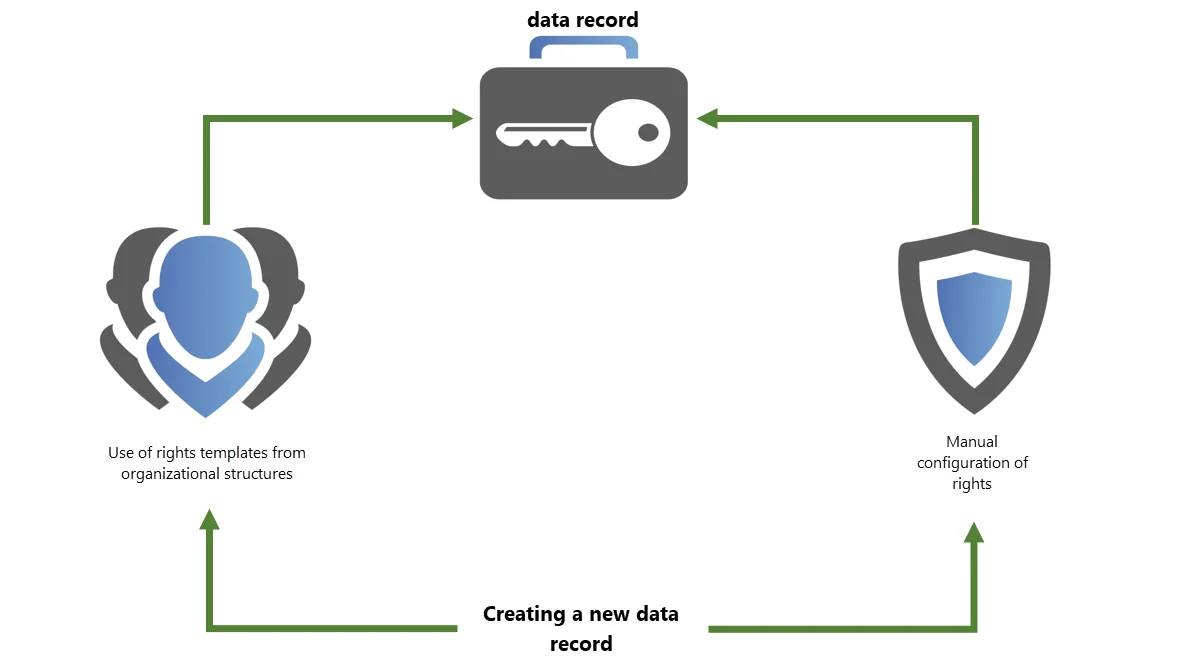
Conclusion
The Manual setting of permissions enables the configuration of rights for both existing and also new records. The option of Predefining rights represents a very efficient alternative. Instead of having to separately grant permissions for every record, a “preset” is defined once for each organisational structure. Once this has been done, it is sufficient in future to merely select the organisational structure when creating a record. The permissions are then set automatically. This process is particularly advantageous for those users who should not set their permissions themselves.
CAUTION: The configuration of permissions can be carried out manually or automatically as described. If you want to change previously set permissions later, this has to be done manually. Retrospectively defining rights is not possible.