Fine Tune a Threat
Selecting a threat in the Threats list displays details for that threat. The Threat Description box displays the name and description of the threat.
The Threat Configuration Box contains a Processing tab, an Exclusions tab, and in some cases a Settings tab.
Processing Tab
The Processing tab contains the configuration options for processing the threat.
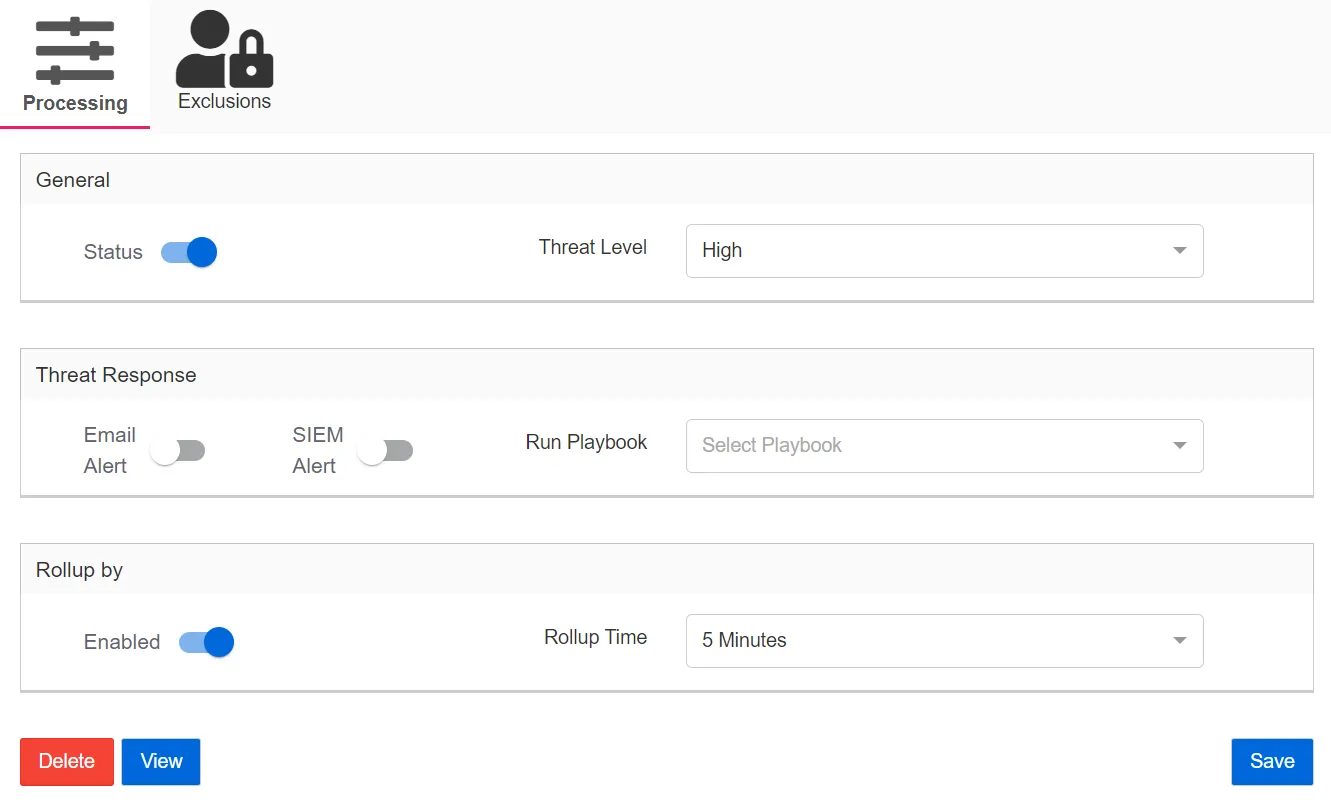
General:
-
Status – When set to ON, this threat will be detected by Threat Manager. When set to OFF, this threat will not be detected by Threat Manager. When a threat status is OFFand then set to ON, a dialog will display wherein which data will be processed is determined.
-
Threat Level – The relative severity level, or risk level, of the threat. Threat level controls the visibility of the threat and can be used to sort, filter, and influence various dashboards and visualizations throughout the console. This setting does not influence the behavior of the threat response.
- High – Indicates a serious threat that should be investigated immediately. The high threat level setting can be used as a filter on the Threats Page.
- Medium – Indicates a potentially serious threat of activities leading to a serious threat that should be investigated. The medium threat level setting can be used as a filter on the Threats Page.
- Low – Indicates activity that is a potential risk or a bad practice. The low threat level setting can be used as a filter on the Threats Page.
- Audit – Indicates activity that is not necessarily a threat, but should be monitored. The audit setting can be used as a filter on the Threats Page. Some threats will auto-escalate from audit to a higher level, for example, threats with a high threat event count or if the perpetrators of the threat are sensitive users. Audit events are also shown on the Home Page.
- Informational – Indicates first-time client use or first-time host use, which can be common events but may also indicate a threat
Threat Response:
Assigning a threat response designates a playbook to automatically be executed immediately when a threat of this type is detected.
- Email Alert – Select On to send email notifications when the threat is detected. Select Off to turn off email notifications.
- SIEM Alert – Select On to forward threat information to a SIEM service when the threat is detected. Select Off to turn off forwarding threat information to a SIEM service.
- Run Playbook – Select the playbook that will be used to respond to the threat.
Rollup:
NOTE: Rollup is not available for all threat types.
- Enabled – Enables rollups when set to ON. The default state is dependent on the threat type.
- Rollup Time – The timeframe for the rollup. Select a timeframe from the drop-down list:
- 1 Minute
- 5 Minutes
- 15 Minutes
- 30 Minutes
- 1 Hour
- 8 Hours
- 24 Hours
If rollup is enabled, multiple events from the same perpetrator will be associated with a single threat. For the given rollup criteria, if additional threat events are received within the selected rollup time, then the threat events are appended to an existing threat instead of creating a new threat. For example, if a user creates 1000 ransomware files in the configured rollup timeframe, it is reported as 1 ransomware threat with 1000 events, whereas without rollup many threats would be created. The configured threat response (Email, SIEM, or Playbooks) will be triggered only once when the threat is initially detected regardless of rollup configuration. When a threat rolls up, it will also update the detection time of the threat, which will push it to the top of the Threats Page timeline.
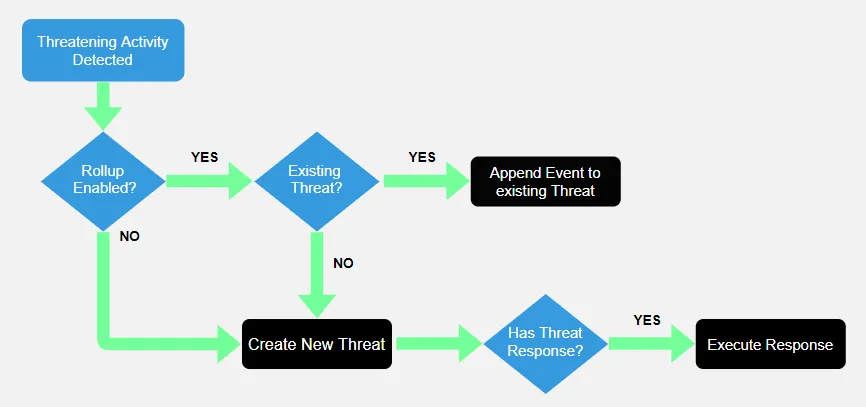
The diagram provides an outline of the rollup process.
Exclusions Tab
The Exclusions tab lists existing exclusions for the threat. Exclusions allow rule-based definitions to be defined for specific criteria to be excluded from threat detection for the threat type.
To view details of an existing exclusion, click the arrow next to the exclusion or the name of the exclusion.
Exclusion Details:
- Add New Filter – Click the Add New Filter button to include an additional filter rule for the exclusion.
- Delete Filter – Click the smaller Delete Icon to the right of the filter to delete that filter.
- Save – Click Save to save changes made to the exclusion.
- Cancel – Click Cancel to close the exclusion details and disregard any changes made to the exclusion.
- Delete Exclusion – Click the larger Delete Icon to the right of the Cancel button below the filter(s) to delete the exclusion. A confirmation window will confirm deletion.
Click Add Exclusion to Add a new Threat Detection Exclusion.
Add Threat Detection Exclusions
Follow the steps to add an exclusion to the threat type.
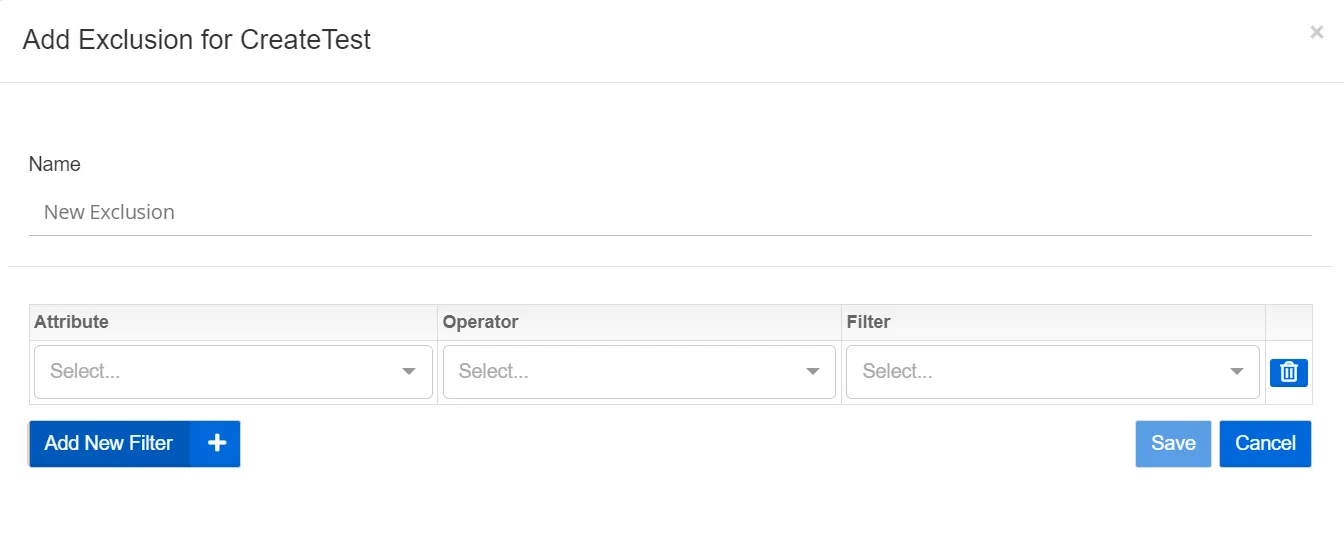
Step 1 – Click Add Exclusion. The Add Exclusion for [Threat Type] window opens.
Step 2 – Select a Name for the exclusion
Step 3 – Select an Attribute from the Attribute drop-down list:
- User
- Host
- Client
- File
Step 4 – Select an Operator from the Operator drop-down list.
Step 5 – Select a Filter by searching for the value and selecting it from the drop-down list. Or, manually enter the value for the selected exclusion type in the following format:
- Computer – [domain][hostname]
- Client – [domain][hostname]
- User – [domain][username]
- File – Folder path and full path to file. This exclusion also supports the asterisk wildcard: *
Step 6 – (Optional) Click Add New Filter to include an additional filter rule for the exclusion.
Step 7 – Click Saveto save the exclusion details. Click Cancel to close the modal and disregard any changes made to the exclusion.
The exclusion is added to the Exclusions list and the specified activity will immediately be excluded from threat detection for the threat type.
Settings Tab
The Settings Tab provides additional threat-specific settings that are required for some threats.
NOTE: The Settings tab is only displayed for threats that require additional settings.
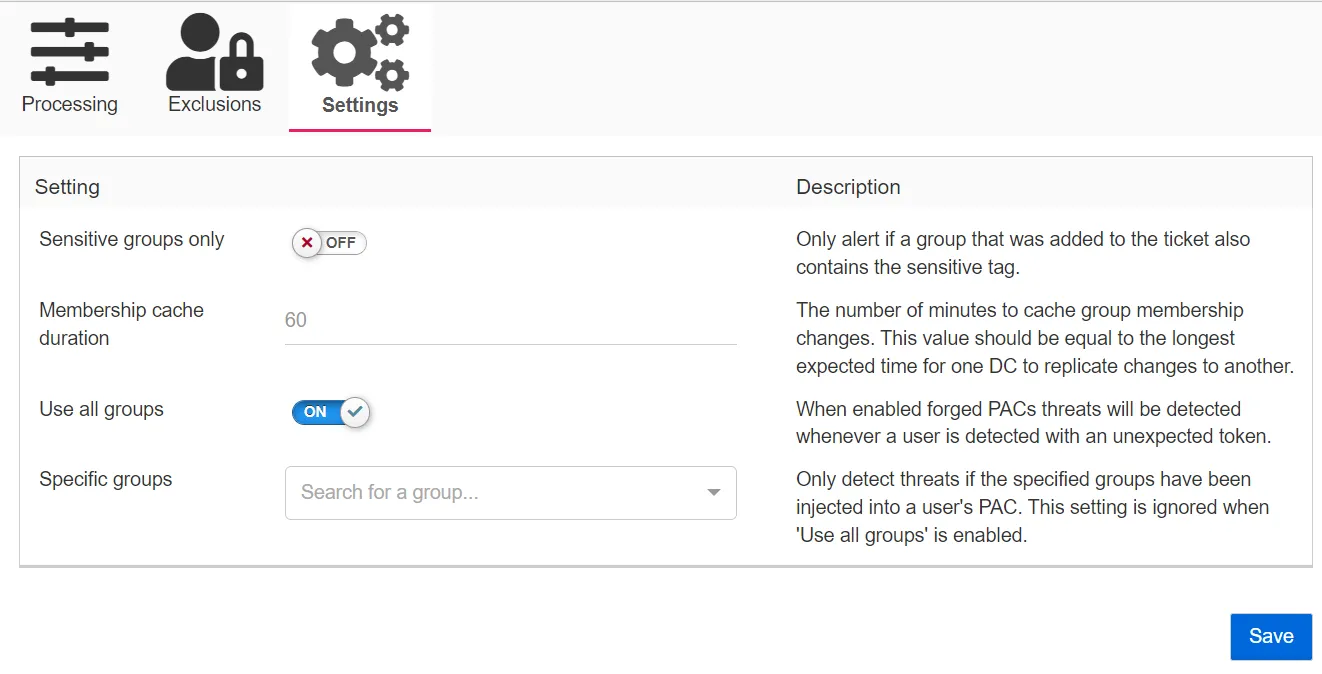
This tab shows the settings that are required for the Forged Ticket threat.
- Sensitive groups only – When enabled, Forged Ticket threats will only be detected if a group that was added to the forged ticket is tagged as sensitive.
- Membership cache duration – The number of minutes to cache group membership changes. This value should equal the longest expected time for one DC to replicate changes.
- Use all groups – When enabled, Forged Ticket threats will be detected whenever a user is detected with an unexpected token.
- Specific groups – Only detect threats if the specified groups have been injected into a user's Privilege Account Certificate (PAC). This setting is ignored when the Use all groups setting is enabled.