About PingCastle
"For CISO, by CISO"
PingCastle was born based on a finding: security based only on technology does not work. That's why the company focuses on process and people rather than just technology. PingCastle does not sell products !
The company does not provide solutions to protect your infrastructure. Instead, it provides tools to discover what you have to protect, evaluate its security level and provide insights on if the budget you have provided has been successfully used.
PingCastle's objective is not to reach a perfect security but to impulse changes using the management. And with low effort, I think you'll get support to change the situation !
Vincent LE TOUX
License
The source code of the program is licensed to the Non-Profit Open Software License ("Non-Profit OSL") 3.0.
- Regarding the binary code, Being part of a commercial package is forbidden except if a license is purchased. Check the "our services" section on https://www.pingcastle.com for more information.
The program is allowed to run only during its support date. Support can be extended by purchasing additional support.
Methodology
The PingCastle tool is just one part of a global methodology aiming at securing Active Directories.

You can get more information about this methodology by visiting the website https://www.pingcastle.com/methodology/
How to use PingCastle
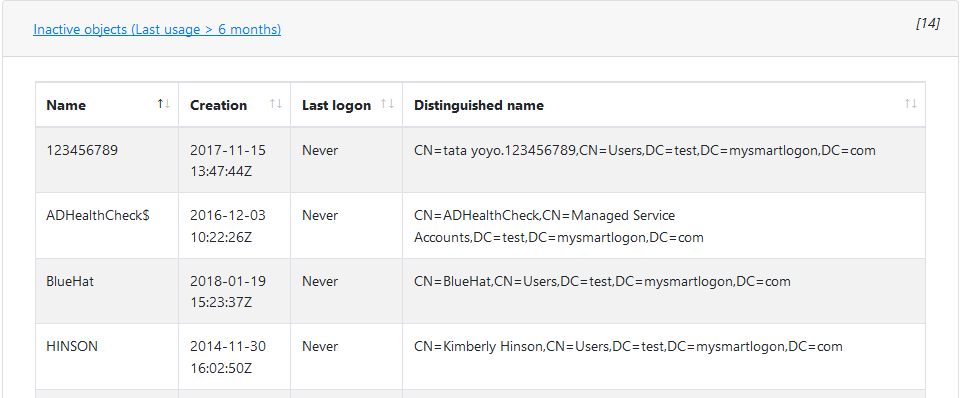
The following sections describe how to use PingCastle.
Requirements
Active Directory Account
The PingCastle program needs an Active Directory account to connect to the AD to audit. No requirements is needed for this account. It can be an account without any privileges or even an account from a trusted domain. This account doesn't require to be part of the local administrators group.
Server Side
There is no requirement on the server side.
However it is strongly recommended (but not mandatory) for performance reasons to install on the server side a component named "Active Directory Web service" aka ADWS. It is installed by default on any domain where at least one domain controller has the OS Windows 2008 R2 or later. Having this component installed can divide the time required to compute the report by a factor of 10.
ADWS can be installed manually on Windows 2003 and Windows 2008 require .NET Framework 3.5SP1. The hot fix that may be needed for these OS is located here.
Client side
- PingCastle requires .Net 4, available on all modern OS. However it can be compiled to run manually on .Net2. It fulfill then the following requiement:
The program is supported on every Operating System supported by
Microsoft without the installation of any component nor any local
privilege.
From Windows Vista to Windows 10 and Windows 2008 to Windows 2016 in
both 32 and 64 bits.
In addition, the program is known to be working on Windows 2000 with the
.net framework 2, Windows XP and Windows 2003.
The analysis tool (PingCastle.exe) requires DotNet 3.0 (or next versions) which is available by default since Windows Vista. It can be run under DotNet 2.0 but with fewer functionalities.
Starting from PingCastle 2.7, PingCastle.exe can be run without the .config file next to the program. But in this case, the program will be run under the .Net framework where it has been compiled (and not the other .Net framework). Windows does show a popup to suggest the installation of the missing framework.
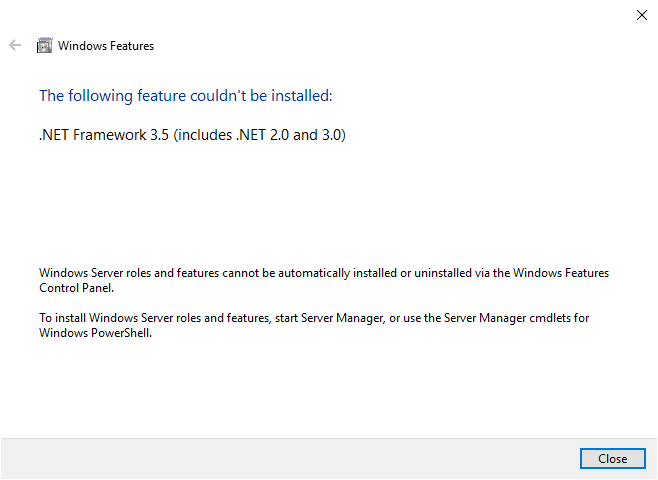
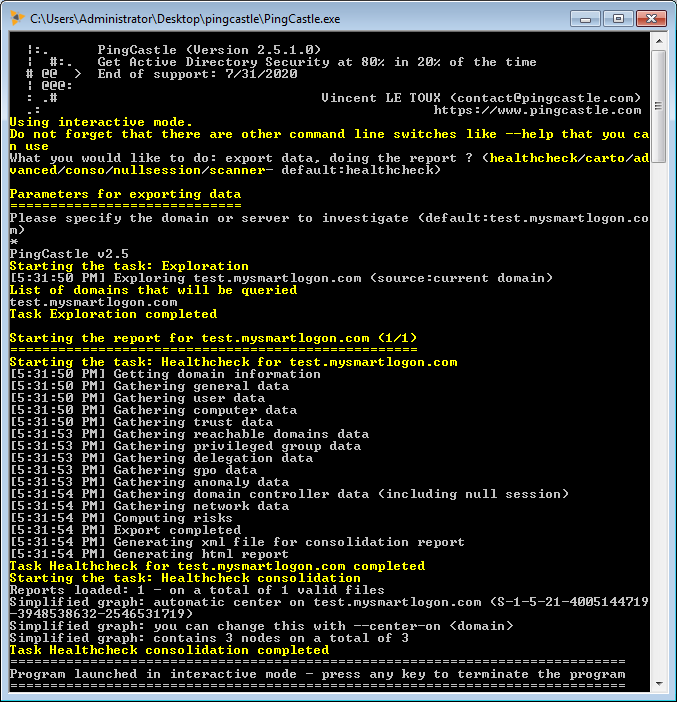
How it works
PingCastle is a standalone program (not requiring installation) which produces reports for human or machine.
PingCastle reads its own machine readable reports to build analysis or dashboard.
Installation
PingCastle Basic Edition is provided in a zip file. You need a program such as 7zip or the native unzip program to decompress the file.
For the most operating systems, PingCastle does not need any more actions.
For Windows 2000, the dotnet framework 2.0, which is the last supported version, need to be installed.
The two files required to run scans are PingCastle.exe and PingCastle.exe.config
Run the program
- The best way is just to double click on PingCastle.exe
This run the program in a mode called the "interactive mode.
The program can be run using a command line. A command line can be run by searching for "cmd" or "command line" in the start menu.
Then a drag and drop of the file "PingCastle.exe" automatically populates the command line with the binary. The same can be done with other files ending with ".exe"
Getting help
PingCastle can display its help on a command line.
Indeed PingCastle has a lot of switches which can be displayed using the command line:
PingCastle.exe --help
Do not forget also to check the website https://www.pingcastle.com or on twitter @mysmartlogon
Generating log file for support requests
PingCastle can collect logs with the --log switch
However when a command line argument is submitted, the interactive mode is disabled and the module has to be launched manually. To avoid that, the "interactive mode" can be activated manually using the command:
PingCastle.exe --log --interactive
Performing an Active Directory health check
The report can be generated in the interactive mode by choosing "healthcheck" or just by pressing Enter. Indeed it is the default analysis mode.
It can be run using the command:
PingCastle --healthcheck --server mydomain.com
Active Directory risk level analysis
When the health check is run, an html file and an xml file are generated. The html file represent the report of the active directory. It is designed for humans. The xml contains some of the data used to generate the html file and can be used to consolidate date on multiple active directories. It is designed to be computer read (PingCastle).
- The xml file is required for all analysis, including global overview or cartography.
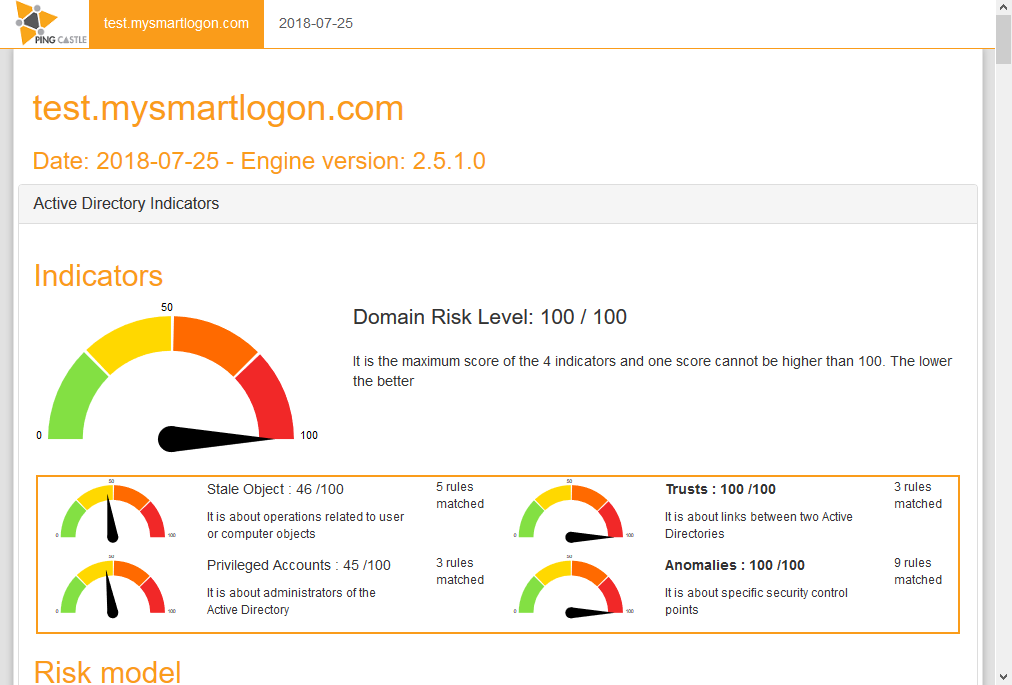
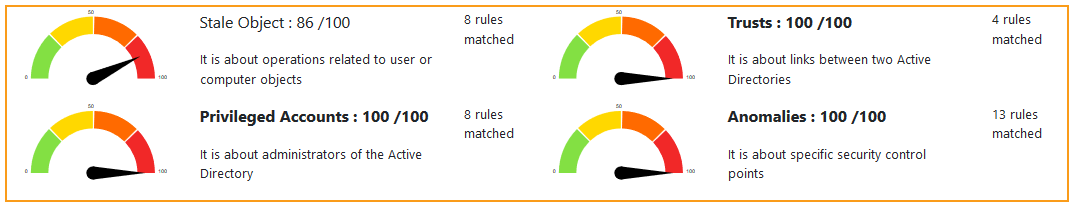
The report is divided in 3 parts:
1 -- Scores
The Score is computed by the maximum of the 4 sub scores:
-
Privileged accounts -- It is about administrators.
-
Trusts -- It is about the links between Active Directories (reminder: one AD can compromise one other via trusts).
-
Stale objects -- Stale objects represent everything about the AD objects and their life cycle: computer and user creation, delegation.
-
Security anomalies -- Everything that doesn't fit into the previous categories and related to security checks
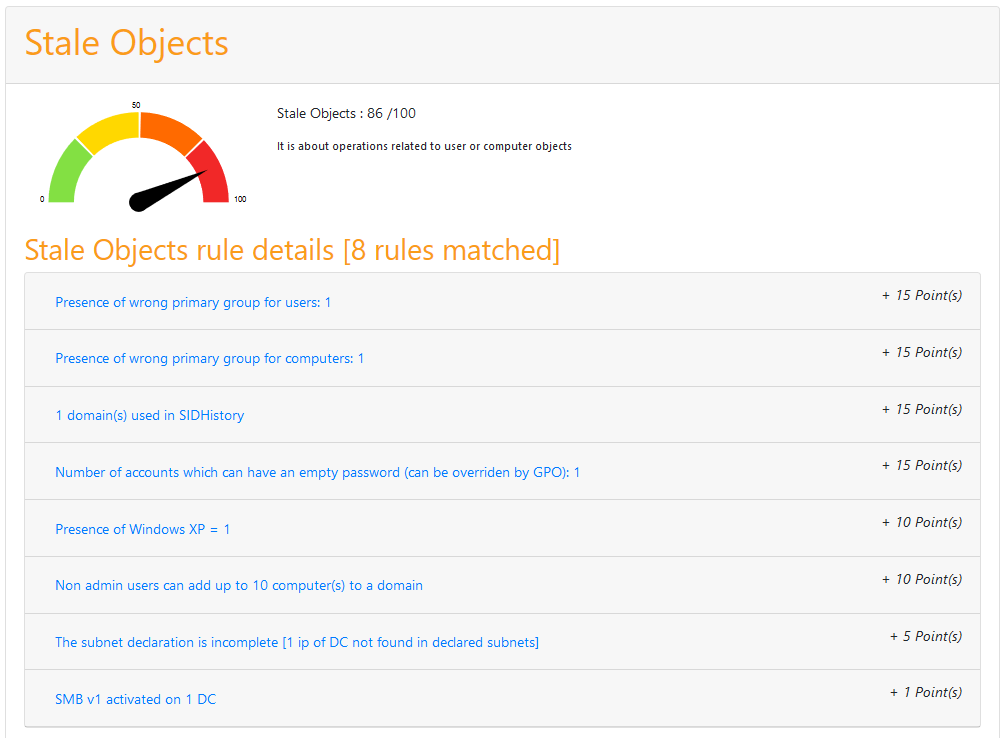
The details of the rules triggered is shown with some indication and the number of points calculated (the total cannot be above 100).
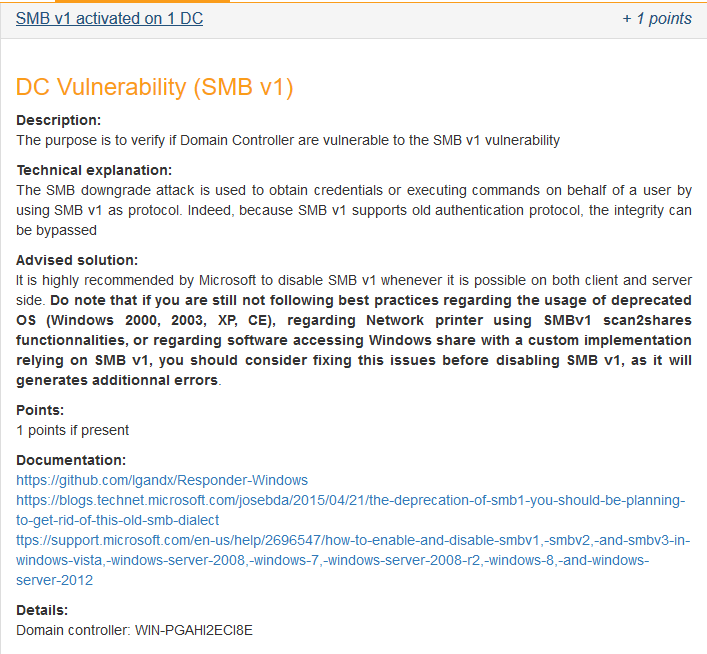
When the rule is clicked, a short explanation of the rule is shown with some indication on how to solve the situation.
2 -- General information
- Contains the generated date, domain
3 -- Details
- The Detail zone shows general information about users, computers, trusts, group policies, ...
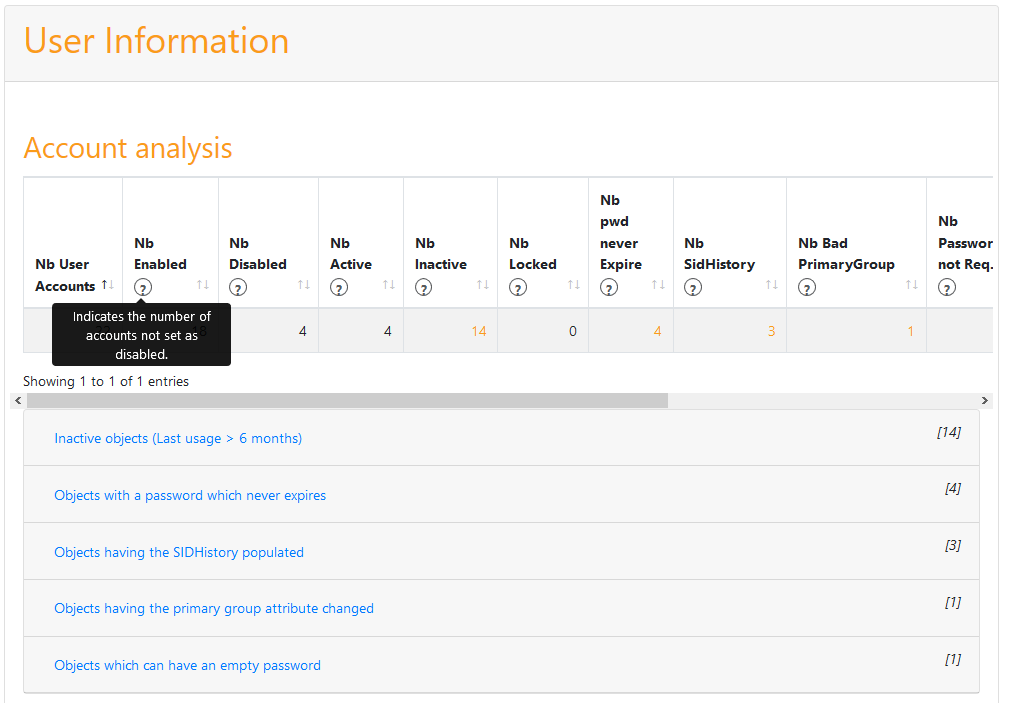
Some information can be seen in detail by clicking on the associated link. It contains data to help identify the underlying objects.
Perform domain discovery
Option 1: performing multiple health check reports (recommended)
If you want to get a quick status of your infrastructure, run the program with the "healthcheck" mode (just press enter) and enter as domain the asterisk (*).
All reachable domains will be scanned, the reachable mode will be activated and the consolidation report will be made automatically. This takes from a few minutes to one hour.
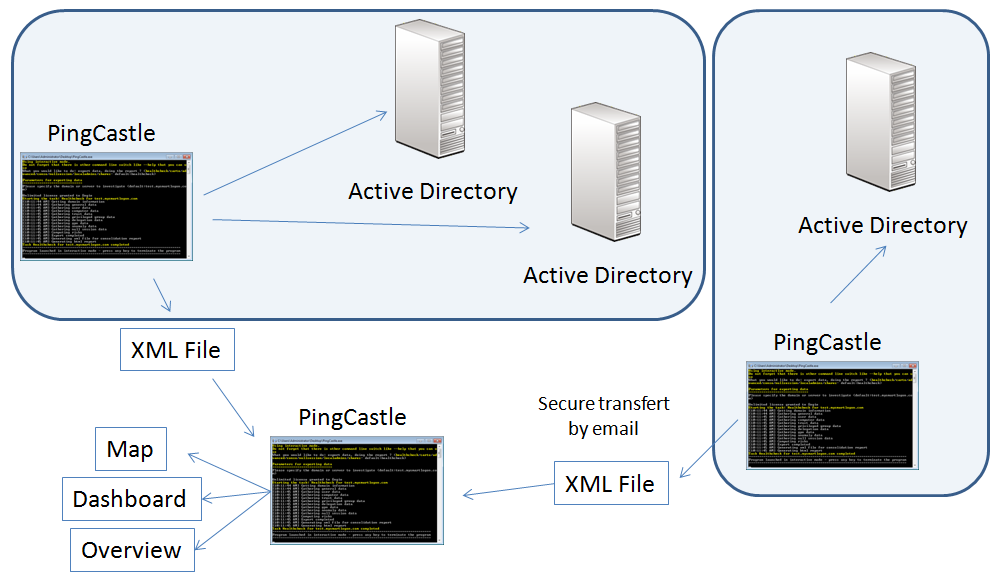
Then open the cartography reports (see below).
- Xml reports generated from multiple point of view can be used to have a consolidated map. Do not forget to check the Getting an overview or dashboard section.
Option 2: when having existing health check reports
The map can be generated in the interactive mode by choosing "conso". This mode performs the consolidation report and build the maps.
Option 3: perform a quick domain exploration (fastest but not scalable)
If you need only a quick map (< 5 minutes of execution), enter "carto" when using the interactive mode or run the program with the switch --carto.
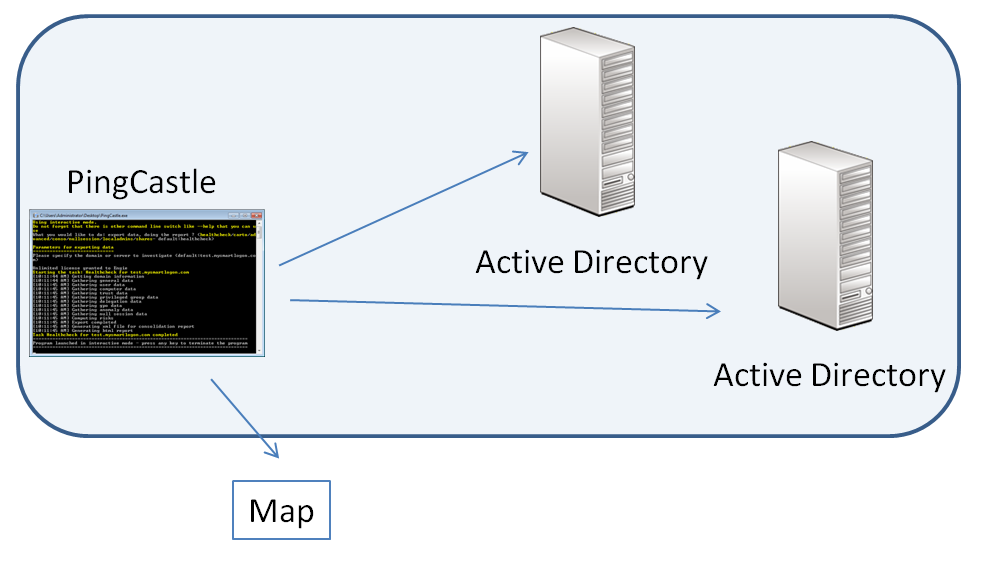
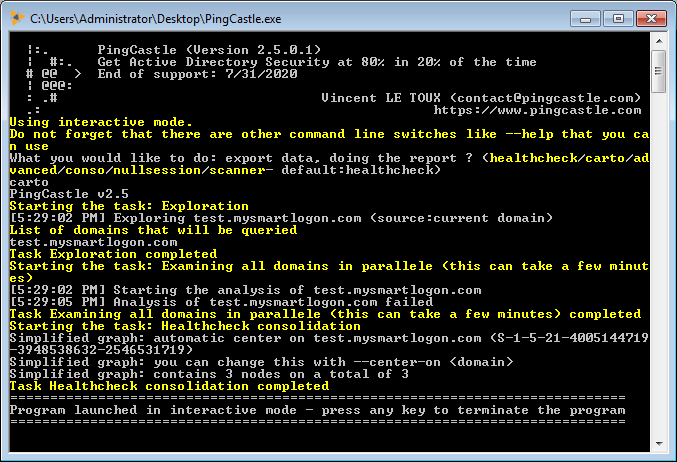
The program discovers all the reachable domains, does a light scan and produce the same map than in the health check consolidation mode. The SID Filtering status is accurate but the individual scores are not available. Scans are performed in parallel. Cartography reports cannot be combined when run on more than one point of view. If you need to combine data from multiple AD, you should run the healthchecking reports and consolidate their reports.
Maps
There are two kinds of map. The first one is the most complete but can be difficult to read. To avoid this difficulty, a simplified most exists where a domain is connected to others only using a single trust. It builds a hierarchy.
When available, the Active Directory health check score is displayed and colored by on it. Trusts are also colored based on the SID Filtering state.
Full domain map
The full domain map is represented by the files xxx_full_node_map.html. Each map is a dynamic map. Each node can be moved.
Example of graph produced by the tool
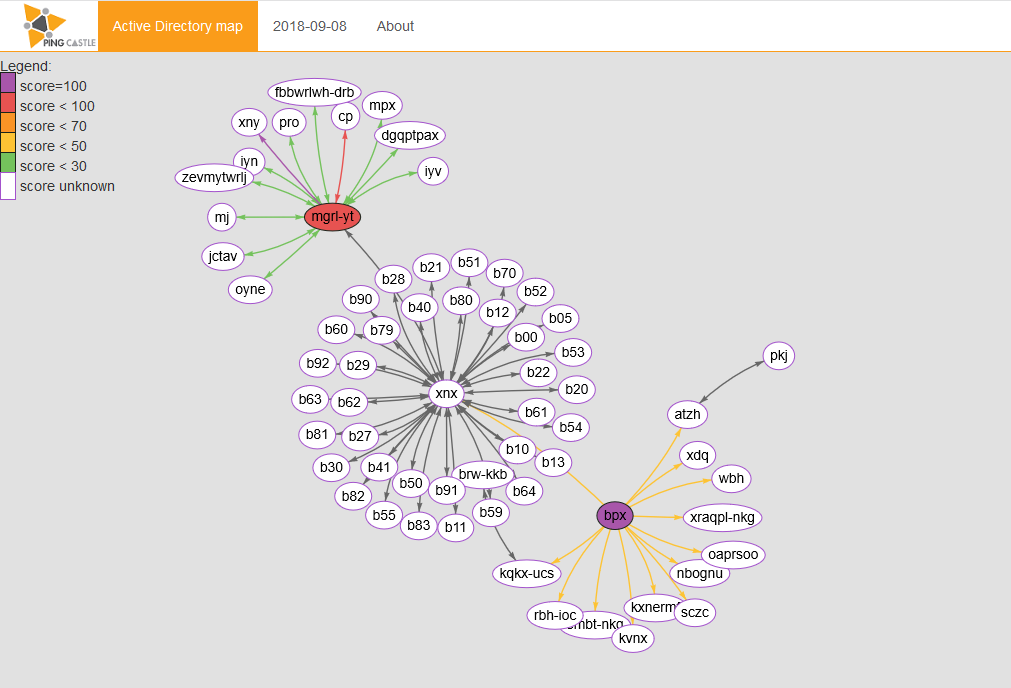
The colored circles are the domain on which the reports have been run. The color depends on the score. The purple bordered circles are the domains on which the script has not been run but that they program found using trust link.
Legend:
When the mouse is on a circle, the full name of the domain appears:
If the mouse is hold on a trust, the detail is shown in a popup:

Simple domain map
The simple domain map is represented by the files xxx_simple_node_map.html.
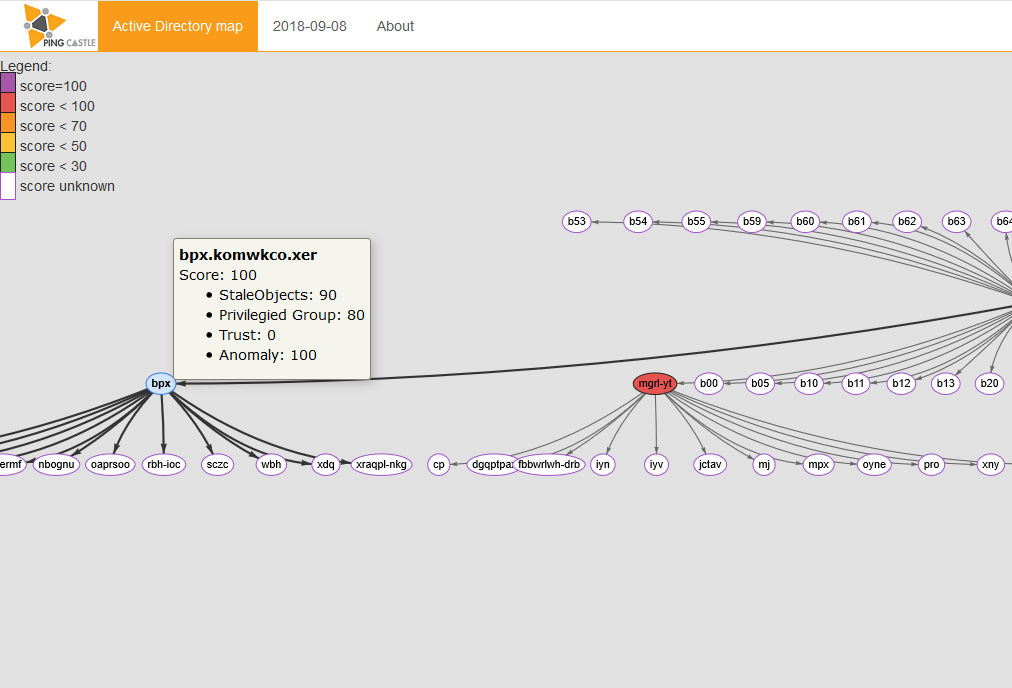
This is the same map except that a domain is present only one time in the graph and connected with only one trust. The domain which has the most trust is automatically selected to be at the center of the graph. The domain at the center can be specified manually.
Hilbert map
The simple domain map is represented by the files xxx_hilbert_map.html.
Networks are big and it can be difficult to have a visual representation of them. This report displays what is called a Hilbert map. Indeed, fractal functions are used to compress a 1D space (IP addresses of the networks), into 2D for a visual representation. Each square represent a network. It can be used to detect non occupied space or networks which are overlapping.
This report is divided into 4 areas:
-
the first one give an overview of all the networks
-
the second one zoom deeper into the selected network
-
the first one displays the list of networks
-
the last one show the list of domain controllers identified
On the viewer Window, sources can be selected to avoid an overlapping with two sources.
There is a mouse over popup which gives you detail about a select IP (and the networks where it does belong) and a search function can be use to find a specific IP address.

Deploying PingCastle
PingCastle has been designed to be scalable and used in a decentralized architecture.
To be the most effective, PingCastle needs to have the risk reports for all domains. Because PingCastle doesn't need an account in the domain to audit, you can take benefits of trusts to perform this task.
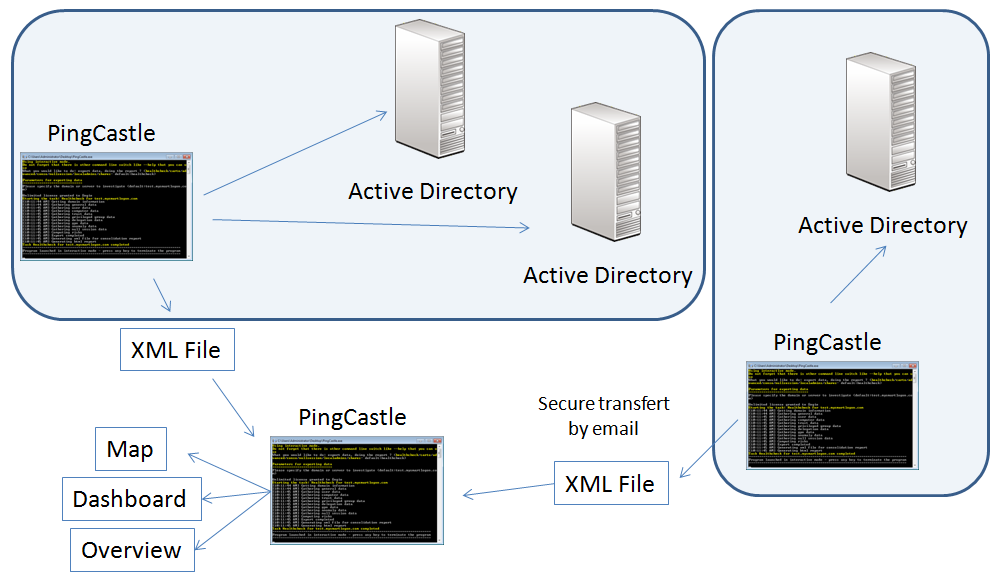
Involvement of the management
The management involvement is a critical factor of success. Here is how you can proceed.
You can start the project by running the tool without notifying the domain administrators to get a first overview. The healthcheck mode run on all trusted server (server set as "*") or the carto mode can help built a big picture of all domains involved.
Then you can deploy officially in a small perimeter and use the report results to challenge the domain administrators. Based on the risk indicators or on the delay required to fix the problems, you can take the opportunity to involve the management here.
Here some arguments which can help you involve the management about this kind of project:
-
Active Directory's security is crucial: the probability that an auditor compromise an Active Directory is about 90%
-
Management has to prove to external auditors that actions are being made on that topic
-
The tool doesn't need any setup, installation, server, project, ... Cost & effort are minimal
-
The risk indicators can be used to prove that the situation has been improved and it can be used for benchmarking (an effective management method)
-
The tool returns anomalies which 80% of them can be fixed within 5 minutes
Decision to take
We recommend that the decision made by the management is about:
-
Deploy the tool on 100% of the domains
- For example set the initial deadline to 3 months and assign discovered trusted domain to the AD owner.
-
Request the implementation of SID Filtering on 100% of the trusts except official migrations
- For example set a list of critical domains and list the trusts linked to that domains without SID Filtering.
-
Follow the progress of these actions on the management meetings.
- For example set a monthly follow up meeting with the people involved.
Getting to 100%
Below is a list of reasons an entity can invoke (or remain silent) to be excepted:
-
Minority share holding company
-
Migration and removal of the domain in the upcoming months
-
Regulations
-
"Confidential information" included in the script
To handle the migration cases, PingCastleReporting supports a "migration" status for the domain auditing & a "migration" status for SID Filtering. In the SID Filtering case, an end date has to be defined. We recommend 3 to 12 months. Migration should be an excuse for removing anomalies, not running the script (a 5 minutes effort !).
For "confidential information", the xml report doesn't include any personal information nor administrator accounts. If the level of information included is too high, a configuration switch exists to lower the level of information. If the problem is about the transfer of the data in an unsafe channel, the tool can encrypt the xml report to solve this problem.
For other issues, we recommend to insist if there are trusts to existing domains. Indeed, a trust facilitates the attacker job because he knows that there is a domain via the trust information, that there can be credentials in memory (mimikatz) or that he can absuse network connection (LLMR spoofing with Python Responder). If you can't get a report, we suggest to remove the trust to these domains.
Then for domains without a trust, you can formally transfer the responsibility of the Active Directory compromise and put the domain status to "Out Of Scope".
Deploying PingCastle in decentralized locations
PingCastle can be run on every domain of a company using the command:
PingCastle --healthcheck
Reports can then be regrouped to produce a global view. See below for the technics (encryption, transfert by email) to centralize the reports.
Deploying PingCastle in centralized locations
PingCastle can be run on a Bastion Active Directory, generally used to perform administration tasks. In this case, all the domains will be scanned.
PingCastle --healthcheck --server *
The program can be run on every forest root and be limited to that perimeter
PingCastle --healthcheck --server *.forest.root
The tool can be run on every forest child and explore the child and its trusted domains. In this case the forest root is excluded.
PingCastle --healthcheck --explore-trust --server child.forest.root
PingCastle can explore all the domains of all the trusted forests from another forest. This is useful when the root and child doesn't share the same name.
PingCastle --healthcheck --explore-forest-trust --server anotherforest.root
If needed, exceptions can be set to not scan domains. For example to not scan the Bastion domain multiple times. In this case use the option --explore-exception <domains> where domains are comma separated domain name.
Updating PingCastle
Since PingCastle 2.7, a new update program is delivered. It downloads the latest release from the github official releases. In option, it can download the beta release or wait that the release has reached a specific age.
Here is the options available:
--api-url http://xx : use an alternative url for checking for updates
--force-download : download the latest release even if it is not the
most recent. Useful for tests
--use-preview : download preview release if it is the most recent
--wait-for-days 30 : ensure the releases has been made public for at
least X days
Centralizing reports
Encryption
Sometimes, domains are unconnected or it is not possible to make the schedule tasks centralize in a single share all the reports. To deal with this case, PingCastle can encrypt the reports to send them in an unsafe channel.
A RSA key pair need to be generated and the public key needs to be shared with all the instance of the program. When producing risks reports and generating the .xml files, add the flag --encrypt to perform the encryption.
You can generate a keypair using the following command and copy the public key in the .config file to be deployed.
PingCastle.exe --generate-key
Starting the task: Generate Key
Public Key (used on the encryption side):
<encryptionSettings encryptionKey="default">
<RSAKeys>
<!-- encryption key -->
<KeySettings name="default"
publicKey="<RSAKeyValue><Modulus>h
4smrLAZZ30QwWXHcT1oNz3hH3Ax2R9T75DlioGFCIdLb0QhUn3N8NWgJ2ZgyUNXn4qU1b0DslOIhK+Cq
oqCPvXuHjK6TGrMyphtcbZvvgbLxfyalJemczx1+pOuBlqqVdalE94rnnnBr761WIJJnkJdZ0rzYsebn
DwGuk9kiw8=</Modulus><Exponent>AQAB</Exponent></RSAKeyValue
>"/>
<!-- end -->
</RSAKeys>
</encryptionSettings>
Private Key (used on the decryption side):
<encryptionSettings encryptionKey="default">
<RSAKeys>
<!-- decryption key -->
<KeySettings name="39b5d076-17be-4999-b43e-b894a55446a1"
privateKey="<R
SAKeyValue><Modulus>h4smrLAZZ30QwWXHcT1oNz3hH3Ax2R9T75DlioGFCIdLb0QhUn3
N8NWgJ2ZgyUNXn4qU1b0DslOIhK+CqoqCPvXuHjK6TGrMyphtcbZvvgbLxfyalJemczx1+pOuBlqqVda
lE94rnnnBr761WIJJnkJdZ0rzYsebnDwGuk9kiw8=</Modulus><Exponent>AQAB<
/Exponent><P>uwgX794pe7O3vIiQR5v03WK3Ug5LUAbXpPF6Xq4qGb3TGprZaJQq5rZ2u
J4qwRanOa5pI/zv7RhG/4ItesBuAw==</P><Q>uYaNLEp9Vh8F29tSH+M4z+OjxPl+UL
LRjLrssFLTTNsdnrHgAtdJ1lxfIm/gTUa0qPLa9Y/xkUb1khK/+tV3BQ==</Q><DP>Fd
feI8+IfMACh2xTnWljca+jxVuSBCioasUhC4m/tP3sd8D5/zK+x+8rcmhWifKBWUU7Vk6mHsSlFhY4BY
wPzQ==</DP><DQ>gzfwh8AT0CLXEP6ZomYi257lST8xoUAoyEG5gKjEPJrJ42Fp0HiXB
9+Dhibc3atBwjEqvv5VXGx06iEK2g27RQ==</DQ><InverseQ>HRKFjYwrXqgO4v8Q+J
SOqR6lSvQ15Z6V4AE23i4xfeuIYWwVf0t8AwgkDfFRQnEyh24byuh5PPzUbDOsUY+eYg==</Inver
seQ><D>QQ6pIXnkt6dvw2P2toOi4eDxjQVs56oBv5rske5YzB8kNeOdmtqHXnEqzb519iQ8
incZuP1gKNevTwBu1yxkFuFh0dzjS3iBjHvYGtDo5mARiZ1nN8QNI2zKE+Q6qXF8Z+wN3Fv3oBDQXATI
6IQbgkAxLTMo4CUmtUQ6GvjwFwE=</D></RSAKeyValue>"/>
<!-- end -->
</RSAKeys>
</encryptionSettings>
Done
Task Generate Key completed
Then copy the private key section in the PingCastle and PingCastleReporting configuration file (.config) used to consolidate the results. PingCastle will perform the decryption automatically.
The program can generate an encrypted copy of a report (public key needed) and a decrypted copy of a report (private key needed) using the following commands:
PingCastle --reload-report report.xml --encrypt
PingCastle --reload-report encrypted-report.xml
Note: Only one key can be specified for encryption but multiple keys can be used for decryption. Their selection is automatic.
Email
PingCastle can contact if specified a SMTP server to send the reports by email. If the encryption is set, the program will encrypt the reports. Use --sendXmlTo <email> to send only the xml report, --sendHtmlTo <email> to send only the html report and --sendAllTo <email> to send both html and xml report. Email addresses are comma separated ones and the previous flags can be combined.
API
PingCastle can send the report (encrypted or not) using an API.
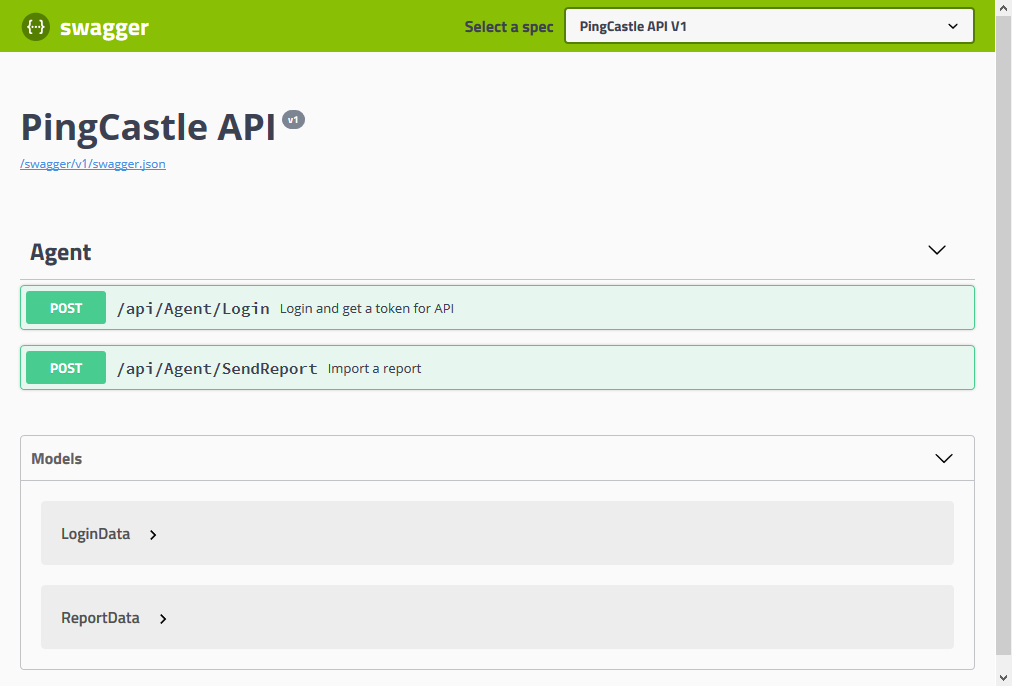
You can query a PingCastle API server or build a client or server from Swagger.
The description of the API in swagger format can be found here.
Getting an overview with multiple reports
How much users or computers to you have ? Should you purchase additional support for Windows XP or Windows 2003 ? Should you plan an administrator cleanup ? Are the requirement for a 8 characters password enforced ?
This is the kind of questions you can answer with the simplest consolidation. Indeed, the program can be used to aggregate the report results.
Operations to perform
The consolidation process is working on the xml files generated by the consolidation report. By default, the files are picked in the directory (or sub directory) where the program is run. If there are duplicate reports, only the most recent is used.

To generate the report, enter "conso" in the interactive mode.
Or type the following command line:
PingCastle --hc-conso
- This report is generated automatically when the healthcheck is performed with the server "*"
Consolidation report
The consolidation report is a concatenation of all data contained in the report, without the detail. It follows the same plan than a simple report.
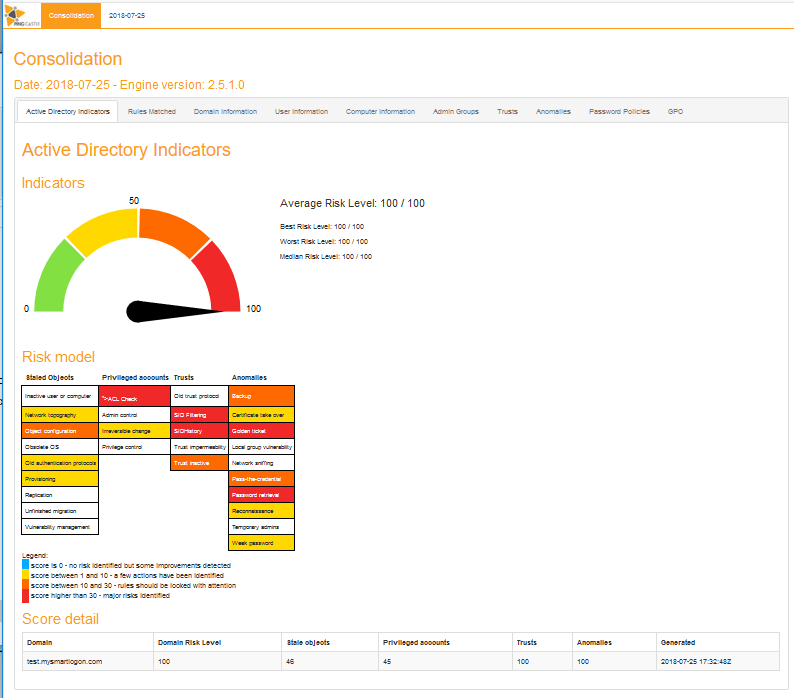
When the consolidation is made, 3 html files are generated.
File ad_hc_summary.html
The first one contains the summary of all the reports: It keeps the same structure than the detailed reports but with a higher level of detail.
- ad_hc_summary_full_node_map.html
The second file is a map build on all trusts. See domain discovery.
- ad_hc_summary_simple_node_map.html
The third file is a map build on all trusts. See domain discovery.
Scanners
PingCastle has some builtin program to check for specific features. These programs are called "scanners" and are accessible from the "scanner" item on the main menu.
When selected, a menu is displayed to select the program. At the bottom, a scanner description is shown.
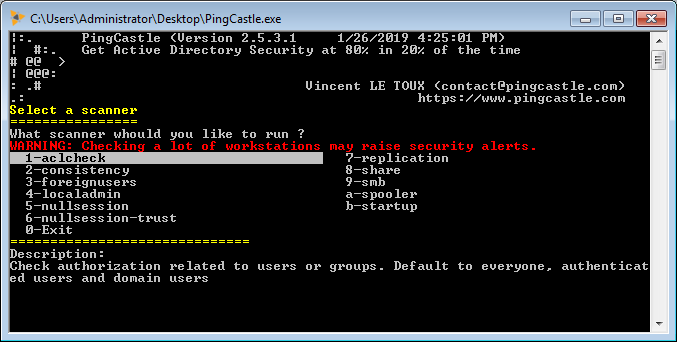
Here are the main scanners
Check for specific user in global permissions
The AclCheck scanner is used to hunt for write permission given to objects on a domain. It is default to the "authenticated users", "domain users", "everyone" groups.
PingCastle --scanner aclcheck --server <domainToExplore>
Local administrators
The local administrator accounts can be used in an attack to recover passwords in memory with tools like mimikatz. You can enumerate most of them without any privilege with PingCastle with the following command:
PingCastle --scanner localadmin --server <domainToExplore>
Local shares
Local shares can be opened to everyone and be storing confidential information like login and passwords or backups. PingCastle can do a quick scan without any privilege and locate open share using the following command:
PingCastle --scanner share --server <domainToExplore>
Start time
Any authenticated users can get the start time of a computer in the domain and even unauthenticated ones if SMB v2 is activated. PingCastle can do a quick scan without any privilege and gather the start time of all computers of the domain:
PingCastle --scanner startup --server <domainToExplore>
SMB version
PingCastle can do a quick scan without any privilege to know which version is supported as server for each computer of a domain:
PingCastle --scanner smb --server <domainToExplore>
Null sessions
Null sessions are an old Windows NT4 problem. It should have been disappears but is still present on 20-30% of the domains. When it is enabled, an auditor with no account on the domain can use this to enumerate all the account of the domain. Then this list can be used to generated wrong authentication attempts and lock the accounts. Or perform brute-force attacks.
You can use PingCastle to attempt to extract a list of user account using this functionality. Run the following command:
PingCastle --scanner nullsession --server <servertotest>
foreignusers
A inbound trust ( an unidirectional trust) is understood as a diode. Nothing is supposed to be extracted. But this is not true. PingCastle can extract the list of users from an inbound trust via a MS-LSAT enumeration.
First, enter the domain to enumerate (eg: the bastion or a domain which is very far)
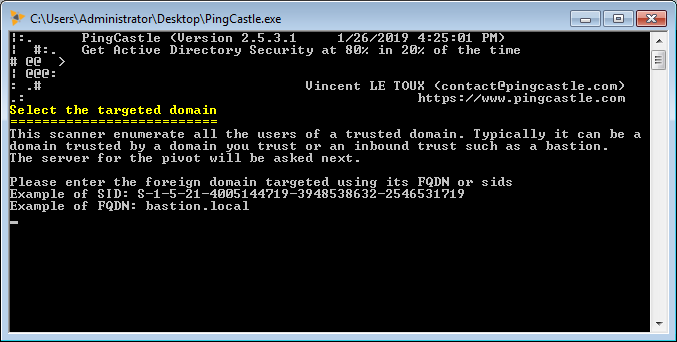
Then enter the domain which will be used as a pivot
PingCastle --scanner foreignusers --foreigndomain <remote domain or sid> --server <pivot domain>
Annex
Command line reference
Here is a short description of the main tasks performed by the program.
Health check
run the health check :
PingCastle --healthcheck --server mydomain.com
run the consolidation of the health check reports:
PingCastle --hc-conso
Next, export rule list:
PingCastle --export-hc-rule
Overview:
Run the report on all reachable domains and built a cartography:
PingCastle --healthcheck --server * --reachable --hc-conso
Built only a cartography without scores:
PingCastle --carto
Advanced mode:
run the export:
PingCastle --advanced-export --server mydomain.com
build the reports:
PingCastle --advanced-report --database thegeneratedsdffile.sdf
Other investigations:
Check the presence of null session:
PingCasle --nullsession --server servertotest
Scan the domains for local administrators:
PingCastle --localadmins --server domainToExplore
Scan the presence of local shares:
PingCastle --shares --server domainToExplore
The available switches can be obtained using the "--help" switch.
PingCastle --help
Full command line options
switch:
--help : display this message
--interactive : force the interactive mode
--log : generate a log file
--log-console : add log to the console
Common options when connecting to the AD
--server <server> : use this server (default: current domain
controller)
the special value * or *.forest do the healthcheck for all domains
--port <port> : the port to use for ADWS or LDPA (default: 9389 or
389)
--user <user> : use this user (default: integrated authentication)
--password <pass> : use this password (default: asked on a secure
prompt)
--protocol <proto> : selection the protocol to use among LDAP or ADWS
(fastest)
: ADWSThenLDAP (default), ADWSOnly, LDAPOnly, LDAPThenADWS
--carto : perform a quick cartography with domains surrounding
--healthcheck : perform the healthcheck (step1)
--api-endpoint <> : upload report via api call eg: http://server
--api-key <key> : and using the api key as registered
--explore-trust : on domains of a forest, after the healthcheck, do the
hc on all trusted domains except domains of the forest and forest trusts
--explore-forest-trust : on root domain of a forest, after the
healthcheck, do the hc on all forest trusts discovered
--explore-trust and --explore-forest-trust can be run together
--explore-exception <domains> : comma separated values of domains
that will not be explored automatically
--encrypt : use an RSA key stored in the .config file to crypt the
content of the xml report
--level <level> : specify the amount of data found in the xml file
: level: Full, Normal, Light
--no-enum-limit : remove the max 100 users limitation in html report
--reachable : add reachable domains to the list of discovered domains
--sendXmlTo <emails>: send xml reports to a mailbox (comma separated
email)
--sendHtmlTo <emails>: send html reports to a mailbox
--sendAllTo <emails>: send html reports to a mailbox
--notifyMail <emails>: add email notification when the mail is
received
--smtplogin <user>: allow smtp credentials ...
--smtppass <pass> : ... to be entered on the command line
--smtptls : enable TLS/SSL in SMTP if used on other port than 465 and
587
--skip-null-session: do not test for null session
--webdirectory <dir>: upload the xml report to a webdav server
--webuser <user> : optional user and password
--webpassword <password>
--rules : Generate an html containing all the rules used by PingCastle.
Do not forget PingCastleReporting includes a similar option but for
.xslx
--generate-key : generate and display a new RSA key for encryption
--hc-conso : consolidate multiple healthcheck xml reports (step2)
--center-on <domain> : center the simplified graph on this domain
default is the domain with the most links
--xmls <path> : specify the path containing xml (default: current
directory)
--filter-date <date>: filter report generated after the date.
--regen-report <xml> : regenerate a html report based on a xml report
--reload-report <xml> : regenerate a xml report based on a xml report
any healthcheck switches (send email, ..) can be reused
--level <level> : specify the amount of data found in the xml file
: level: Full, Normal, Light (default: Normal)
--encrypt : use an RSA key stored in the .config file to crypt the
content of the xml report
the absence of this switch on an encrypted report will produce a
decrypted report
--graph : perform the light compromise graph computation directly to
the AD
--encrypt : use an RSA key stored in the .config file to crypt the
content of the xml report
--max-depth : maximum number of relation to explore (default:30)
--max-nodes : maximum number of node to include (default:1000)
--node <node> : create a report based on a object
: example: "cn=name" or "name"
--nodes <file> : create x report based on the nodes listed on a file
--scanner <type> : perform a scan on one of all computers of the
domain (using --server)
aclcheck
Check authorization related to users or groups. Default to everyone,
authenticated users and domain users
antivirus
Check for computers without known antivirus installed. It is used to
detect unprotected computers but may also report computers with unknown
antivirus.
corruptADDatabase
Try to detect corrupted AD database. To run only when requested by
PingCastle support.
foreignusers
Use trusts to enumerate users located in domain denied such as bastion
or domains too far away.
laps_bitlocker
Check on the AD if LAPS and/or BitLocker has been enabled for all
computers on the domain.
localadmin
Enumerate the local administrators of a computer.
nullsession
Check if null sessions are enabled and provide example(s).
nullsession-trust
Dump the trusts of a domain via null session if possible
share
List all shares published on a computer and determine if the share can
be accessed by anyone
smb
Scan a computer and determine the smb version available. Also if SMB
signing is active.
spooler
Check if the spooler service is remotely active. The spooler can be
abused to get computer tokens when unconstrained delegations are
exploited.
startup
Get the last startup date of a computer. Can be used to determine if
latest patches have been applied.
options for scanners:
--scmode-single : force scanner to check one single computer
--nslimit <number>: Limit the number of users to enumerate (default:
5)
--foreigndomain <sid> : foreign domain targeted using its FQDN or
sids
Example of SID: S-1-5-21-4005144719-3948538632-2546531719
--upload-all-reports: use the API to upload all reports in the current
directory
--api-endpoint <> : upload report via api call eg: http://server
--api-key <key> : and using the api key as registered
Note: do not forget to set --level Full to send all the information
available
List of open source software used
PingCastle uses a set of open source components to perform its job.
The list of components used by PingCastle, but not limited to, is:
-
Bootstrap licensed under the MIT license
-
DataTables licensed under the MIT license
-
Popper.js licensed under the MIT license
-
JQuery licensed under the MIT license
-
vis.js licensed under the MIT license
Scheduling PingCastle report
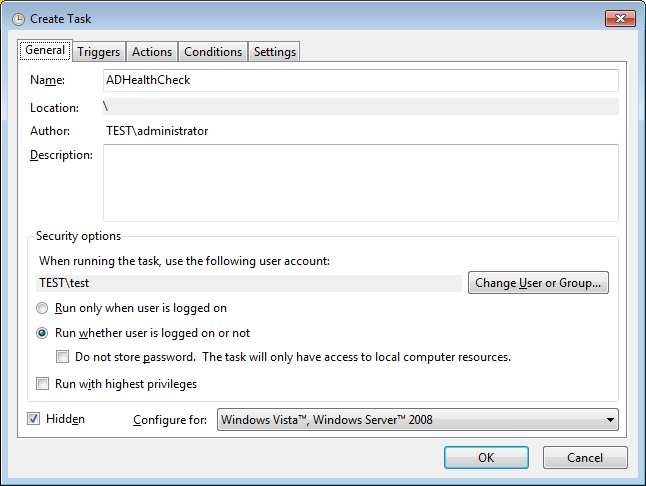
The program is compatible with the "managed service account" available since Windows 2008 R2 and if the scheduled task is run on Windows 2012.
Important setting: check "run whether user is logged on or not" and choose a service account running under the domain (not a local account). Check hidden to hide the console.
Set the schedule:
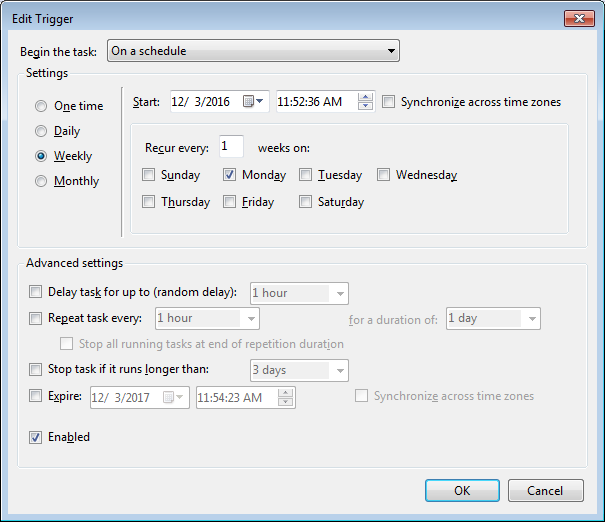
Set the command line:
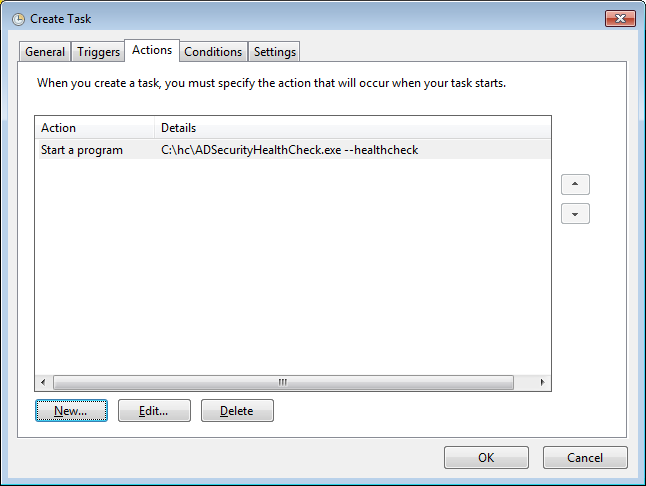
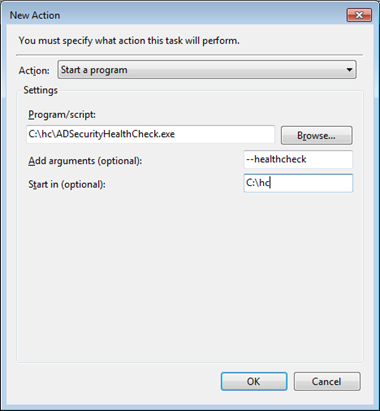
Be sure that the service account has the right to write the report in the current directory.
If you get the following message, be sure that the user as the right to logon as batch job.
This can be modified in the security policies:
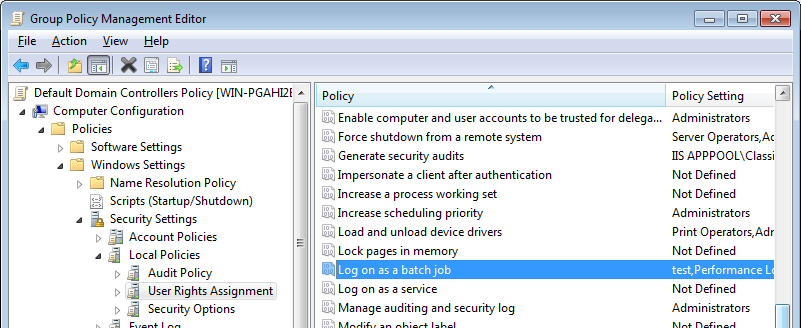
Select "Local Policies" in MSC snap in
Select "User Rights Assignment"
Right click on "Log on as batch job" and select Properties
Click "Add User or Group", and include the relevant user.
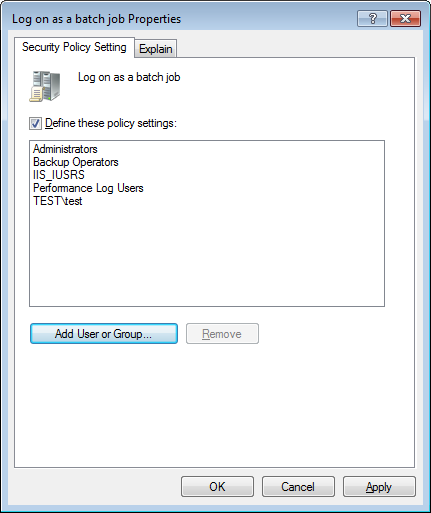
If the button "Add User or Group" is grayed, that means that the setting is overridden by a GPO (by default, the Domain Controller Policy). You can find the GPO by running rsop.msc, locate the setting and look at the "Policy" sheet.